Abstract
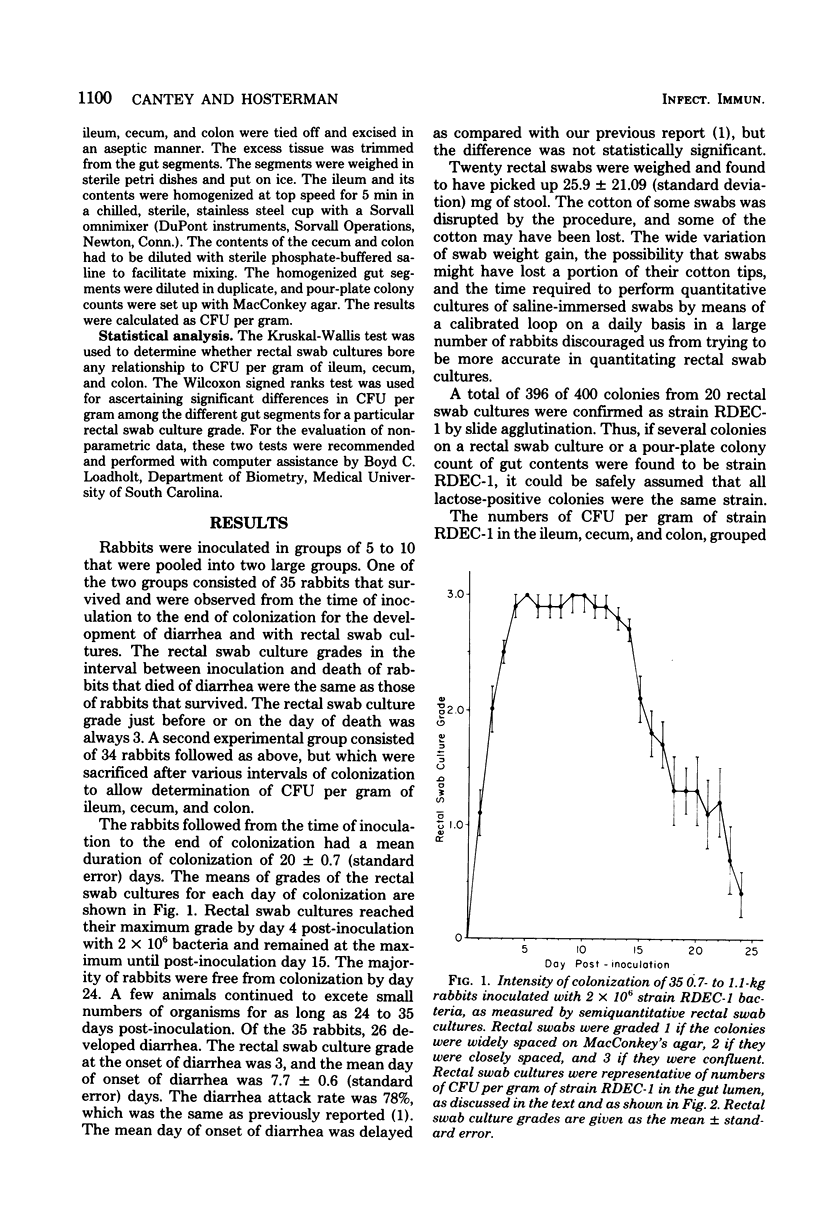
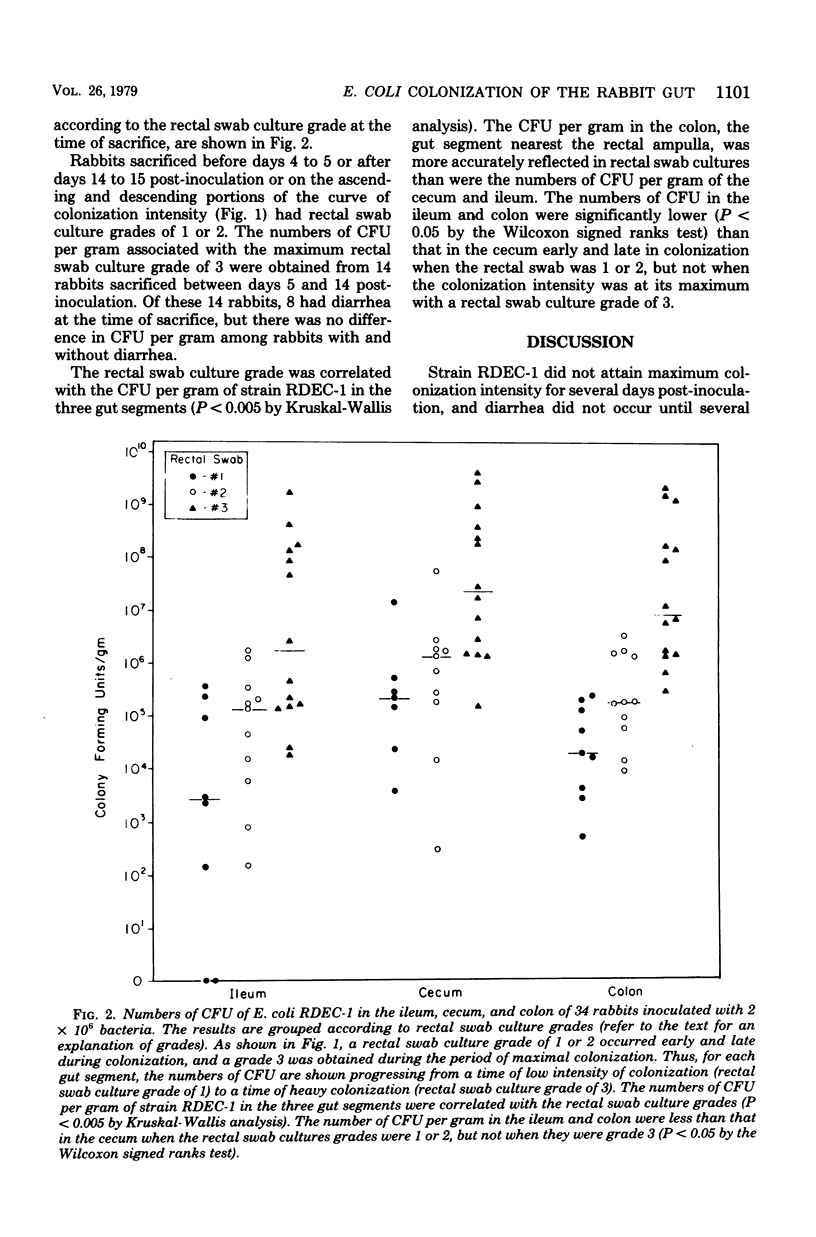
We have reported previously the isolation of an Escherichia coli strain (RDEC-1) that in rabbits is able to colonize the gut, adhere to mucosal epithelial cells of the ileum, cecum, and colon, and cause diarrhea by a novel mechanism. The purpose of the present study was to characterize more fully the colonization of the rabbit gut by strain RDEC-1. Colonization reached a maximum 3 to 4 days post-inoculation with strain RDEC-1 and did not decrease until 15 days post-inoculation. Diarrhea occurred 3 to 4 days after colonization reached its maximum intensity. Semiquantitative rectal swab cultures were found to be correlated with counts of colony-forming units of strain RDEC-1 per gram of ileum, cecum, and colon and their contents and were used to chart the course of colonization of the rabbit gut. The actual number of colony-forming units per gram was dependent on the stage of colonization and ranged from 4.0 X 10(3) to 2.4 X 20(6) in the ileum to 3.1 X 10(5) to 3.6 X 10(7) in the cecum. The number of colony-forming units per gram was not affected by the presence of diarrhea. E. coli RDEC-1 colonizes the ileum, cecum, and colon of rabbits heavily for a relatively long period of time.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cantey J. R., Blake R. K. Diarrhea due to Escherichia coli in the rabbit: a novel mechanism. J Infect Dis. 1977 Mar;135(3):454–462. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.3.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantey J. R., O'Hanley P. D., Blake R. K. A rabbit model of diarrhea due to invasive Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1977 Nov;136(5):640–648. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.5.640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash R. A., Music S. I., Libonati J. P., Snyder M. J., Wenzel R. P., Hornick R. B. Response of man to infection with Vibrio cholerae. I. Clinical, serologic, and bacteriologic responses to a known inoculum. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jan;129(1):45–52. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Tjoa W. S., DuPont H. L. Detection and characterization of colonization factor of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from adults with diarrhea. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):727–736. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.727-736.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Satterwhite T. K., Evans D. J., Jr, DuPont H. L. Differences in serological responses and excretion patterns of volunteers challenged with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli with and without the colonization factor antigen. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):883–888. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.883-888.