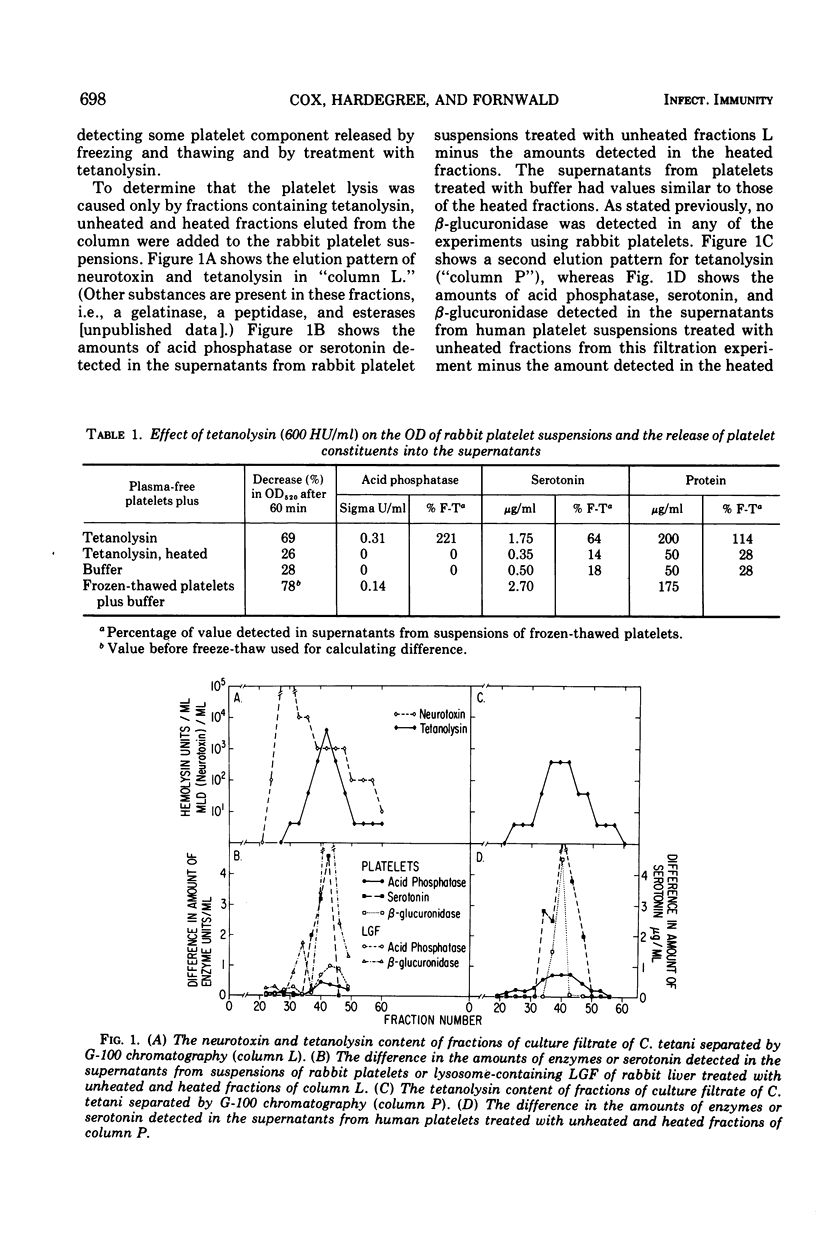
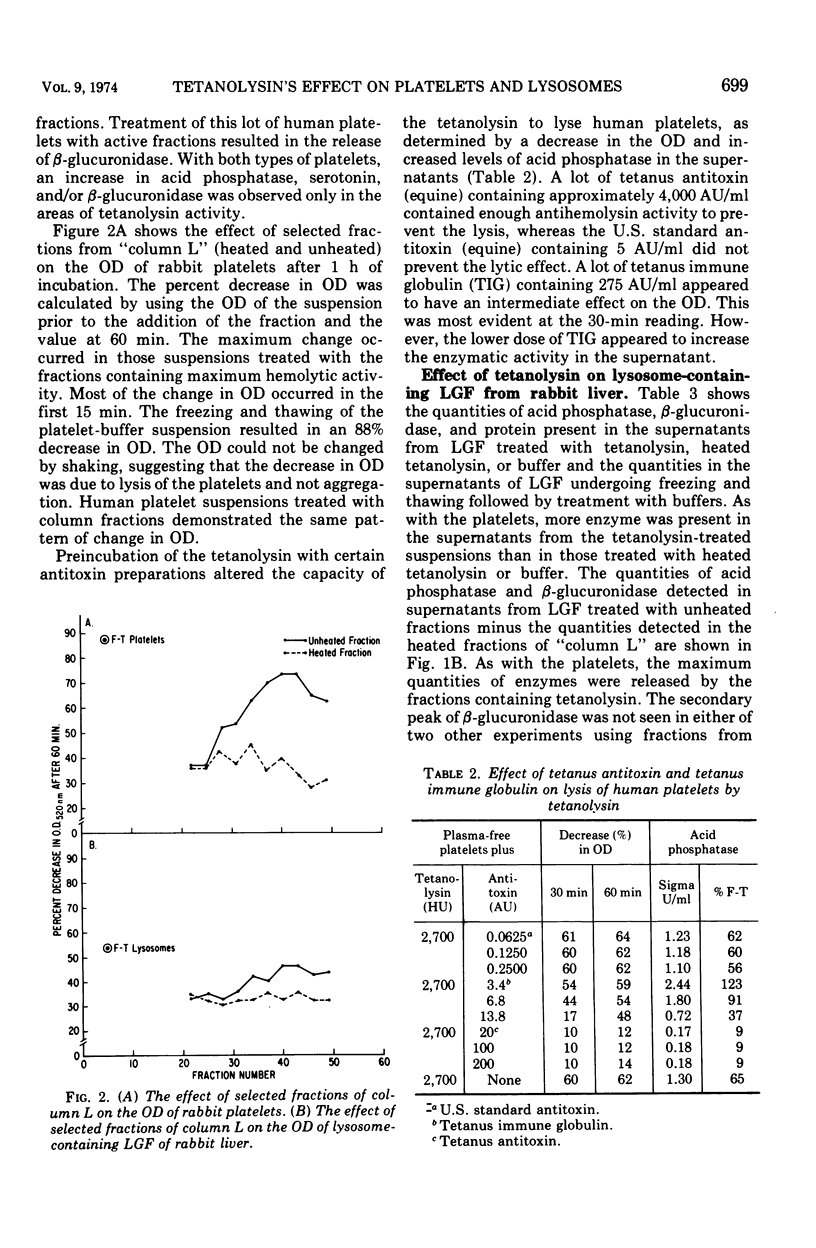
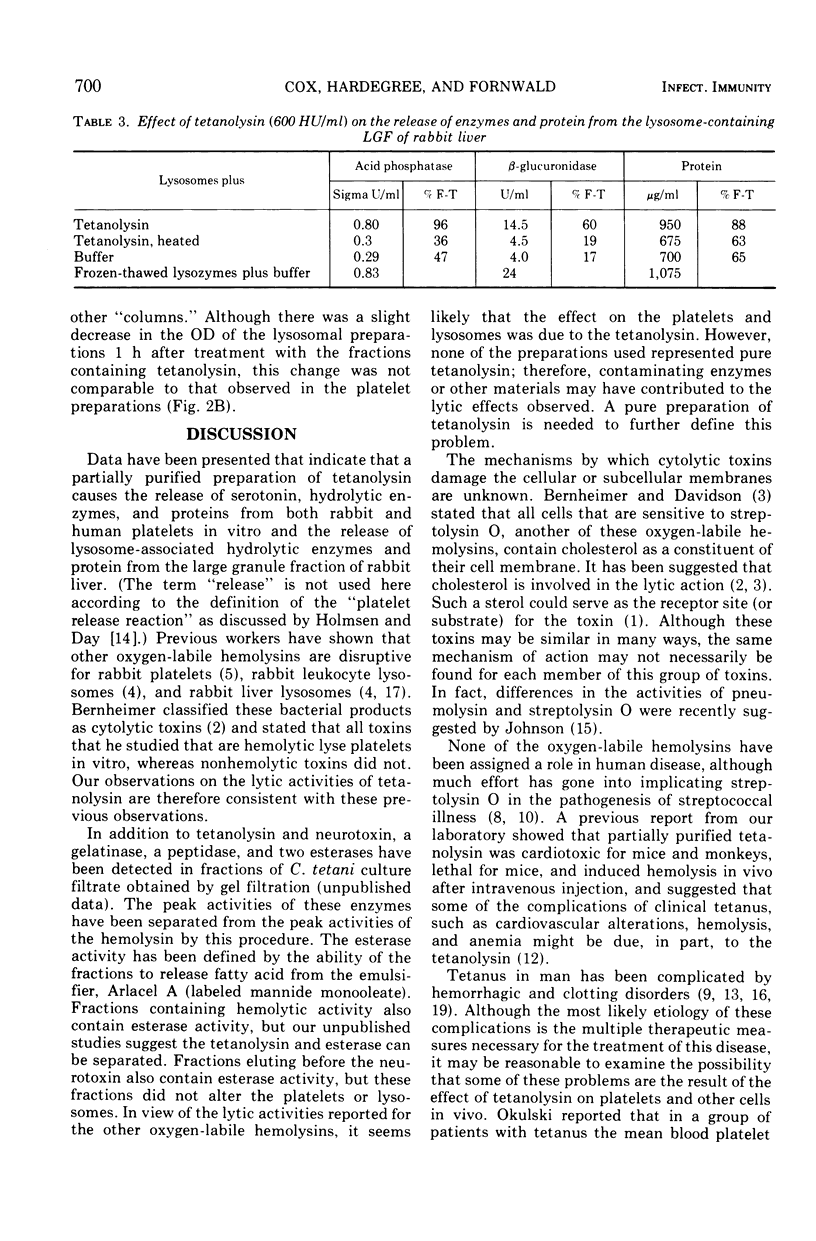
Abstract
Tetanolysin, partially purified, caused the lysis of human and rabbit platelets, as determined by a decrease in the optical density of platelet suspensions and the release of serotonin, enzymes, and protein. This lytic activity was neutralized by antitoxin. In addition, a suspension of the lysosome-containing large granule fraction of rabbit liver released hydrolytic enzymes when exposed to tetanolysin. Thus, tetanolysin can be added to the list of bacterial toxins that are lytic for a variety of cellular or subcellular membranes. These findings provide additional data that suggest that tetanolysin may contribute to the pathogenesis of some of the unusual manifestations observed in clinical tetanus.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNHEIMER A. W., DAVIDSON M. LYSIS OF PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISMS BY STAPHYLOCOCCAL AND STREPTOCOCCAL TOXINS. Science. 1965 May 28;148(3674):1229–1231. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3674.1229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNHEIMER A. W., SCHWARTZ L. L. EFFECT OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL AND OTHER BACTERIAL TOXINS ON PLATELETS IN VITRO. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:209–223. doi: 10.1002/path.1700890121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W. Disruption of wall-less bacteria by streptococcal and staphylococcal toxins. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1677–1680. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1677-1680.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Schwartz L. L. Lysosomal disruption by bacterial toxins. J Bacteriol. 