Abstract
Fourteen freshly isolated strains of Streptococcus sanguis were obtained from the dental plaque of five healthy adults. Whole saliva was collected concomitant with the plaque isolates from the five subjects, and a second whole saliva sample was collected 10 weeks later. All possible combinations of the first five saliva samples, the second five saliva samples, and 14 strains of bacteria were tested for aggregation. Of the 140 combinations examined, 108 of 140 (77%) of the strains aggregated with the first saliva samples and 95 of 140 (68%) aggregated with the second saliva samples. Overall, 72% of the strains aggregated with both the first and second saliva samples. Removal of immunoglobulin A (IgA) from these same salivas resulted in 38 of 108 (35%) of the aggregates decreasing in intensity with the first saliva samples and 27 of 95 (29%) of the aggregates decreasing in intensity with the second saliva samples. No aggregates increased in intensity with saliva samples when IgA had been removed. Removal of IgA from saliva also resulted in a mean decrease of 46% in adherence of S. sanguis to hydroxyapatite coated with the IgA-deficient saliva. Several strains of S. sanguis were shown to aggregate strongly with human salivary and colostral IgA. In addition, S. sanguis strain S7 showed a 31% stimulation of adherence to hydroxyapatite precoated with human salivary IgA over the uncoated controls. Stepwise removal of IgA from saliva resulted in a decrease in aggregation intensity from strong (4+) to weak (1+ to 2+). Similarly, the adherence of S. sanguis to hydroxyapatite coated with these saliva samples decreased linearly as the salivary IgA was depleted. Alternatively, the addition of a small quantity of salivary IgA (20 μg/ml) to progressively diluted saliva maintained a high level of adherence and strong aggregation until the saliva dilutions reached between 1:8 in the adherence experiments and 1:32 for the aggregations. These data indicate that salivary IgA may play an important role in the microbial ecology of human dental plaque formation.
Full text
PDF


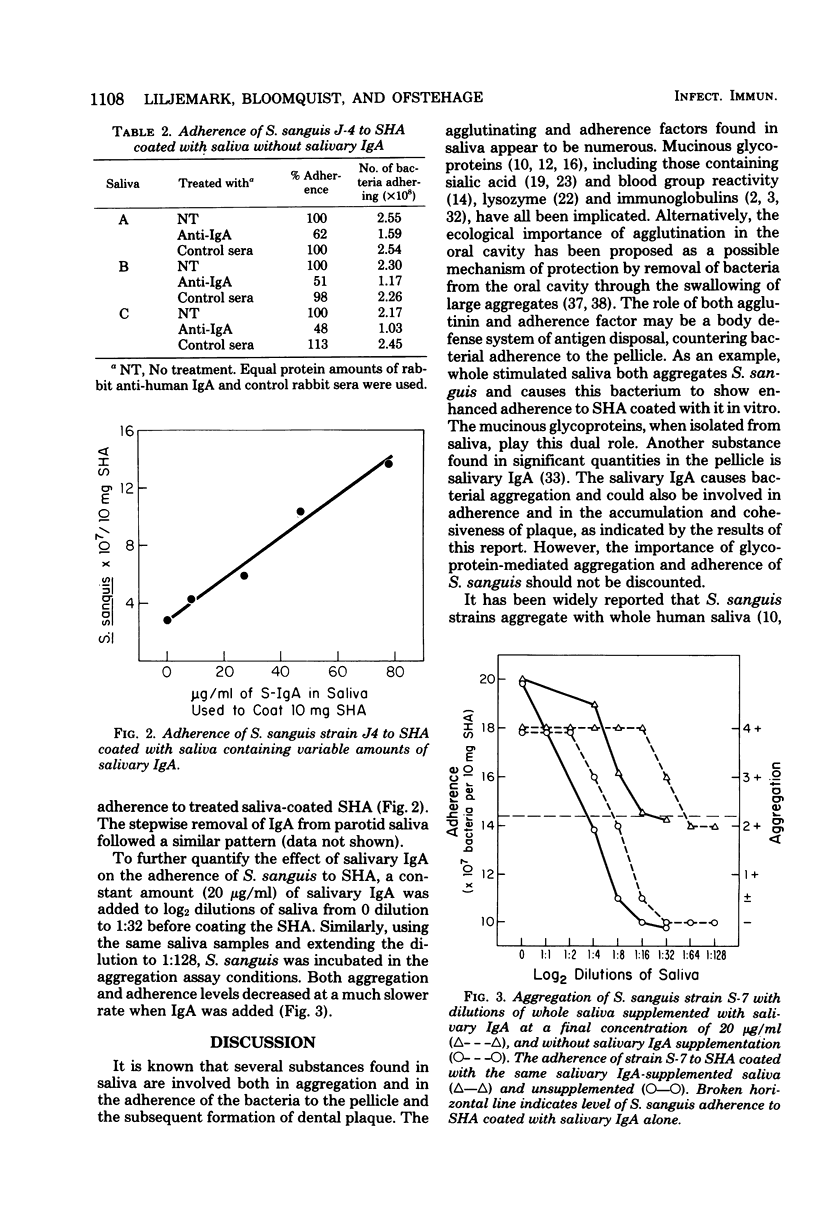


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appelbaum B., Rosan B. Antigens of Streptococcus sanguis: purification and characterization of the b antigen. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):896–904. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.896-904.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold R. R., Cole M. F., Prince S., McGhee J. R. Secretory IgM antibodies to Streptococcus mutans in subjects with selective IgA deficiency. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1977 Nov;8(3):475–486. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(77)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold R. R., Mestecky J., McGhee J. R. Naturally occurring secretory immunoglobulin A antibodies to Streptococcus mutans in human colostrum and saliva. Infect Immun. 1976 Aug;14(2):355–362. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.2.355-362.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Fjellanger I., Gjeruldsen S. T. Adsorption of immunolgobulin A onto oral bacteria in vivo. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):242–249. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.1.242-249.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratthall D., Gibbons R. J. Changing agglutination activities of salivary immunoglobulin A preparations against oral streptococci. Infect Immun. 1975 Mar;11(3):603–606. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.3.603-606.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J. Presence of various types of non-haemolytic streptococci in dental plaque and in other sites of the oral cavity in man. Odontol Revy. 1967;18(1):55–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. B., Bammann L. L., Gibbons R. J. Comparative estimates of bacterial affinities and adsorption sites on hydroxyapatite surfaces. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):846–853. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.846-853.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford J. M., Taubman M. A., Smith D. J. Minor salivary glands as a major source of secretory immunoglobin A in the human oral cavity. Science. 1975 Dec 19;190(4220):1206–1209. doi: 10.1126/science.1198107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson T., Magnusson I. Affinity for hydroxyapatite of salivary substances inducing aggregation of oral streptococci. Caries Res. 1976;10(1):8–18. doi: 10.1159/000260185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J. Bacterial adherence to mucosal surfaces and its inhibition by secretory antibodies. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1974;45(0):315–325. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-4550-3_38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Qureshi J. V. Selective binding of blood group-reactive salivary mucins by Streptococcus mutans and other oral organisms. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):665–671. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.665-671.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., van Houte J. On the formation of dental plaques. J Periodontol. 1973 Jun;44(6):347–360. doi: 10.1902/jop.1973.44.6.