Abstract
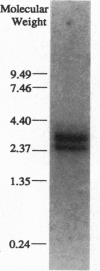
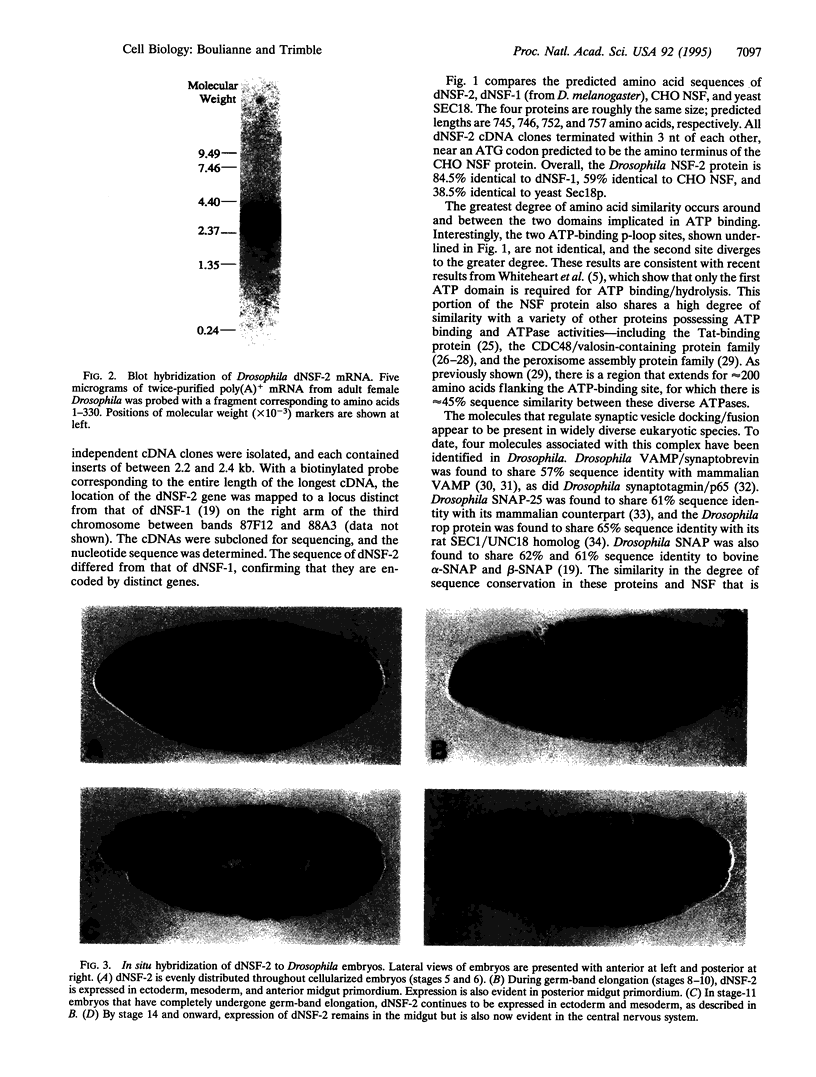
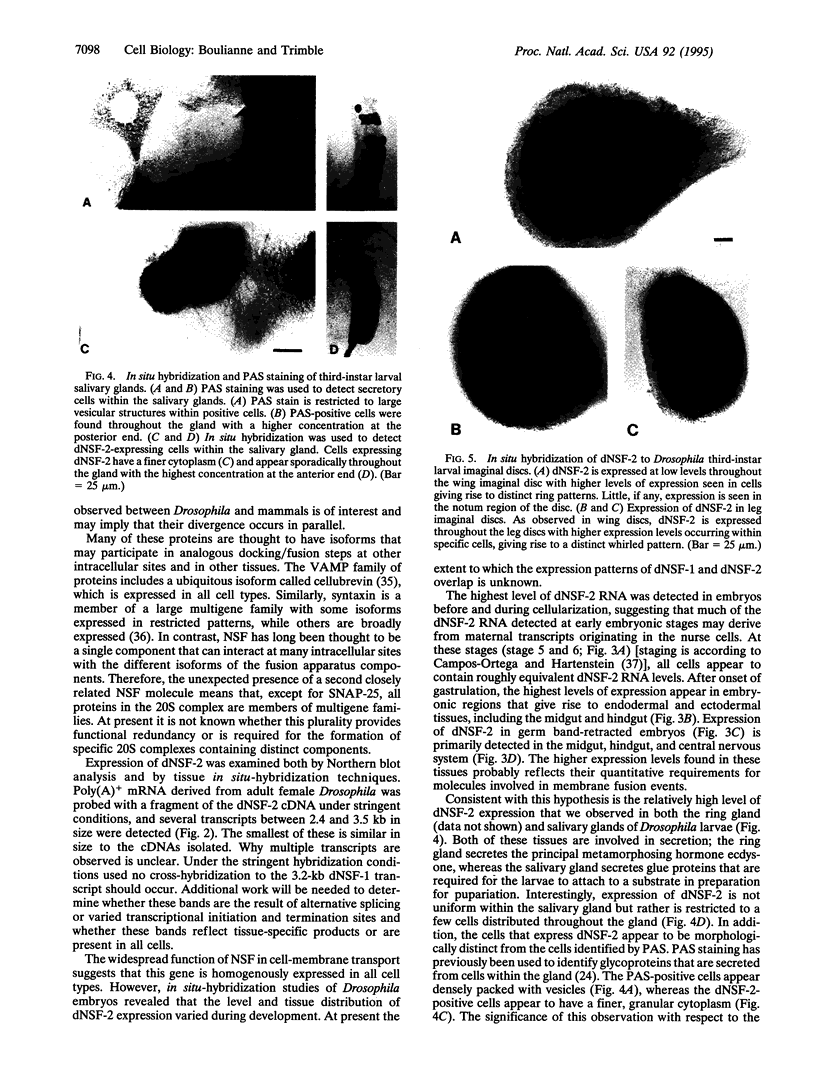
N-Ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein (NSF) is an ATPase known to have an essential role in intracellular membrane transport events. Recently, cDNA clones encoding a Drosophila melanogaster homolog of this protein, named dNSF, were characterized and found to be expressed in the nervous system. We now report the identification of a second homolog of NSF, called dNSF-2 within this species and report evidence that this ubiquitous and widely utilized fusion protein belongs to a multigene family. The predicted amino acid sequence of dNSF-2 is 84.5% identical to dNSF (hereafter named dNSF-1), 59% identical to NSF from Chinese hamster, and 38.5% identical to the yeast homolog SEC18. The highest similarity was found in a region of dNSF-2 containing one of two ATP-binding sites; this region is most similar to members of a superfamily of ATPases. dNSF-2 is localized to a region between bands 87F12 and 88A3 on chromosome 3, and in situ hybridization techniques revealed expression in the nervous system during embryogenesis and in several imaginal discs and secretory structures in the larvae. Developmental modulation of dNSF-2 expression suggests that quantitative changes in the secretory apparatus are important in histogenesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett M. K., Calakos N., Scheller R. H. Syntaxin: a synaptic protein implicated in docking of synaptic vesicles at presynaptic active zones. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):255–259. doi: 10.1126/science.1321498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., García-Arrarás J. E., Elferink L. A., Peterson K., Fleming A. M., Hazuka C. D., Scheller R. H. The syntaxin family of vesicular transport receptors. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):863–873. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90466-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bier E., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. rhomboid, a gene required for dorsoventral axis establishment and peripheral nervous system development in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):190–203. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block M. R., Glick B. S., Wilcox C. A., Wieland F. T., Rothman J. E. Purification of an N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive protein catalyzing vesicular transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7852–7856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calakos N., Bennett M. K., Peterson K. E., Scheller R. H. Protein-protein interactions contributing to the specificity of intracellular vesicular trafficking. Science. 1994 Feb 25;263(5150):1146–1149. doi: 10.1126/science.8108733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiAntonio A., Burgess R. W., Chin A. C., Deitcher D. L., Scheller R. H., Schwarz T. L. Identification and characterization of Drosophila genes for synaptic vesicle proteins. J Neurosci. 1993 Nov;13(11):4924–4935. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-11-04924.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eakle K. A., Bernstein M., Emr S. D. Characterization of a component of the yeast secretion machinery: identification of the SEC18 gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4098–4109. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann R., Wiebel F. F., Flessau A., Rytka J., Beyer A., Fröhlich K. U., Kunau W. H. PAS1, a yeast gene required for peroxisome biogenesis, encodes a member of a novel family of putative ATPases. