Abstract
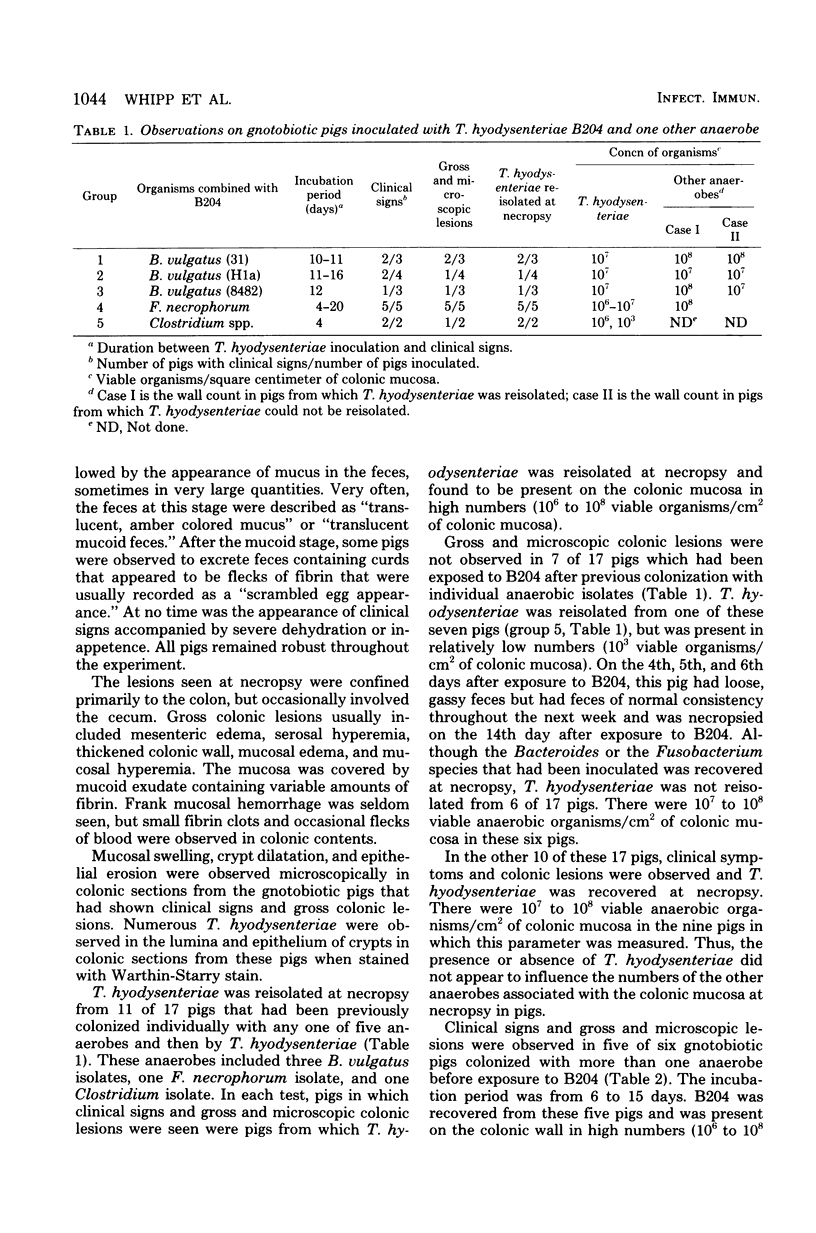
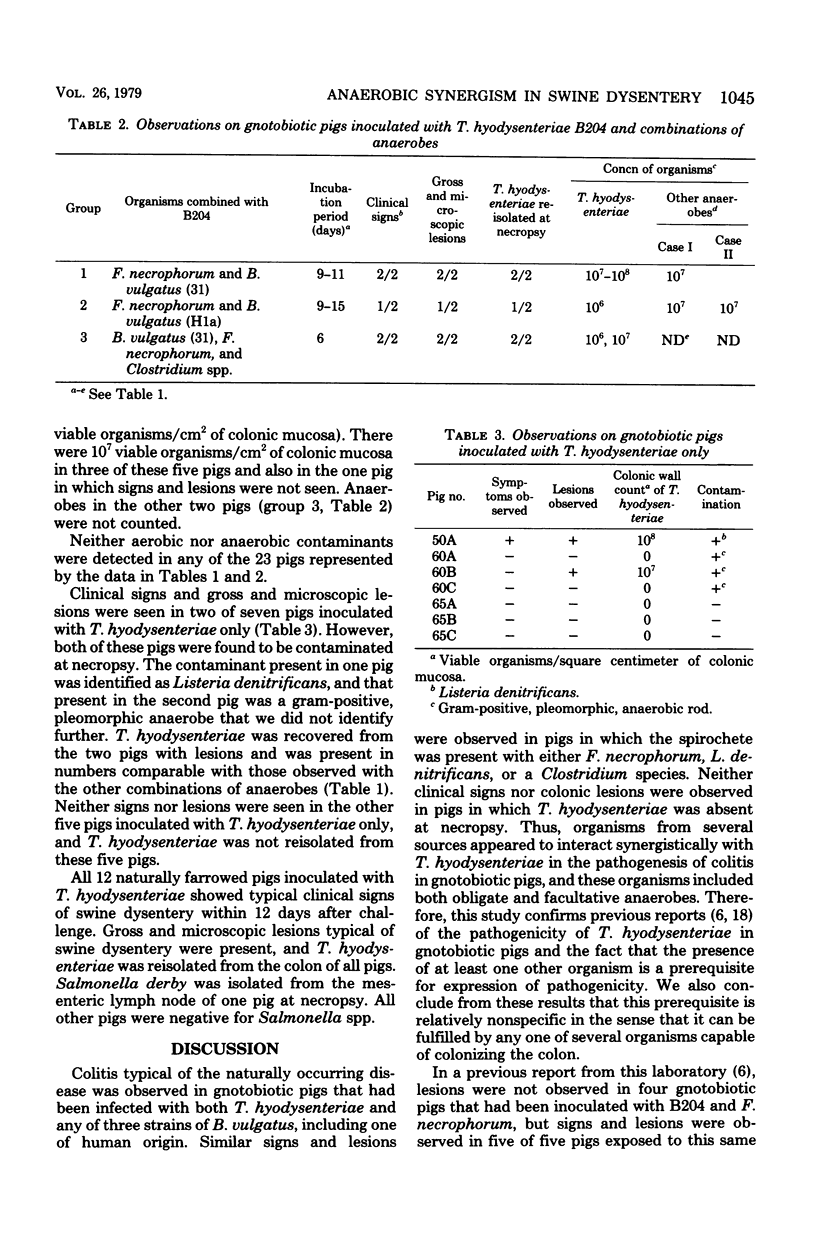
Gnotobiotic pigs were orally exposed to various anaerobes at 6 to 9 days of age and similarly inoculated with Treponema hyodysenteriae B204 3 to 6 days later. Watery diarrhea and fecal excretion of large quantities of mucus and some fibrin clots were observed 4 to 20 days after inoculation with B204 if other anaerobes were present. Colonic lesions characteristic of swine dysentery were observed when B204 was present with Fusobacterium necrophorum, three strains of Bacteroides vulgatus, a Clostridium species, and Listeria denitrificans individually and when some of these microbes were present in various combinations, but not when B204 was present alone. These results are consistent with the conclusion that T. hyodysenteriae is the primary pathogen in the etiology of swine dysentery and that the presence of one or more other anaerobes is a prerequisite for expression of pathogenicity of T. hyodysenteriae. This prerequisite can be met by a variety of anaerobes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akkermans J. P., Pomper W. Aetiology and diagnosis of swine dysentery (Doyle). Tijdschr Diergeneeskd. 1973 Jul 15;98(14):649–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison M. J., Robinson I. M., Bucklin J. A., Booth G. D. Comparison of bacterial populations of the pig cecum and colon based upon enumeration with specific energy sources. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jun;37(6):1142–1151. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.6.1142-1151.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandenburg A. C., Miniats O. P., Geissinger H. D., Ewert E. Swine dysentery: inoculation of gnotobiotic pigs with Treponema hyodysenteriae and Vibrio coli and a Peptostreptococcus. Can J Comp Med. 1977 Jul;41(3):294–301. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E. The anaerobic mesophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1950 Mar;14(1):1–49. doi: 10.1128/br.14.1.1-49.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamdy A. H., Glenn M. W. Transmission of swine dysentery with Treponema hyodysenteriae and Vibrio coli. Am J Vet Res. 1974 Jun;35(6):791–797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. L., Alexander T. J., Whipp S. C., Robinson I. M., Glock R. D., Matthews P. J. Swine dysentery: studies of gnotobiotic pigs inoculated with Treponema hyodysenteriae, Bacteroides vulgatus, and Fusobacterium necrophorum. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Feb 15;172(4):468–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. L., Glock R. D., Christensen C. R., Kinyon J. M. Inoculation of pigs with Treponema hyodysenteriae (new species) and reproduction f the disease. Vet Med Small Anim Clin. 1972 Jan;67(1):61–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R., Olander H. J., Kanitz D. L., Qureshi S. A study of swine dysentery by immunofluorescence and histology. Vet Pathol. 1977 Sep;14(5):490–507. doi: 10.1177/030098587701400509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R., Olander H. J., Williams C. B. Swine dysentery: pathogenicity of Treponema hyodysenteriae. Am J Vet Res. 1975 Jul;36(7):971–977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinyon J. M., Harris D. L., Glock R. D. Enteropathogenicity of various isolates of Treponema hyodysenteriae. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):638–646. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.638-646.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinyon J. M., Harris D. L. Growth in Treponema hyodysenteriae in liquid medium. Vet Rec. 1974 Sep 7;95(10):219–220. doi: 10.1136/vr.95.10.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low A. G., Partridge I. G., Sambrook I. E. Studies on digestion and absorption in the intestines of growing pigs. 2. Measurements of the flow of dry matter, ash and water. Br J Nutr. 1978 May;39(3):515–526. doi: 10.1079/bjn19780067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. C., Simon J., Byerly C. S. The etiology of swine dysentery. I. Oral inoculation of germ-free swine with Treponema hyodysenteriae and Vibrio coli. Vet Pathol. 1974;11(6):515–526. doi: 10.1177/030098587401100606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. C., Simon J., Byerly C. S. The etiology of swine dysentery. II. Effect of a known microbial flora, weaning and diet on disease production in gnotobiotic and conventional swine. Vet Pathol. 