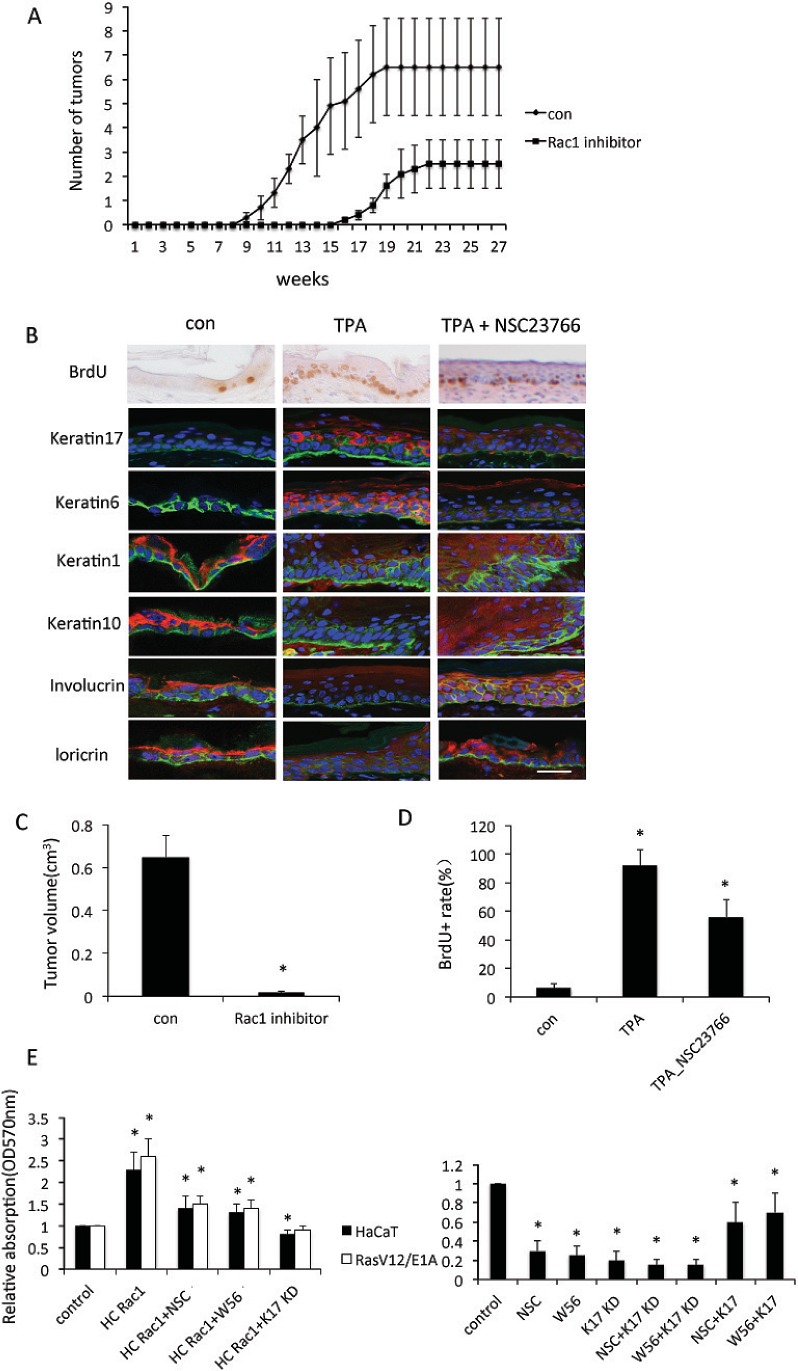
Figure 2. Rac1 is involved in keratinocyte proliferation.
A, 8 week old mice were subjected to DMBA/TPA-induced skin carcinogenesis for 30 weeks. Mice were separated with two groups (n = 10): Control (con) mice treated with DMBA/TPA only; mice (Rac1 inhibitor) were treated with 10 mM Rac1 inhibitor NSC23766 30 min prior to TPA treatment. Average number of tumors per mouse. B, Staining for BrdU incorporation, keratin 6, keratin 1, keratin10, keratin17, involucrin or loricrin (red). α6 (green) was used to stain basal layer. DAPI (blue) counterstaining indicates nuclei. Scale bar: 20 μm. Nontreated mice (con), TPA-treated mice (TPA), or TPA+NSC23766 treated mice (TPA+NSC23766). C, Quantification of tumor volumes at the endpoint of DMBA/TPA treatments. * p<0.01 compare to NSC23766 untreated mice. D, Quatification of BrdU positive cells in epidermis. * p<0.01 compare to control. E, Proliferation of keratinocytes. Keratinocyte cell line HaCaT or RasV12/E1A-transfected keratinocytes were transfected with high-cycling (HC) Rac1 plasmid or small hairpin RNA against keratin 17 (KD), or treated with Rac1 inhibitor (NSC or W56). Proliferation of keratinocytes was measured by crystal violet assay. Assays were performed in triplicate. The means with SD are shown (n=8 replicates/group).