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):499–510. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90234-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fröhlich K. U., Fries H. W., Rüdiger M., Erdmann R., Botstein D., Mecke D. Yeast cell cycle protein CDC48p shows full-length homology to the mammalian protein VCP and is a member of a protein family involved in secretion, peroxisome formation, and gene expression. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(3):443–453. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.3.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia E. P., Gatti E., Butler M., Burton J., De Camilli P. A rat brain Sec1 homologue related to Rop and UNC18 interacts with syntaxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):2003–2007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham T. R., Emr S. D. Compartmental organization of Golgi-specific protein modification and vacuolar protein sorting events defined in a yeast sec18 (NSF) mutant. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(2):207–218. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller K. J., Brownstein M. J. Use of a cDNA clone to identify a supposed precursor protein containing valosin. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):542–545. doi: 10.1038/325542a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon H. T., Ushkaryov Y. A., Edelmann L., Link E., Binz T., Niemann H., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. Cellubrevin is a ubiquitous tetanus-toxin substrate homologous to a putative synaptic vesicle fusion protein. Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):346–349. doi: 10.1038/364346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelbock P., Dillon P. J., Perkins A., Rosen C. A. A cDNA for a protein that interacts with the human immunodeficiency virus Tat transactivator. Science. 1990 Jun 29;248(4963):1650–1653. doi: 10.1126/science.2194290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Ferro S., Schekman R. Order of events in the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):461–469. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor V., Augustine G. J., Betz H. Synaptic vesicle exocytosis: molecules and models. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):785–787. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90352-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordway R. W., Pallanck L., Ganetzky B. Neurally expressed Drosophila genes encoding homologs of the NSF and SNAP secretory proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5715–5719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyler G. A., Higgins G. A., Hart R. A., Battenberg E., Billingsley M., Bloom F. E., Wilson M. C. The identification of a novel synaptosomal-associated protein, SNAP-25, differentially expressed by neuronal subpopulations. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):3039–3052. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perin M. S., Johnston P. A., Ozcelik T., Jahn R., Francke U., Südhof T. C. Structural and functional conservation of synaptotagmin (p65) in Drosophila and humans. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):615–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. M., Walsh M. J., Franke W. W. An abundant and ubiquitous homo-oligomeric ring-shaped ATPase particle related to the putative vesicle fusion proteins Sec18p and NSF. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1757–1767. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08300.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rexach M. F., Schekman R. W. Distinct biochemical requirements for the budding, targeting, and fusion of ER-derived transport vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(2):219–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.2.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risinger C., Blomqvist A. G., Lundell I., Lambertsson A., Nässel D., Pieribone V. A., Brodin L., Larhammar D. Evolutionary conservation of synaptosome-associated protein 25 kDa (SNAP-25) shown by Drosophila and Torpedo cDNA clones. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):24408–24414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Mechanisms of intracellular protein transport. Nature. 1994 Nov 3;372(6501):55–63. doi: 10.1038/372055a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Warren G. Implications of the SNARE hypothesis for intracellular membrane topology and dynamics. Curr Biol. 1994 Mar 1;4(3):220–233. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schekman R. Genetic and biochemical analysis of vesicular traffic in yeast. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;4(4):587–592. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90076-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söllner T., Whiteheart S. W., Brunner M., Erdjument-Bromage H., Geromanos S., Tempst P., Rothman J. E. SNAP receptors implicated in vesicle targeting and fusion. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):318–324. doi: 10.1038/362318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Baumert M., Perin M. S., Jahn R. A synaptic vesicle membrane protein is conserved from mammals to Drosophila. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1475–1481. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90193-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble W. S., Cowan D. M., Scheller R. H. VAMP-1: a synaptic vesicle-associated integral membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4538–4542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteheart S. W., Brunner M., Wilson D. W., Wiedmann M., Rothman J. E. Soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion attachment proteins (SNAPs) bind to a multi-SNAP receptor complex in Golgi membranes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):12239–12243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteheart S. W., Rossnagel K., Buhrow S. A., Brunner M., Jaenicke R., Rothman J. E. N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein: a trimeric ATPase whose hydrolysis of ATP is required for membrane fusion. J Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;126(4):945–954. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.4.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. W., Whiteheart S. W., Wiedmann M., Brunner M., Rothman J. E. A multisubunit particle implicated in membrane fusion. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(3):531–538. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.3.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. W., Wilcox C. A., Flynn G. C., Chen E., Kuang W. J., Henzel W. J., Block M. R., Ullrich A., Rothman J. E. A fusion protein required for vesicle-mediated transport in both mammalian cells and yeast. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):355–359. doi: 10.1038/339355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]