1974;11(6):527–534. doi: 10.1177/030098587401100607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. C., Simon J., Byerly C. S. The etiology of swine dysentery. III. The role of selected gram-negative obligate anaerobes. Vet Pathol. 1975;12(1):46–54. doi: 10.1177/030098587501200107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. C. Swine dysentery: a perspective. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1978;22:133–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miniats O. P., Jol D. Gnotobiotic pigs-derivation and rearing. Can J Comp Med. 1978 Oct;42(4):428–437. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W. Mechanisms in the pathogenesis of diarrhea: a review. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Feb 15;172(4):443–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Gyles C. L. The relationship between two apparently different enterotoxins produced by enteropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli of porcine origin. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Aug;3(3):387–401. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-3-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Halls S. Observations by the ligated intestinal segment and oral inoculation methods on Escherichia coli infections in pigs, calves, lambs and rabbits. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(2):499–529. doi: 10.1002/path.1700930211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Songer J. G., Kinyon J. M., Harris D. L. Selective medium for isolation of Treponema hyodysenteriae. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jul;4(1):57–60. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.1.57-60.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. J., Alexander T. J. The production of dysentery in swine by feeding cultures containing a spirochaete. Br Vet J. 1971 Nov;127(11):58–61. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)37282-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxler G. L., Schmidt D. A., Whitehair C. K. Technique for rearing gnotobiotic pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1966 Jan;27(116):300–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcock B. P. Experimental Klebsiella and Salmonella infection in neonatal swine. Can J Comp Med. 1979 Apr;43(2):200–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



