Abstract
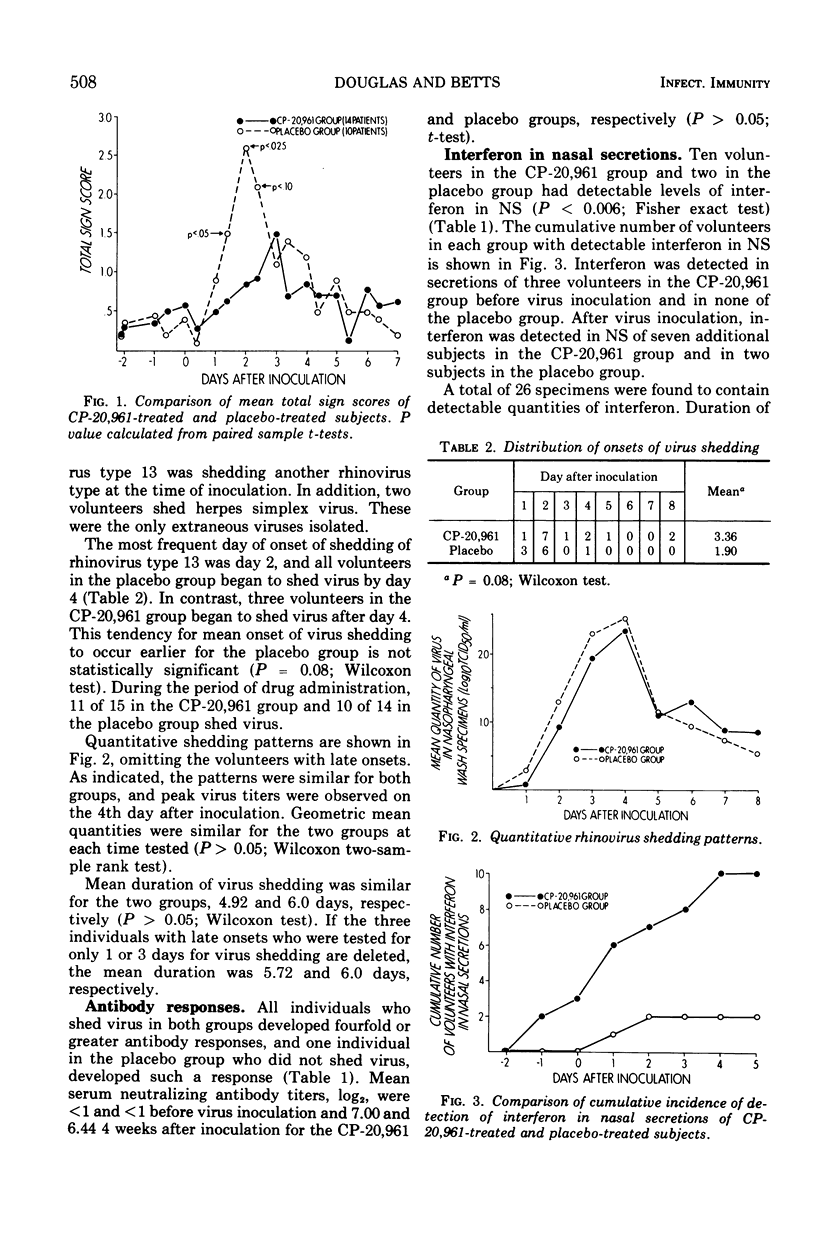
Nasal administration of an interferon inducer, CP-20,961 (N, N-dioctadecyl-N′, N′-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)propanediamine), was evaluated in a double-blind, placebo-controlled study of experimental rhinovirus infection in 29 volunteers. Detectable nasal interferon developed in 10 of 15 subjects treated with CP-20,961, and 2 of 14 in the group receiving placebo (P < 0.006). Titers of CP-20,961-induced interferon ranged from 10 to 250 international units, concentrations similar to those observed in rhinovirus infections. Ten in the CP-20,961 group and eight in the placebo group became ill (P > 0.05). However, mean total sign scores were significantly diminished among CP-20,961-treated subjects as compared with placebo-treated subjects (P < 0.025). No significant effect was noted on quantitative virus shedding patterns or neutralizing antibody responses. These findings suggest that such concentrations of induced interferon do not protect against rhinovirus infection, and that factors other than interferon may be important in recovery from rhinovirus infection.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cate T. R., Douglas R. G., Jr, Couch R. B. Interferon and resistance to upper respiratory virus illness. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jun;131(2):631–636. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas R. G., Jr, Couch R. B. Parenteral inactivated rhinovirus vaccine: minimal protective effect. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Mar;139(3):899–902. doi: 10.3181/00379727-139-36262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas R. G., Jr Pathogenesis of rhinovirus common colds in human voluteers. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1970 Jun;79(3):563–571. doi: 10.1177/000348947007900320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatmaitan B. C., Stanley E. D., Jackson G. G. The limited effect of nasal interferon induced by rhinovirus and a topical chemical inducer on the course of infection. J Infect Dis. 1973 Apr;127(4):401–407. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.4.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. A., Baron S., Perkins J. C., Worthington M., Van Kirk J. E., Mills J., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Evaluation of an interferon inducer in viral respiratory disease. JAMA. 1972 Feb 28;219(9):1179–1184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNIGHT V. THE USE OF VOLUNTEERS IN MEDICAL VIROLOGY. Prog Med Virol. 1964;6:1–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merigan T. C., Reed S. E., Hall T. S., Tyrrell D. A. Inhibition of respiratory virus infection by locally applied interferon. Lancet. 1973 Mar 17;1(7803):563–567. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90714-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETRALLI J. K., MERIGAN T. C., WILBUR J. R. ACTION OF ENDOGENOUS INTERFERON AGAINST VACCINIA INFECTION IN CHILDREN. Lancet. 1965 Aug 28;2(7409):401–405. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)90755-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins J. C., Tucker D. N., Knopf H. L., Wenzel R. P., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Comparison of protective effect of neutralizing antibody in serum and nasal secretions in experimental rhinovirus type 13 illness. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Dec;90(6):519–526. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker D., Kiernat J., Gauntt C. Interferon induction by rhinoviruses and effect of interferon on rhinovirus yields in human cell lines. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 May;143(1):23–27. doi: 10.3181/00379727-143-37245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Stinebring W. R. Interferon appearance stimulated by endotoxin, bacteria, or viruses in mice pre-treated with Escherichia coli endotoxin or infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Nature. 1965 Oct 30;208(5009):456–458. doi: 10.1038/208456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



