Abstract
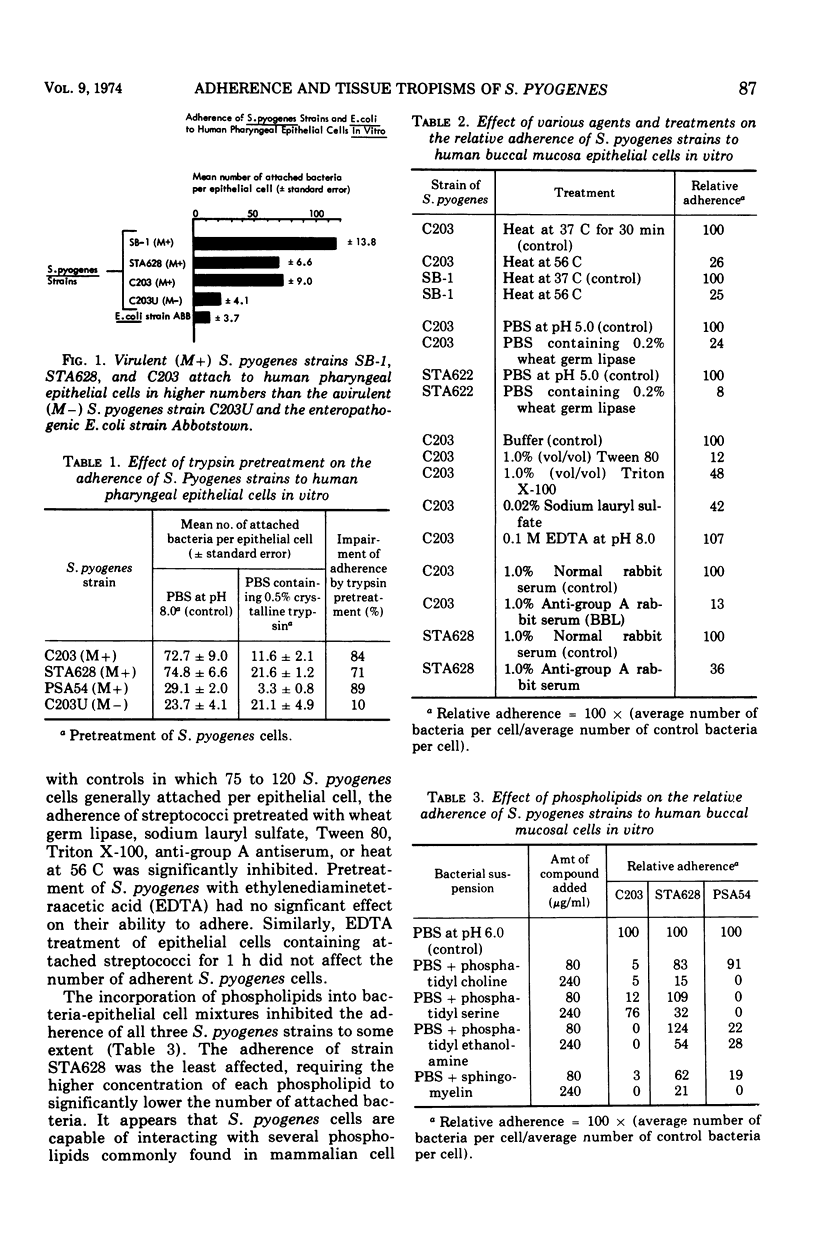
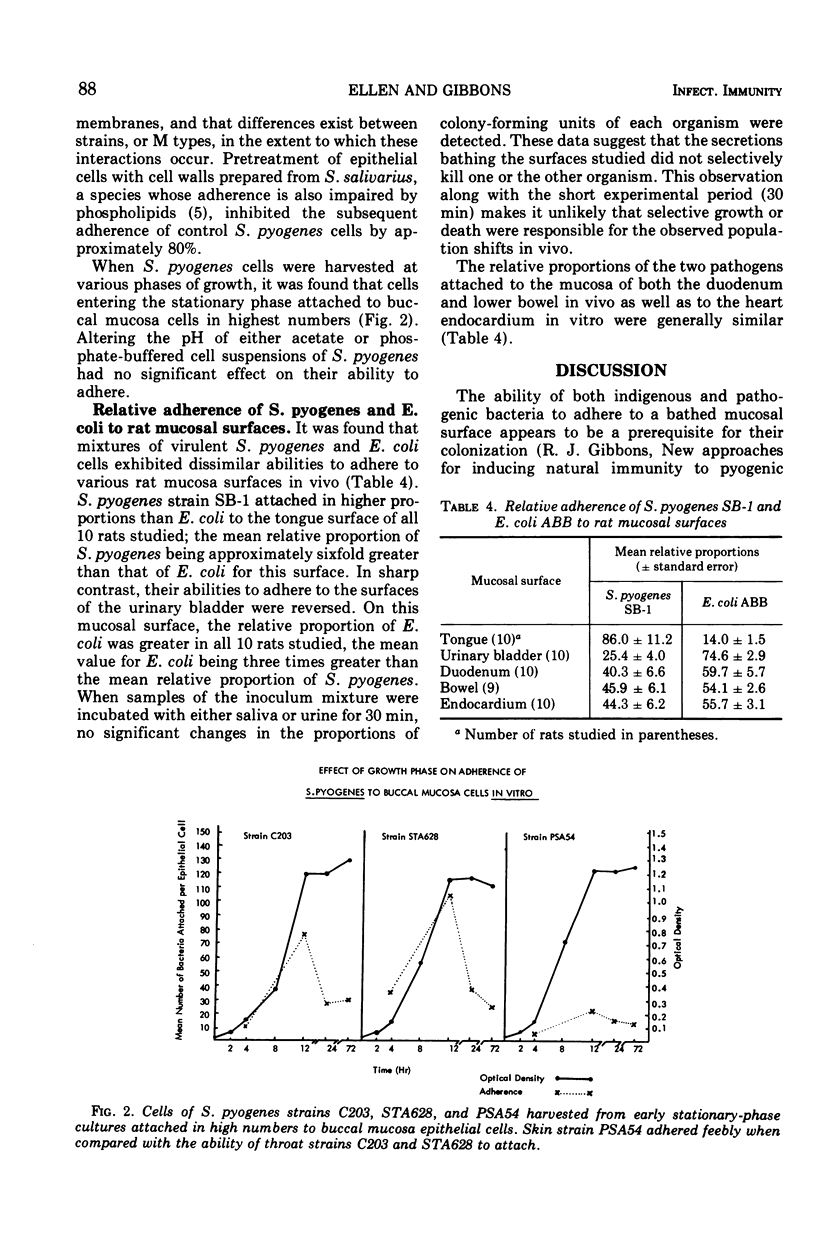
Virulent M protein-containing strains of Streptococcus pyogenes were found to adhere well to human pharyngeal cells in vitro. In contrast, an avirulent M - strain and an enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strain adhered feebly. When various rat tissues were exposed to mixtures of a virulent S. pyogenes strain and an enteropathogenic E. coli strain, the relative proportions of the two pathogenic strains recovered from mucosal surfaces differed among the sites studied. S. pyogenes cells were found to adhere in higher proportions than enteropathogenic E. coli cells to the mucosal surfaces of rat tongues, whereas on surfaces of the urinary bladder, their affinities were reversed. The data indicate that bacterial adherence is influenced by the specificity of both the bacterial and epithelial surfaces, and they suggest that adherence may influence the tissue tropisms of pathogens. Early stationary-phase cells of S. pyogenes attached better to epithelial cells than did bacteria in other growth phases. The adherence of S. pyogenes cells was impaired by pretreatment with trypsin, wheat germ lipase, Tween 80, Triton X-100, sodium lauryl sulfate, heat at 56 C, anti-group A antiserum, the presence of phospholipids, and preincubation of the epithelial cells with Streptococcus salivarius cell walls. Altering the pH or treatment with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid had no effect on the ability of S. pyogenes cells to adhere.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arbuckle J. B. The location of Escherichia coli in the pig intestine. J Med Microbiol. 1970 May;3(2):333–340. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-2-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P., Gibbons R. J. M protein-associated adherence of Streptococcus pyogenes to epithelial surfaces: prerequisite for virulence. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):826–830. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.826-830.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Van Houte J., Liljemark W. F. Parameters that effect the adherence of Streptococcus salivarius to oral epithelial surfaces. J Dent Res. 1972 Mar-Apr;51(2):424–435. doi: 10.1177/00220345720510023101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., van Houte J. Selective bacterial adherence to oral epithelial surfaces and its role as an ecological determinant. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):567–573. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.567-573.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hard G. C. Electron microscopic examination of Corynebacterium ovis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1480–1485. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1480-1485.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Rutter J. M. Role of the K88 antigen in the pathogenesis of neonatal diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli in piglets. Infect Immun. 1972 Dec;6(6):918–927. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.6.918-927.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Gibbons R. J. Ability of Veillonella and Neisseria species to attach to oral surfaces and their proportions present indigenously. Infect Immun. 