1964 May;87(5):1100–1104. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.5.1100-1104.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett J. L., Harris P. J. Studies on the sympathetic nervous system in tetanus. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1973;276(3-4):447–460. doi: 10.1007/BF00499897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DES PREZ R. M., HOROWITZ H. I., HOOK E. W. Effects of bacterial endotoxin on rabbit platelets. I. Platelet aggregation and release of platelet factors in vitro. J Exp Med. 1961 Dec 1;114:857–874. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.6.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg I. Mechanisms of cell and tissue injury induced by group A streptococci: relation to poststreptococcal sequelae. J Infect Dis. 1972 Sep;126(3):294–340. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.3.294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDEGREE M. C. SEPARATION OF NEUROTOXIN AND HEMOLYSIN OF CLOSTRIDIUM TETANI. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Jun;119:405–408. doi: 10.3181/00379727-119-30195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRISON G. A., ROSEN M., GOODALL P. HAEMORRHAGIC COMPLICATIONS DURING THE TREATMENT OF TETANUS. Lancet. 1964 Feb 29;1(7331):463–464. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)90796-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardegree M. C., Palmer A. E., Duffin N. Tetanolysin: in-vivo effects in animals. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jan;123(1):51–60. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Day H. J. The selectivity of the thrombin-induced platelet release reaction: subcellular localization of released and retained constituents. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 May;75(5):840–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. K. Properties of purified pneumococcal hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):755–760. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.755-760.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARACA M., STEFANINI M. An unusual acquired coagulation defect. JAMA. 1962 Jan 13;179:165–168. doi: 10.1001/jama.1962.03050020000013b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNKEL H. G., TISELIUS A. Electrophoresis of proteins on filter paper. J Gen Physiol. 1951 Sep;35(1):89–118. doi: 10.1085/jgp.35.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingdon G. C., Sword C. P. Effects of Listeria monocytogenes Hemolysin on Phagocytic Cells and Lysosomes. Infect Immun. 1970 Apr;1(4):356–362. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.4.356-362.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okulski J. The blood coagulation system in tetanus patients. Acta Med Pol. 1969;10(3):291–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Axelrod J., Zweig M. A sensitive and specific fluorescence assay for tissue serotonin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1965 May;14(5):831–835. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(65)90102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSMANN G., THOMAS L. Studies on lysosomes. I. The effects of endotoxin, endotoxin tolerance, and cortisone on the release of acid hydrolases from a granular fraction of rabbit liver. J Exp Med. 1962 Oct 1;116:433–450. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.4.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



