Abstract
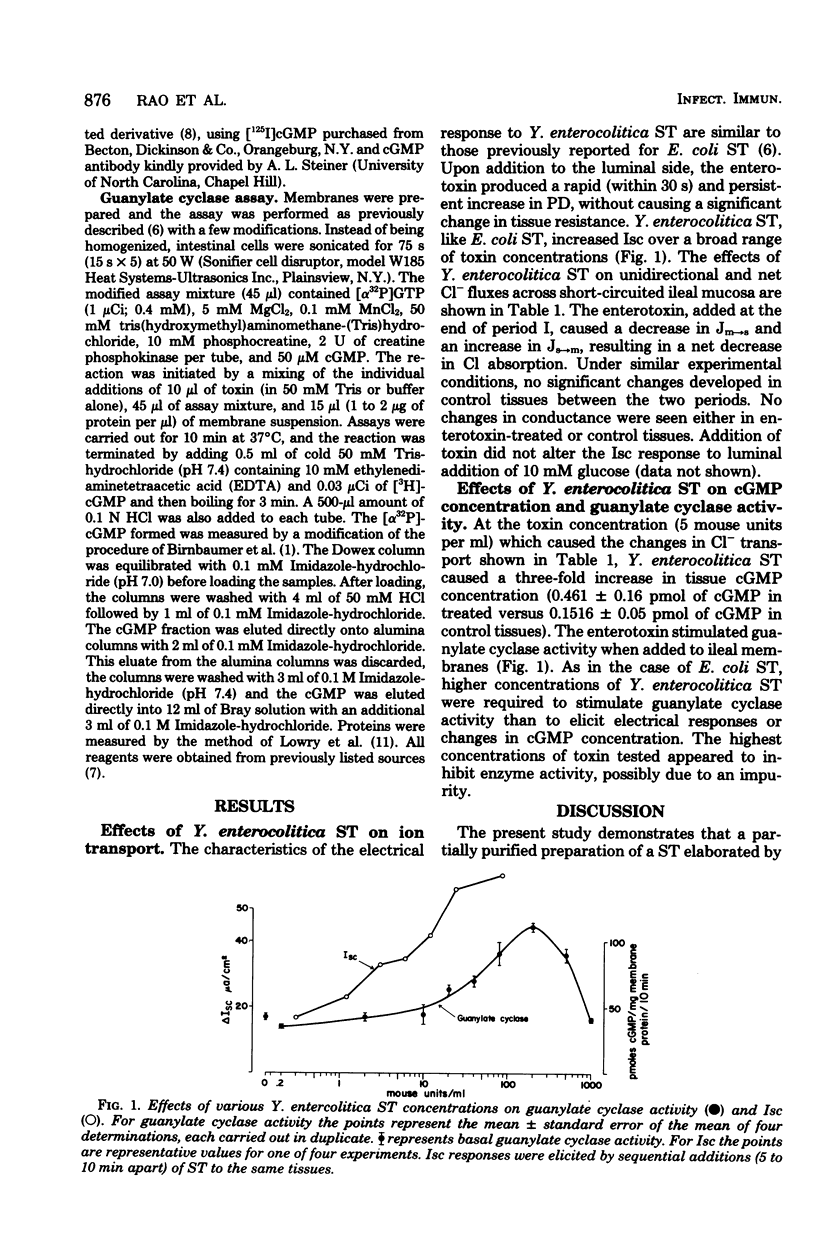
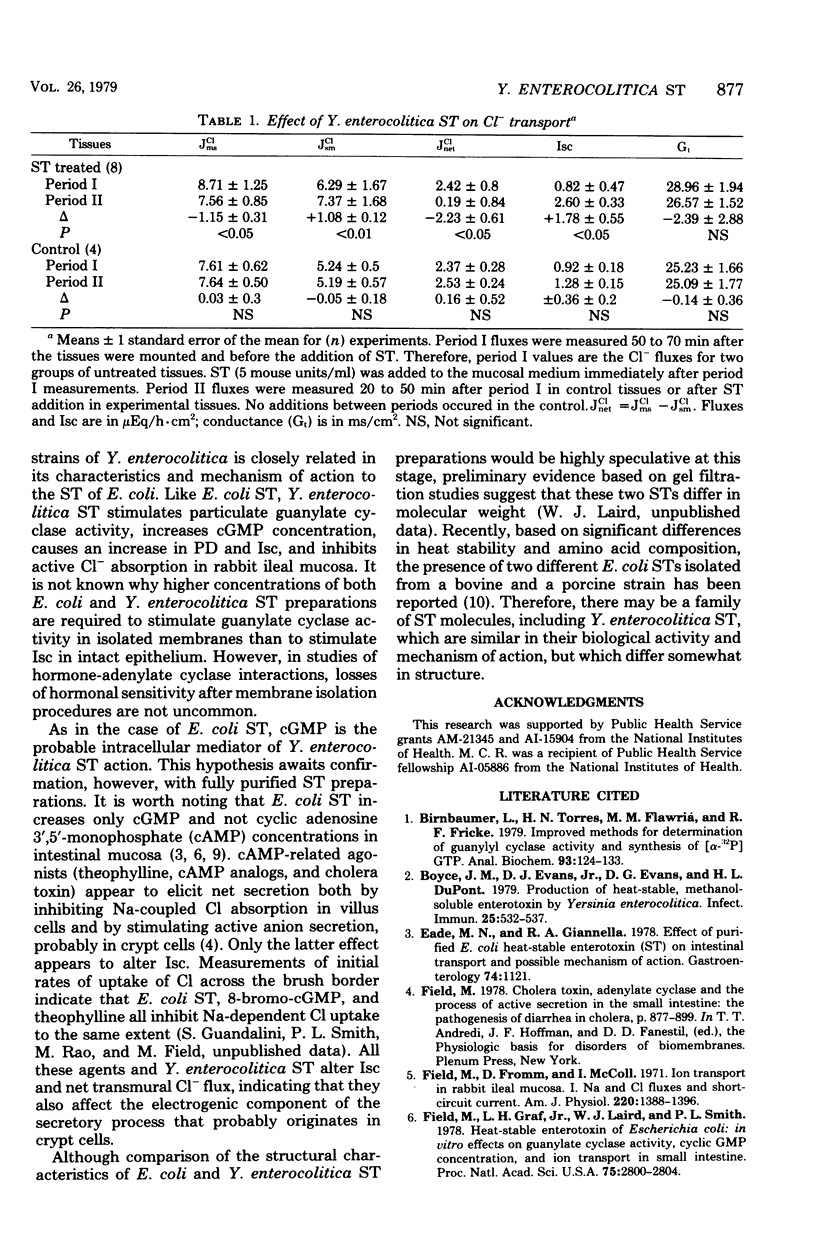
Strains of Yersinia enterocolitica produce a heat-stable enterotoxin which is positive in the suckling mouse bioassay. Partial purification by a procedure previously worked out for heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin yielded a substance which increases particulate guanylate cyclase activity and short-circuit current and inhibits active Cl-absorption in rabbit ileal mucosa. These effects of Y. enterocolitica enterotoxin are similar to those of heat-stable E. coli enterotoxin, suggesting a common mechanism of action.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnbaumer L., Torres H. N., Flawiá M. M., Fricke R. F. Improved methods for determination of guanylyl cyclase activity and synthesis of [alpha-32P]GTP. Anal Biochem. 1979 Feb;93(1):124–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyce J. M., Evans E. J., Jr, Evans D. G., DuPont H. L. Production of heat-stable, methanol-soluble enterotoxin by Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):532–537. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.532-537.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Fromm D., McColl I. Ion transport in rabbit ileal mucosa. I. Na and Cl fluxes and short-circuit current. Am J Physiol. 1971 May;220(5):1388–1396. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.5.1388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Graf L. H., Jr, Laird W. J., Smith P. L. Heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: in vitro effects on guanylate cyclase activity, cyclic GMP concentration, and ion transport in small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2800–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Sheerin H. E., Henderson A., Smith P. L. Catecholamine effects on cyclic AMP levels and ion secretion in rabbit ileal mucosa. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jul;229(1):86–92. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. F., Brooker G. Femtomole sensitive radioimmunoassay for cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP after 2'0 acetylation by acetic anhydride in aqueous solution. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;1(4):207–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. M., Murad F., Chang B., Guerrant R. L. Role of cyclic GMP in the action of heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1978 Feb 23;271(5647):755–756. doi: 10.1038/271755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitany R. A., Scoot A., Forsyth G. W., McKenzie S. L., Worthington R. W. Evidence for two heat-stable enterotoxins produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):965–966. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.965-966.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., Mors V. Production of enterotoxin by Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):908–911. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.908-911.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Still C. S., Miliotis M. D., Koornhof H. J. Mechanism of action of Yersinia enterocolitica enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):680–684. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.680-684.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