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERGUSON W. W., JUNE R. C. Experiments on feeding adult volunteers with Escherichia coli 111, B4, a coliform organism associated with infant diarrhea. Am J Hyg. 1952 Mar;55(2):155–169. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Banwell J. G., Chatterjee B. D., Jacobs B., Sack R. B. Acute undifferentiated human diarrhea in the tropics. I. Alterations in intestinal micrflora. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):881–889. doi: 10.1172/JCI106560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Banwell J. G., Jacobs B., Chatterjee B. D., Mitra R., Brigham K. L., Neogy K. N. Intestinal microflora in Asiatic cholera. II. The small bowel. J Infect Dis. 1970 Jan;121(1):38–45. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann A., Wilson M. R. Adherence of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to intestinal epithelium in vivo. Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):866–880. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.866-880.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hanley P. D., Cantey J. R. Surface structures of Escherichia coli that produce diarrhea by a variety of enteropathic mechanisms. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):874–878. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.874-878.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oseasohn R., Ahmad S., Islam M. A., Rahman A. S. Clinical and bacteriological findings among families of cholera patients. Lancet. 1966 Feb 12;1(7433):340–342. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91322-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH H. W., JONES J. E. OBSERVATIONS ON THE ALIMENTARY TRACT AND ITS BACTERIAL FLORA IN HEALTHY AND DISEASED PIGS. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:387–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Linggood M. A. Observations on the pathogenic properties of the K88, Hly and Ent plasmids of Escherichia coli with particular reference to porcine diarrhoea. J Med Microbiol. 1971 Nov;4(4):467–485. doi: 10.1099/00222615-4-4-467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Inman L. R., O'Hanley P. D., Cantey J. R., Lushbaugh W. B. Scanning and transmission electron microscopic study of Escherichia coli O15 (RDEC-1) enteric infection in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):686–694. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.686-694.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulloch E. F., Jr, Ryan K. J., Formal S. B., Franklin F. A. Invasive enteropathic Escherichia coli dysentery. An outbreak in 28 adults. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Jul;79(1):13–17. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-1-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



