Abstract
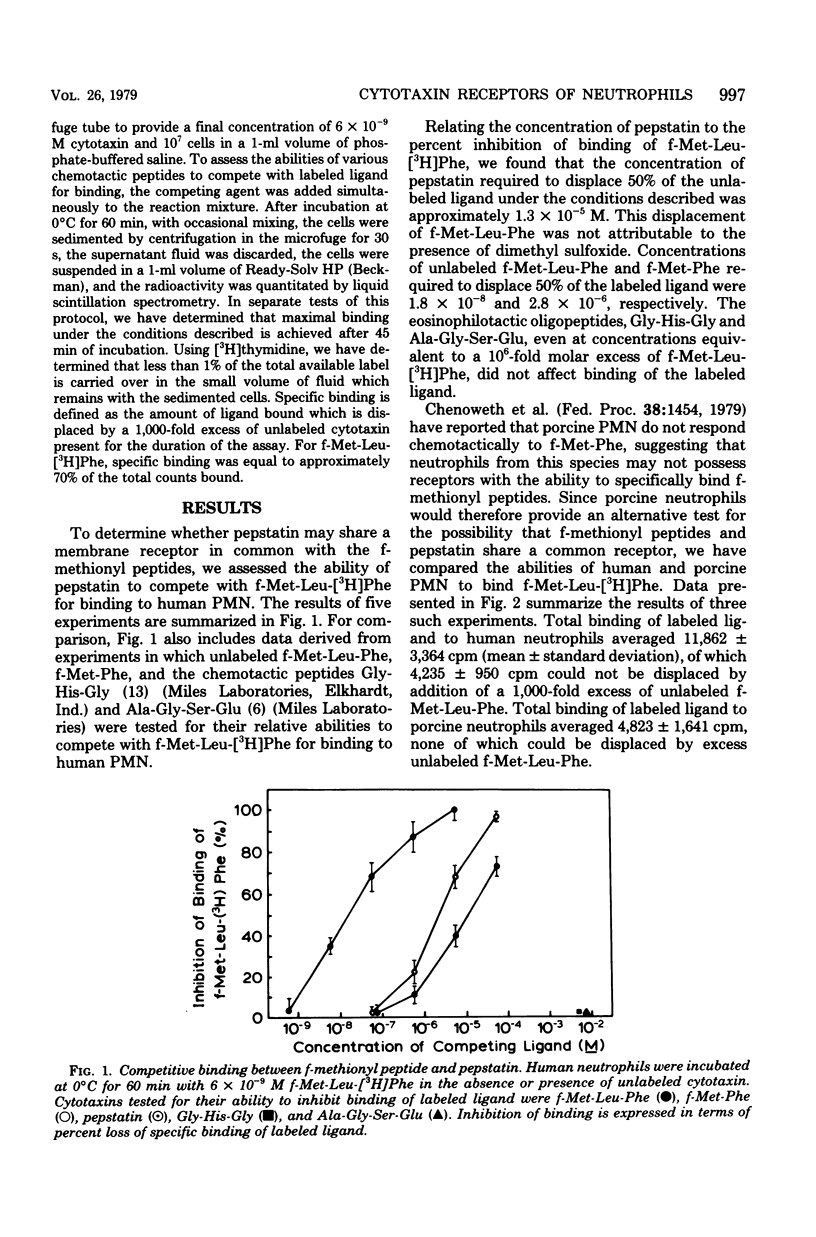
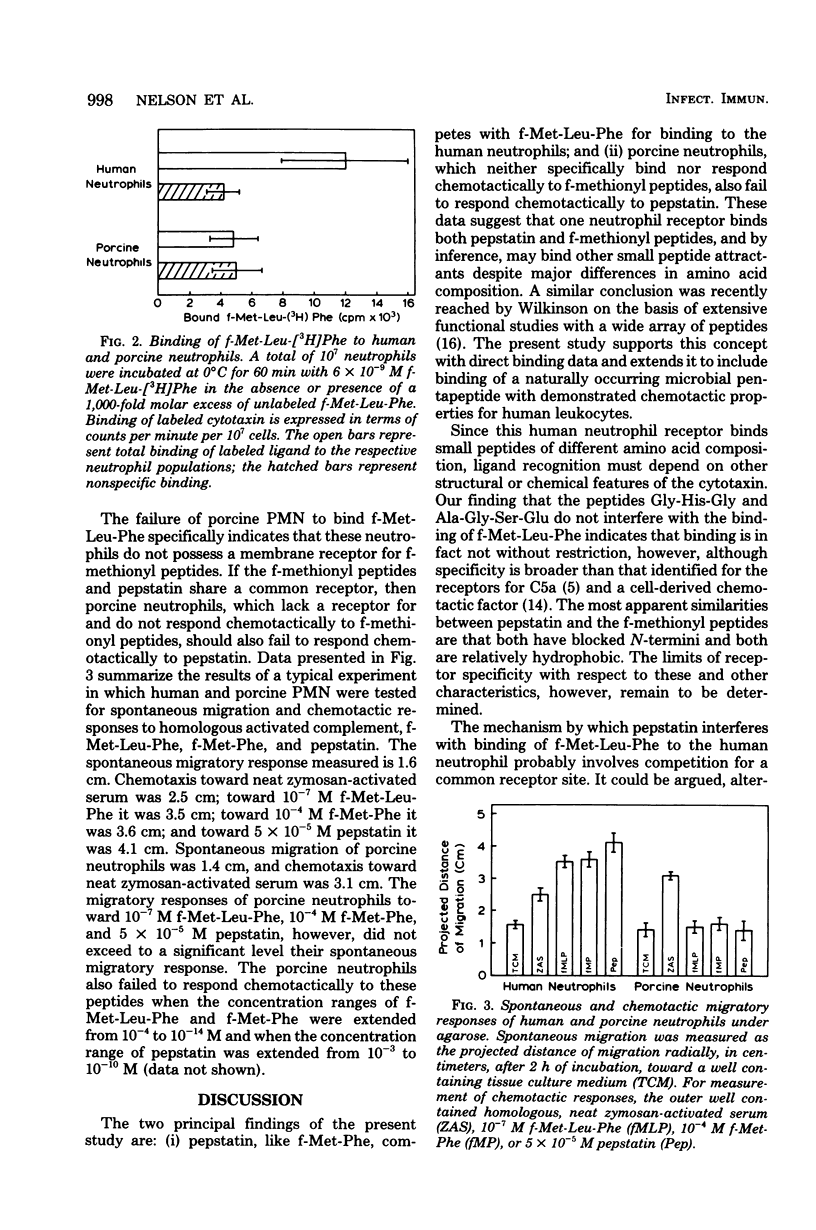
Pepstatin, a chemotactic microbial pentapeptide, competes with f-Met-Leu-[3H]Phe for binding to human neutrophils. Furthermore, porcine neutrophils, which neither specifically bind nor respond chemotactically to the synthetic f-methionyl peptides, also fail to respond chemotactically to pepstatin. These results suggest that pepstatin shares a receptor on the neutrophil with f-methionyl peptides, despite their completely different amino acid compositions. The specificity of this cytotaxin receptor may therefore be broader than expected and depend on ligand characteristics distinct from primary structure.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman S. K., Douglas S. D. Pepstatin A--a human leukocyte chemoattractant. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 Oct;14(2):244–250. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyagi T., Kunimoto S., Morishima H., Takeuchi T., Umezawa H. Effect of pepstatin on acid proteases. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Oct;24(10):687–694. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyagi T., Morishima H., Nishizawa R., Kunimoto S., Takeuchi T. Biological activity of pepstatins, pepstanone A and partial peptides on pepsin, cathepsin D and renin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Dec;25(12):689–694. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Schiffmann E., Day A. R., Freer R. J., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Demonstration of a receptor on rabbit neutrophils for chemotactic peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):810–817. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90375-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Dingle J. T. The inhibition of tissue acid proteinases by pepstatin. Biochem J. 1972 Apr;127(2):439–441. doi: 10.1042/bj1270439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenoweth D. E., Hugli T. E. Demonstration of specific C5a receptor on intact human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3943–3947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. Purification and synthesis of eosinophilotactic tetrapeptides of human lung tissue: identification as eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4123–4127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAdoo M. H., Dannenberg A. M., Jr, Hayes C. J., James S. P., Sanner J. H. Inhibition of cathepsin D-type proteinase of macrophages by pepstatin, a specific pepsin inhibitor, and other substances. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):655–665. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.655-665.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishima H., Takita T., Umezawa H. The chemical synthesis of pepstatin A. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Sep;25(9):551–552. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani H., Hiromi K., Satoi S., Oda K., murao S. Studies on the interaction between Streptomyces pepsin inhibitor and several acid proteinases by means of a zinc(II)-dye complex as a probe. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jun 24;391(2):415–421. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90266-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. D., Quie P. G., Simmons R. L. Chemotaxis under agarose: a new and simple method for measuring chemotaxis and spontaneous migration of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1650–1656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showell H. J., Freer R. J., Zigmond S. H., Schiffmann E., Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Becker E. L. The structure-activity relations of synthetic peptides as chemotactic factors and inducers of lysosomal secretion for neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1154–1169. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spilberg I., Mandell B., Mehta J., Sullivan T., Simchowitz L. Dissociation of the neutrophill functions of exocytosis and chemotaxis. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Aug;92(2):297–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spilberg I., Mehta J. Demonstration of a specific neutrophil receptor for a cell-derived chemotactic factor. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jan;63(1):85–88. doi: 10.1172/JCI109282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Aoyagi T., Morishima H., Matsuzaki M., Hamada M. Pepstatin, a new pepsin inhibitor produced by Actinomycetes. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 May;23(5):259–262. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C. Synthetic peptide chemotactic factors for neutrophils: the range of active peptides, their efficacy and inhibitory activity, and susceptibility of the cellular response to enzymes and bacterial toxins. Immunology. 1979 Mar;36(3):579–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Snyderman R., Pike M. C., Lefkowitz R. J. Specific receptor sites for chemotactic peptides on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1204–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



