Abstract
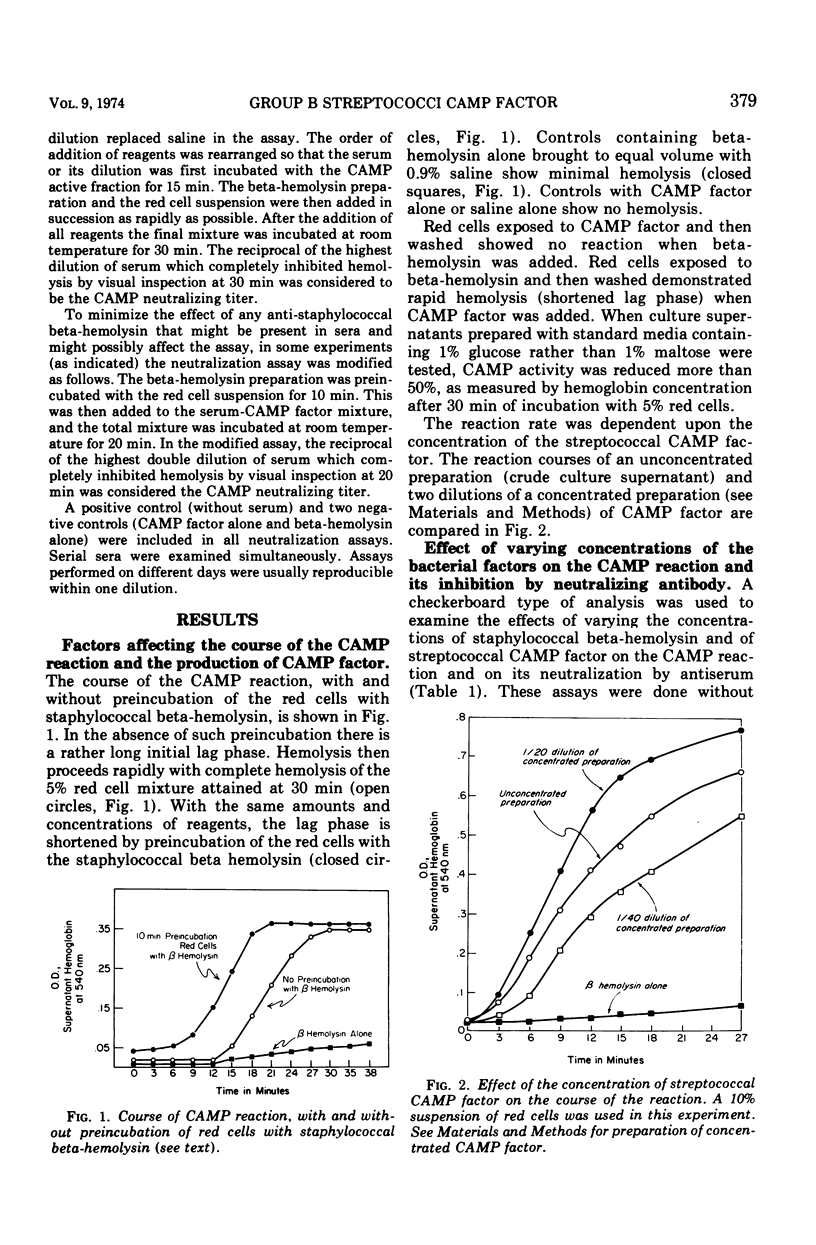
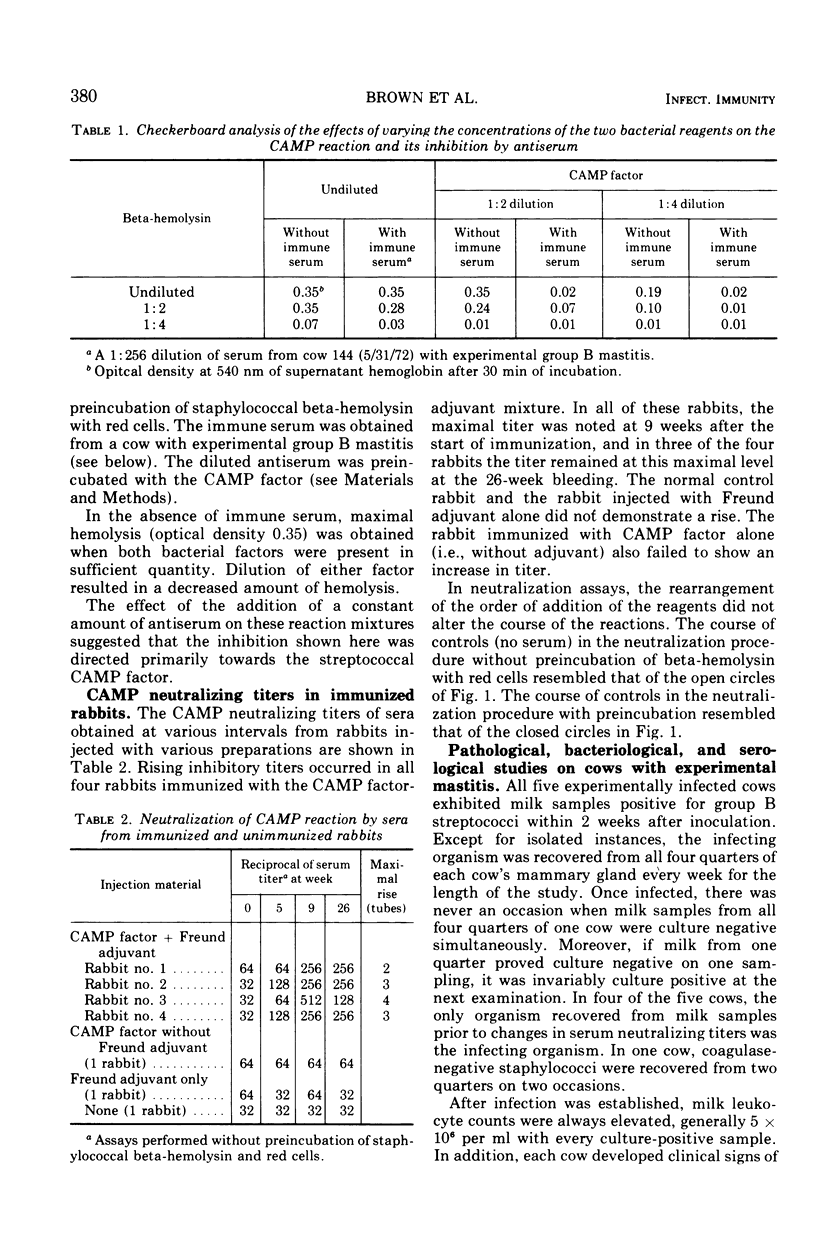
Quantitative assay methods for CAMP factor activity of group B streptococci and for neutralization of this activity by animal sera are described. The course of the CAMP reaction is influenced by preincubation of red cells with staphylococcal beta-hemolysin and the rate of the reaction by the concentration of CAMP factor. The production of CAMP factor is enhanced by substitution of maltose for glucose in culture broth. Rising inhibitory titers to CAMP activity in sera of rabbits injected with sterile culture supernates of group B streptococci suggest that CAMP factor is an antigen in the rabbit. Cows with experimentally induced group B streptococcal mastitis also demonstrated significant rises in neutralizing titers for CAMP activity.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barton L. L., Feigin R. D., Lins R. Group B beta hemolytic streptococcal meningitis in infants. J Pediatr. 1973 Apr;82(4):719–723. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80605-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EICKHOFF T. C., KLEIN J. O., DALY A. K., INGALL D., FINLAND M. NEONATAL SEPSIS AND OTHER INFECTIONS DUE TO GROUP B BETA-HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCI. N Engl J Med. 1964 Dec 10;271:1221–1228. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196412102712401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ESSEVELD H., DANIELS-BOSMAN M. S., LEIJNSE B. Some observations about the CAMP reaction and its application to human beta haemolytic streptococci. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1958;24(2):145–156. doi: 10.1007/BF02548442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrieri P., Wannamaker L. W., Nelson J. Localization and characterization of the hippuricase activity of group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1973 May;7(5):747–752. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.5.747-752.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franciosi R. A., Knostman J. D., Zimmerman R. A. Group B streptococcal neonatal and infant infections. J Pediatr. 1973 Apr;82(4):707–718. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80604-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOOD M., JANNEY A., DAMERON G. Beta hemolytic streptococcus group B associated with problems of the perinatal period. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1961 Oct;82:809–818. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)36146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON A. W., MAYMAN D. Staphylococcal toxins. IV. Factors affecting hemolysis by delta-lysin. Can J Microbiol. 1958 Oct;4(5):477–486. doi: 10.1139/m58-051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelínková J., Neubauer M., Duben J. Group B streptococci in human pathology. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1970;214(3):450–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancefield R. C., Freimer E. H. Type-specific polysaccharide antigens of group B streptococci. J Hyg (Lond) 1966 Jun;64(2):191–203. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORCROSS N. L. Antigenic substances purified from Streptococcus agalactiae. I. Antibody response in infected cattle. Cornell Vet. 1963 Apr;53:301–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULSFORD M. F. Some factors influencing the production of CAMP factor by Streptococcus agalactiae. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1954 Jun;32(3):353–360. doi: 10.1038/icb.1954.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



