Abstract
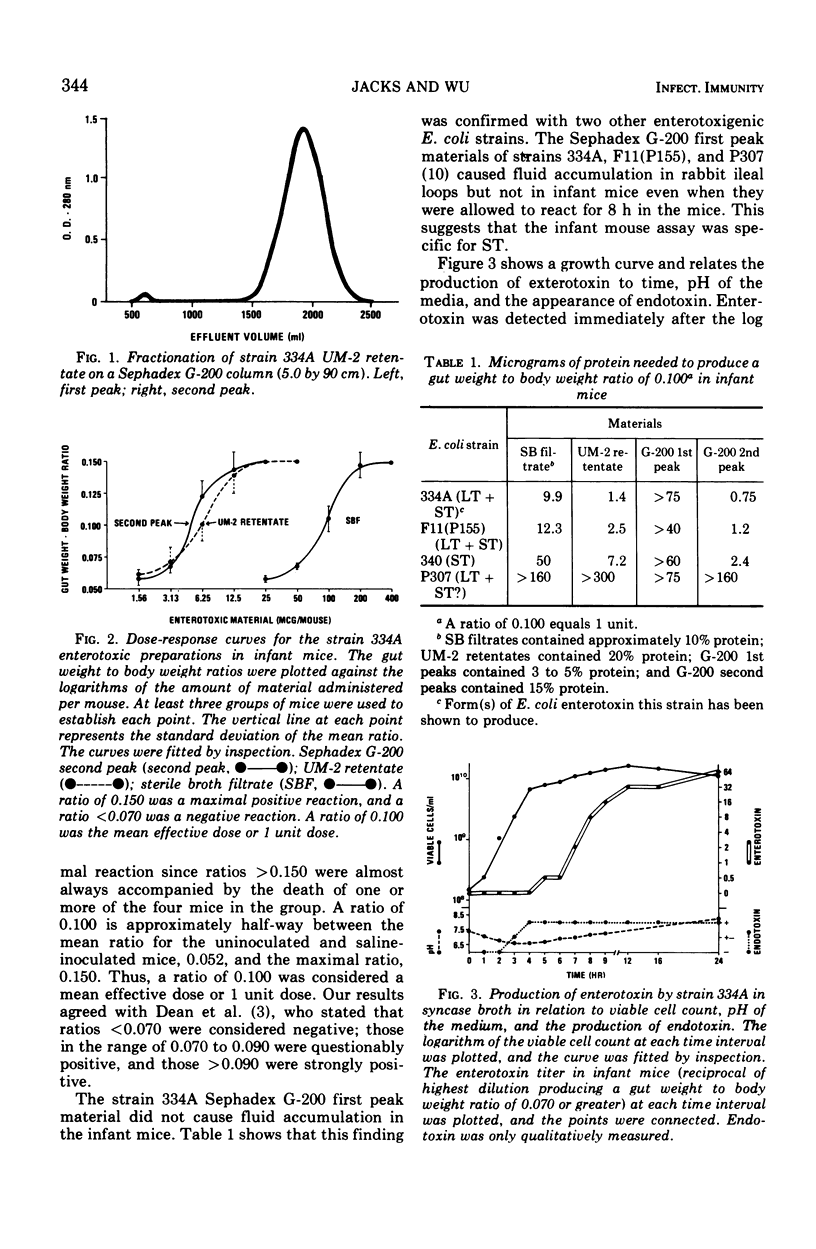
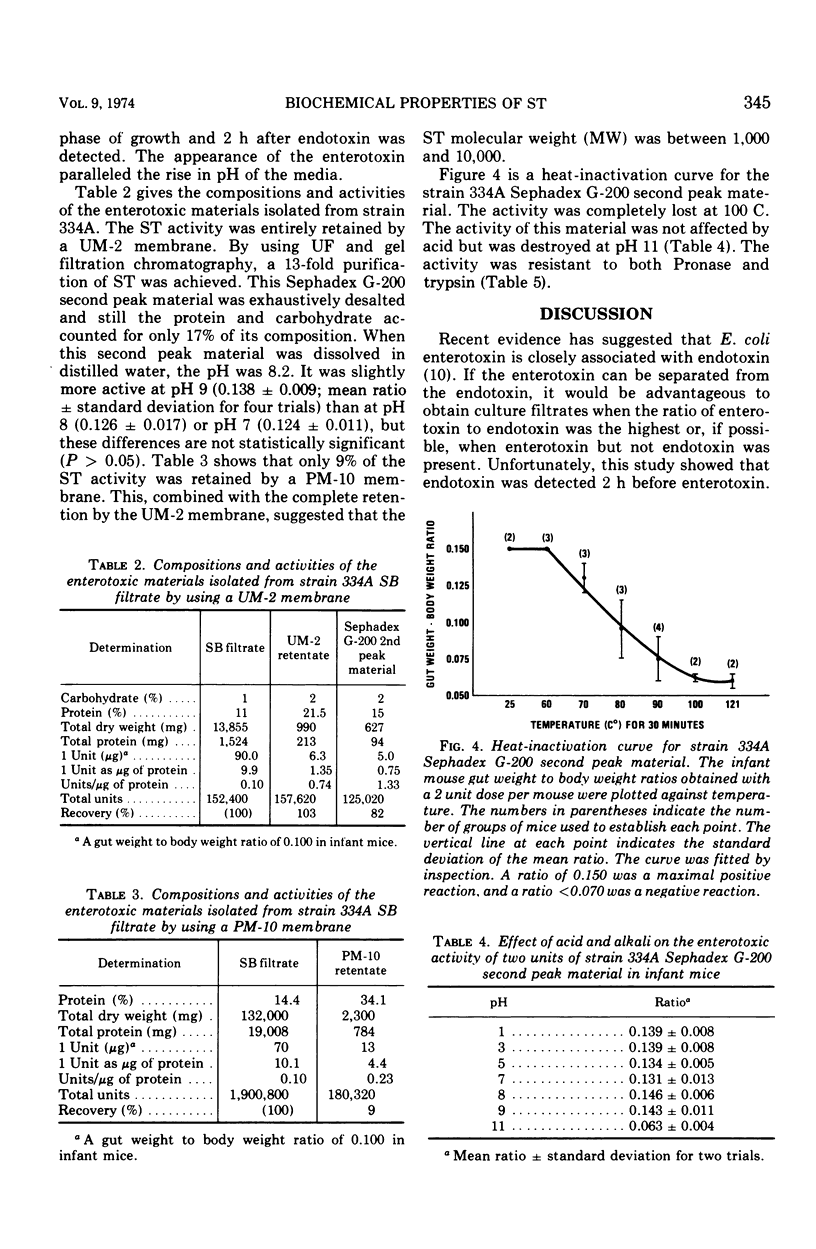
The low-molecular-weight, heat-stable type of Escherichia coli enterotoxin (ST) was obtained from sterile syncase broth filtrates of human and animal enteropathogenic E. coli strains. ST was assayed in infant mice, and it was found that this assay was specific for ST in that the high-molecular-weight, heat-labile type of E. coli exterotoxin would not cause fluid accumulation in these animals. ST was first detected in the broth of a culture of human strain 334A(015:H11) 5 h after inoculation, immediately after the log phase of growth; the highest concentration of ST occurred at 24 h after inoculation. ST was purified 13-fold by ultrafiltration and gel filtration chromatography. The purest preparation contained 15% protein and 2% carbohydrate. The mean effective dose or 1 unit dose in infant mice was 5.0 μg/mouse. The ST molecular weight was between 1,000 and 10,000, and its activity was resistant to acid, trypsin, and Pronase.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bywater R. J. Dialysis and ultrafiltration of heat-stable enterotoxin from Escherichia coli. J Med Microbiol. 1972 Aug;5(3):337–343. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-3-337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crutchley M. J., Marsh D. G., Cameron J. Free Endotoxin. Nature. 1967 Jun 3;214(5092):1052–1052. doi: 10.1038/2141052a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Pierce N. F. Differences in the response of rabbit small intestine to heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):873–880. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.873-880.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Atthasampunna P., Chulasamaya M., Charunmethee P. Pathogenesis of experimental cholera: biologic ativities of purified procholeragen A. J Immunol. 1966 Mar;96(3):440–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L., Barnum D. A. A heat-labile enterotoxin from strains of Eschericha coli enteropathogenic for pigs. J Infect Dis. 1969 Oct;120(4):419–426. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMEL B. C. A modified spectrophotometric determination of chymotrypsin, trypsin, and thrombin. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Dec;37:1393–1399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T. M., Wu B. J., Braemer A. C., Bidlack D. E. Properties of the enterotoxic component in Escherichia coli enteropathogenic for swine. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):178–189. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.178-189.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler E. M. Enterotoxic activity of filtrates of escherichia coli in young pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1968 Dec;29(12):2263–2274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larivière S., Gyles C. L., Barnum D. A. A comparative study of the rabbit and pig gut loop systems for the assay of Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Can J Comp Med. 1972 Oct;36(4):319–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Wallace C. K. Stimulation of jejunal secretion by a crude Escherichia coli enterotixin. Gastroenterology. 1972 Sep;63(6):439–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Gorbach S. L., Banwell J. G., Jacobs B., Chatterjee B. D., Mitra R. C. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from patients with severe cholera-like disease. J Infect Dis. 1971 Apr;123(4):378–385. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.4.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Gyles C. L. The relationship between two apparently different enterotoxins produced by enteropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli of porcine origin. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Aug;3(3):387–401. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-3-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipp S. C., Moon H. W. Modification of enterosorption in experimental enteric colibacillosis of swine inoculated with Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1973 Mar;127(3):255–260. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.3.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