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay D. I., Gibbons R. J., Spinell D. M. Characteristics of some high molecular weight constituents with bacterial aggregating activity from whole saliva and dental plaque. Caries Res. 1971;5(2):111–123. doi: 10.1159/000259739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket S., Donaldson C. G. Saliva-induced aggregation of oral streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1127–1133. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1127-1133.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus F. W., Orstavik D., Hurst D. C., Cook C. H. The acquired pellicle: variability and subject-dependence of specific proteins. J Oral Pathol. 1973;2(3):165–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1973.tb01680.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. J., Herzberg M. C., Levine M. S., Ellison S. A., Stinson M. W., Li H. C., van Dyke T. Specificity of salivary-bacterial interactions: role of terminal sialic acid residues in the interaction of salivary glycoproteins with Streptococcus sanguis and Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):107–115. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.107-115.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Schauer S. V., Bloomquist C. G. Compounds which affect the adherence of Streptococcus sanguis and Streptococcus mutans to hydroxyapatite. J Dent Res. 1978 Feb;57(2):373–379. doi: 10.1177/00220345780570023901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Schauer S. V. Competitive binding among oral strptococci to hydroxyapatite. J Dent Res. 1977 Feb;56(2):157–165. doi: 10.1177/00220345770560021001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride B. C., Gisslow M. T. Role of sialic acid in saliva-induced aggregation of Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):35–40. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.35-40.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. R., Mestecky J., Arnold R. R., Michalek S. M., Prince S. J., Babb J. L. Induction of secretory antibodies in humans following ingestion of Streptococcus mutans. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;107:177–184. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3369-2_21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J., McGhee J. R., Michalek S. M., Arnold R. R., Crago S. S., Babb J. L. Concept of the local and common mucosal immune response. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;107:185–192. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3369-2_22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalek S. M., McGhee J. R., Mestecky J., Arnold R. R., Bozzo L. Ingestion of Streptococcus mutans induces secretory immunoglobulin A and caries immunity. Science. 1976 Jun 18;192(4245):1238–1240. doi: 10.1126/science.1273589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngel J. G., Kunz L. J. Simplified storage and retrieval of stock cultures. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Apr;23(4):837–838. doi: 10.1128/am.23.4.837-838.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orstavik D., Kraus F. W., Henshaw L. C. In vitro attachment of streptococci to the tooth surface. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):794–800. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.794-800.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orstavik D., Kraus F. W. The acquired pellicle: enzyme and antibody activities. Scand J Dent Res. 1974;82(3):202–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1974.tb00381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orstavik D. The in-vitro attachment of an oral Streptococcus sp. to the acquired tooth enamel pellicle. Arch Oral Biol. 1978;23(3):167–173. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(78)90212-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosan B. Antigens of Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):205–211. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.205-211.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbman M. A., Smith D. J. Effects of local immunization with Streptococcus mutans on induction of salivary immunoglobulin A antibody and experimental dental caries in rats. Infect Immun. 1974 Jun;9(6):1079–1091. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.6.1079-1091.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taubman M. A. Immunoglobulins of human dental plaque. Arch Oral Biol. 1974 Jun;19(6):439–446. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(74)90149-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomasi T. B., Jr Secretory immunoglobulins. N Engl J Med. 1972 Sep 7;287(10):500–506. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197209072871008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Houte J., Gibbons R. J., Banghart S. B. Adherence as a determinant of the presence of Streptococcus salivarius and Streptococcus sanguis on the human tooth surface. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 Nov;15(11):1025–1034. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90115-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Gibbons R. J. Inhibition of bacterial adherence by secretory immunoglobulin A: a mechanism of antigen disposal. Science. 1972 Aug 25;177(4050):697–699. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4050.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Gibbons R. J. Inhibition of streptococcal attachment to receptors on human buccal epithelial cells by antigenically similar salivary glycoproteins. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):711–718. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.711-718.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