1971 Sep;4(3):264–268. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.3.264-268.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Gibbons R. J. Proportional distribution and relative adherence of Streptococcus miteor (mitis) on various surfaces in the human oral cavity. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):852–859. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.852-859.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Gibbons R. J. Suppression of Candida albicans by human oral streptococci in gnotobiotic mice. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):846–849. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.846-849.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine L., Reeves M. W. Correlation of M protein production with those factors found to influence growth and substrate utilization of Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):668–680. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.668-680.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punsalang A. P., Jr, Sawyer W. D. Role of pili in the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):255–263. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.255-263.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTON M. R. J., HORNE R. W. Studies of the bacterial cell wall. II. Methods of preparation and some properties of cell walls. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1951 Jul;7(2):177–197. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(51)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirm S., Orskov F., Orskov I., Birch-Andersen A. Episome-carried surface antigen K88 of Escherichia coli. 3. Morphology. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):740–748. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.740-748.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Hsu K. C., Gotschlich E. C. Electron microscopic studies on streptococci. I. M antigen. J Exp Med. 1969 Nov 1;130(5):1063–1091. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.5.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Houte J., Gibbons R. J., Pulkkinen A. J. Adherence as an ecological determinant for streptococci in the human mouth. Arch Oral Biol. 1971 Oct;16(10):1131–1141. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(71)90042-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Houte J., Gibbons R. J., Pulkkinen A. J. Ecology of human oral lactobacilli. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):723–729. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.723-729.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannamaker L. W. Differences between streptococcal infections of the throat and of the skin. I. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jan 1;282(1):23–31. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197001012820106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Gibbons R. J. Inhibition of bacterial adherence by secretory immunoglobulin A: a mechanism of antigen disposal. Science. 1972 Aug 25;177(4050):697–699. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4050.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



