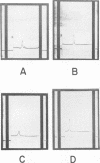
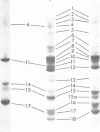
Abstract
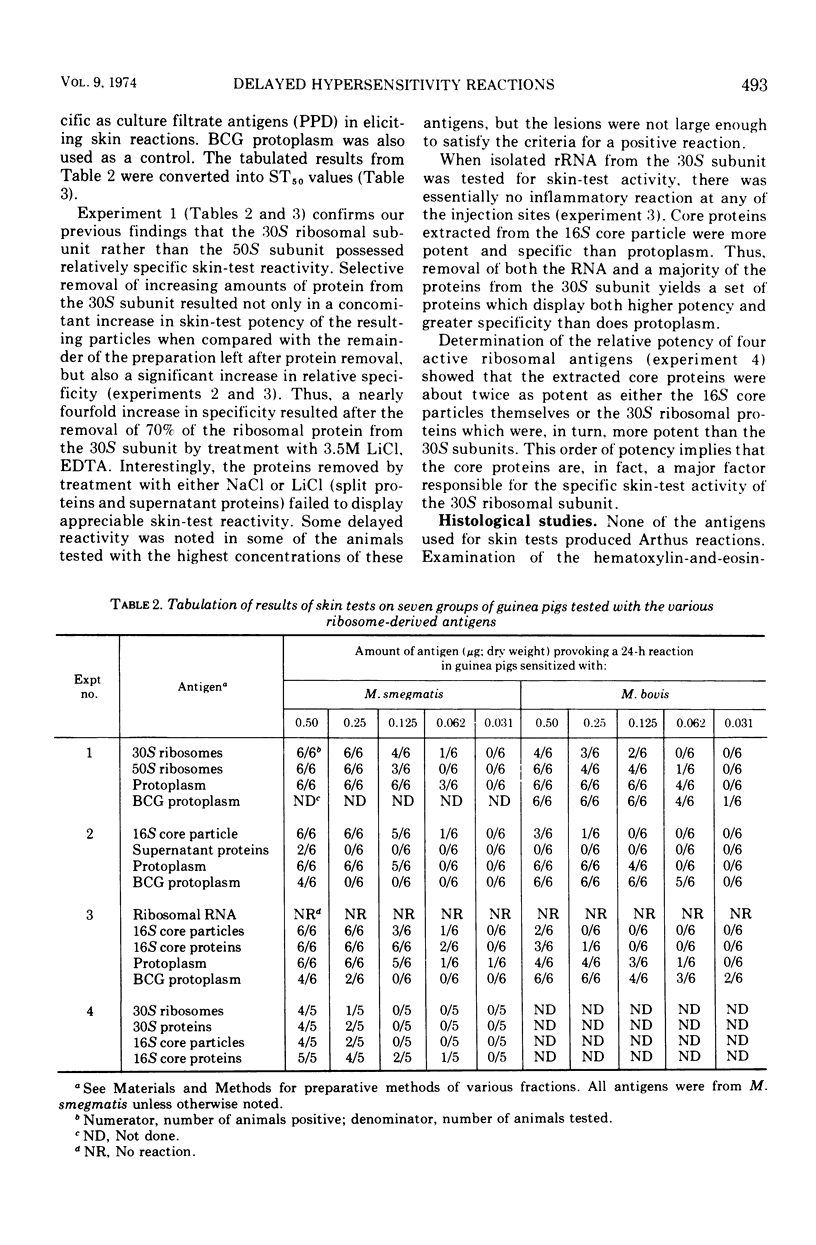
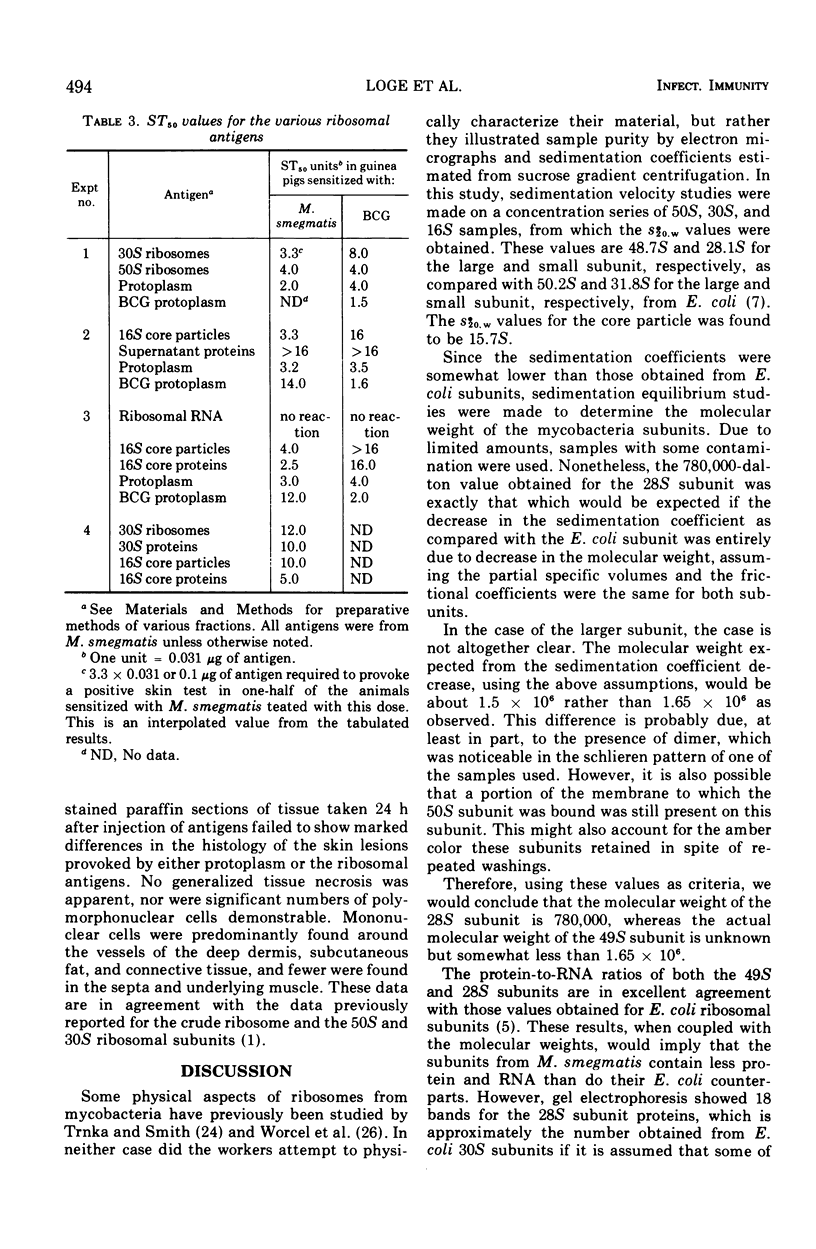
Ribosomal subunits from Mycobacterium smegmatis were analyzed by using sedimentation velocity, sedimentation equilibrium, and acrylamide gel electrophoresis experiments. These s2̊0.w values for the subunits are 48.7S and 28.1S. The molecular weight of the 49S subunit is about 1.65 × 106, and that of the 28S subunit is 7.8 × 105. Both subunits contain about 37% protein and 63% ribonucleic acid. A protein-deficient particle having an s2̊0.w value of 15.7S contains about 11% protein and 89% ribonucleic acid. Skin tests showed all subunits and proteins to be active as agents in provoking delayed hypersensitivity, but the 16S protein-deficient particle, as well as the proteins derived from it, was more specific than the subunits themselves.
Full text
PDF

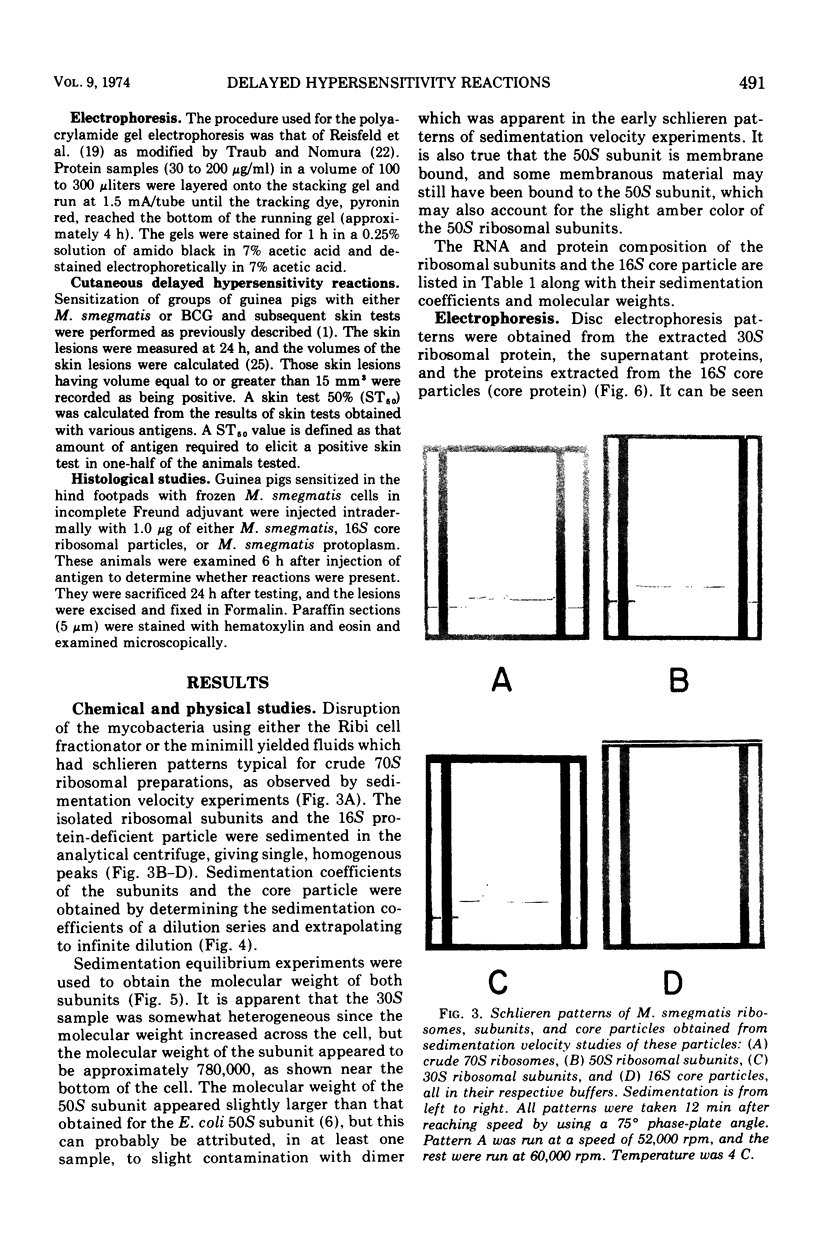
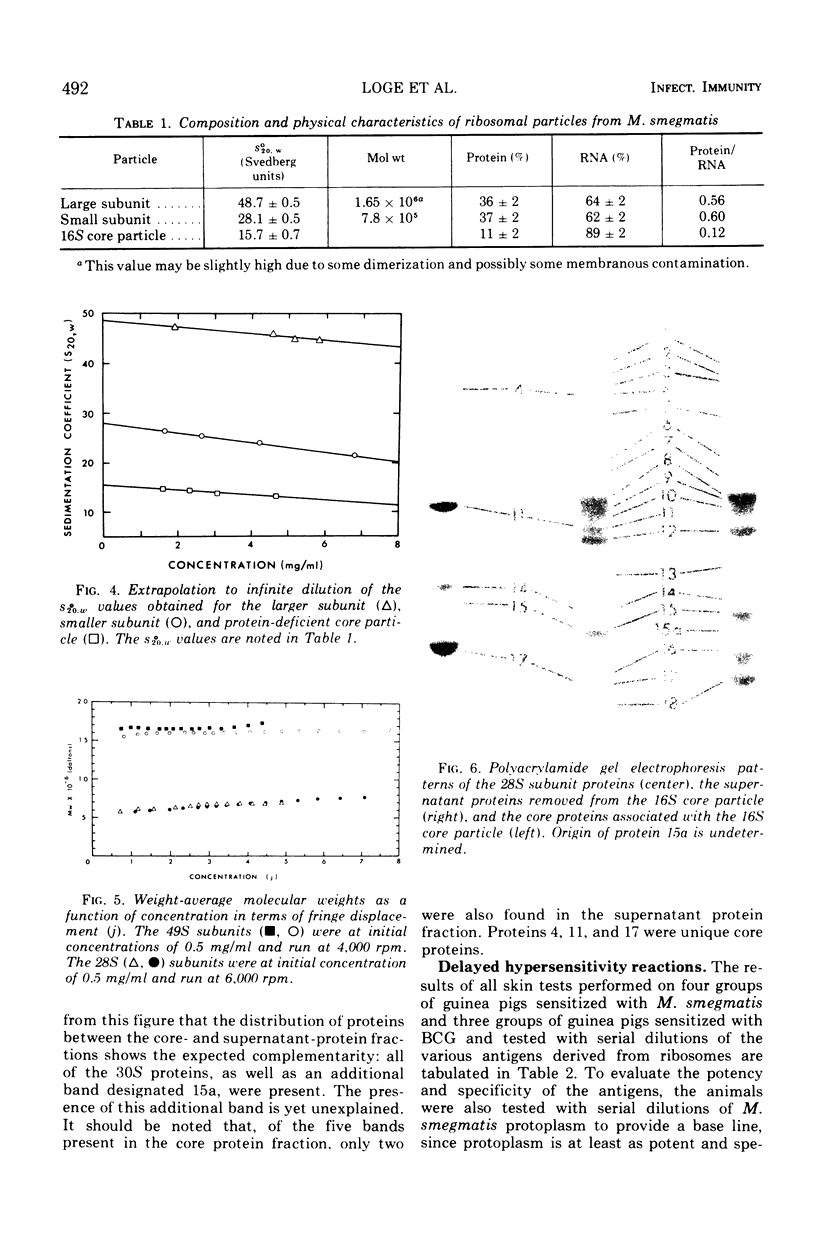


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker R. E., Hill W. E., Larson C. L. Delayed hypersensitivity reactions provoked by ribosomes from acid-fast bacilli. I. Ribosomal isolation, characterization, delayed hypersensitivity, and specificity. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):258–265. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.258-265.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beam R. E., Stottmeier K. D., Kubica G. P. Purified protoplasmic peptides of mycobacteria: isolation of species-specific peptides from protoplasm of mycobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):195–200. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.195-200.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Counts J. M., Kubica G. P. Investigation of protoplasmic extracts of tubercle bacilli as skin test antigens. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Oct;14(10):1053–1058. doi: 10.1139/m68-177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eikenberry E. F., Bickle T. A., Traut R. R., Price C. A. Separation of large quantities of ribosomal subunits by zonal ultracentrifugation. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jan;12(1):113–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy S. J., Kurland C. G., Voynow P., Mora G. The ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli. I. Purification of the 30S ribosomal proteins. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):2897–2905. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. E., Rossetti G. P., Van Holde K. E. Physical studies of ribosomes from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 Sep 14;44(2):263–277. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90174-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. E., Thompson J. D., Anderegg J. W. X-ray scattering study of ribosomes from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 Aug 28;44(1):89–102. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Otaka E., Osawa S. Release of ribosomal proteins from Escherichia coli ribosomes with high concentrations of lithium chloride. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 14;33(1):109–122. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90284-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANAI K., YOUMANS G. P., YOUMANS A. S. Allergenicity of intracellular particles, cell walls, and cytoplasmic fluid from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Bacteriol. 1960 Nov;80:615–621. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.5.615-621.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krembel J., Apirion D. Changes in ribosomal proteins associated with mutants in a locus that affects Escherichia coli ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 28;33(2):363–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90194-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARSON C. L., RIBI E., WICHT W. C., LIST R. Skin reactions produced in rabbits by cell walls and protoplasm of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and M. butyricum. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1961 Feb;83:184–193. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1961.83.2P1.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson C. L., Baker R. E., Baker M. B. A comparison of the ability of protoplasm and culture filtrate (PPD) antigens from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. kansasii and M. batteyi to elicit delayed reactions in infected guinea pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1968 Dec;98(6):1055–1057. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1968.98.6.1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson C., Ribi E., Baker M. B., List R., Baker R., Wicht W. Skin reactions in rabbits sensitized with typical and atypical mycobacteria and tested with homologous and heterologous protoplasm. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1966 Dec;94(6):923–932. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1966.94.6.923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Ortiz L., Solarolo E. B., Bojalil L. F. Delayed hypersensitivity to ribosomal protein from BCG. J Immunol. 1971 Oct;107(4):1022–1026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa S., Ito T., Otaka E. Differentiation of the ribosomal protein compositions in the genus Escherichia and its related bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):168–178. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.168-178.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISFELD R. A., LEWIS U. J., WILLIAMS D. E. Disk electrophoresis of basic proteins and peptides on polyacrylamide gels. Nature. 1962 Jul 21;195:281–283. doi: 10.1038/195281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitnik-Elson P., Atsmon A. Detachment of ribosomal proteins by salt. I. Effect of conditions on the amount of protein detached. J Mol Biol. 1969 Oct 14;45(1):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley W. M., Jr, Bock R. M. Isolation and physical properties of the ribosomal ribonucleic acid of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1965 Jul;4(7):1302–1311. doi: 10.1021/bi00883a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub P., Nomura M. Structure and function of E. coli ribosomes. V. Reconstitution of functionally active 30S ribosomal particles from RNA and proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):777–784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub P., Nomura M. Structure and function of Escherichia coli ribosomes. I. Partial fractionation of the functionally active ribosomal proteins and reconstitution of artificial subribosomal particles. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jun 28;34(3):575–593. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90182-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trnka L., Smith D. W. Influence of cell disruption methods on polyuridylic acid dependent polyphenylalanine synthesis by isolated ribosomes of mycobacteria. Experientia. 1968 Nov 15;24(11):1109–1110. doi: 10.1007/BF02147786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAKSMAN B. H., MATOLTSY M. Quantitative study of local passive transfer of tuberculin sensitivity with peritoneal exudate cells in the guinea pig. J Immunol. 1958 Sep;81(3):235–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worcel A., Goldman D. S., Sachs I. B. Properties and fine structure of the ribosomes from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):122–129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. The relationship between sedimentation value and immunogenic acitivity of mycobacterial ribonucleic acid. J Immunol. 1973 Feb;110(2):581–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann R. A., Muto A., Fellner P., Ehresmann C., Branlant C. Location of ribosomal protein binding sites on 16S ribosomal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1282–1286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]