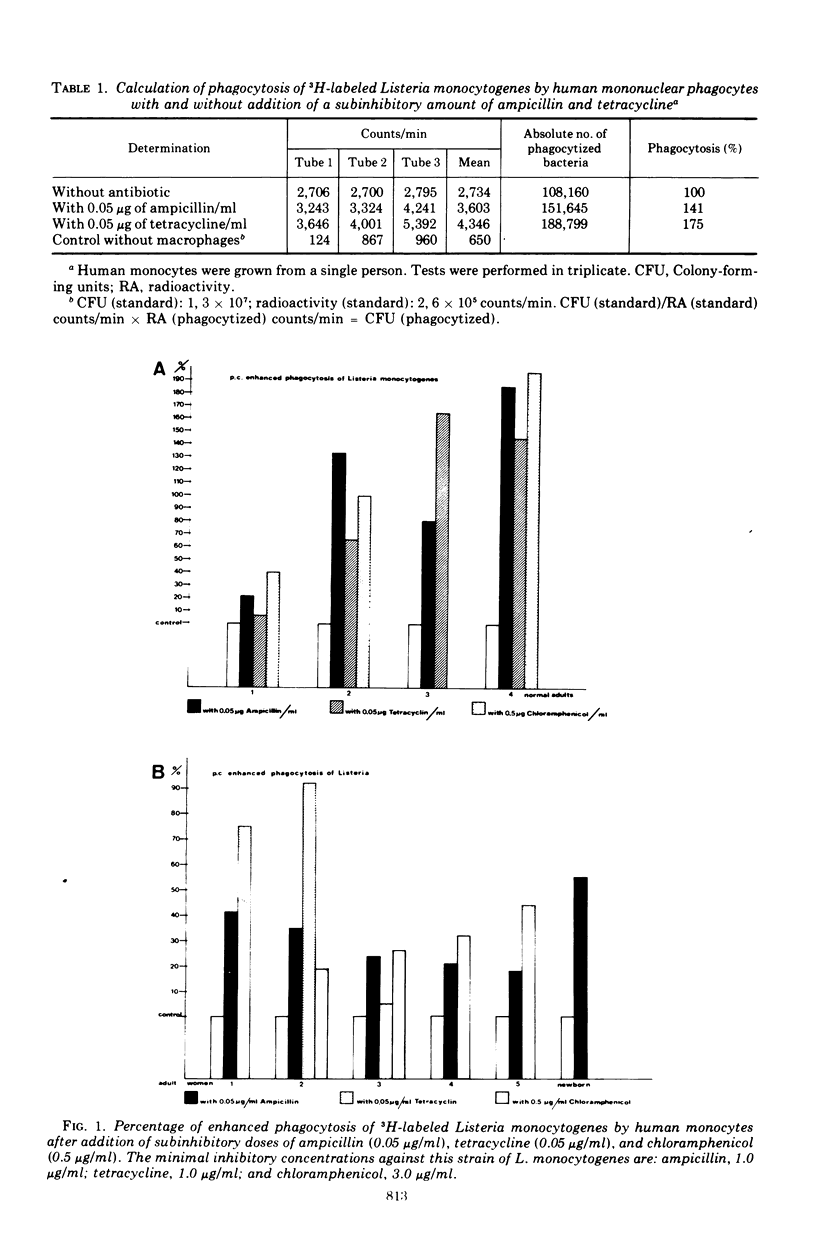
Abstract
An in vitro system was developed to test the phagocytic activity of human macrophages grown from blood monocytes in the presence of the antibiotics ampicillin, tetracycline, and chloramphenicol. 3H-labeled Listeria monocytogenes served as test organism. Subinhibitory amounts of the antibiotics enhanced the phagocytic activity significantly (P < 0.025). Macrophages pretreated with the drugs in identical concentrations showed the same phagocytic activity as control cells in the absence of the drugs. Because the drug concentrations used were similar to those that may be attained in man at certain places of inflammation, enhanced phagocytosis in the presence of antibiotics may have clinical significance.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AUSTEN K. F., COHN Z. A. Contribution of serum and cellular factors in host defense reactions. I. Serumfactors in host resistanc. N Engl J Med. 1963 Apr 25;268:933–contd. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196304252681707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adam D., Marget W. Die Rolle des Wirts bei der klinischen Wirkung der antibakteriellen Chemotherapie. Med Klin. 1971 Mar 5;66(10):344–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adam D., Philipp P., Belohradsky B. H. Studies on the influence of host defence mechanisms on the antimicrobial effect of chemotherapeutic agents. Effect of antibiotics on phagocytosis of mouse-peritoneal-macrophages in vitro. Arztl Forsch. 1971 Jun 10;25(6):181–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adam D., Staber F., Belohradsky B. H., Marget W. Effect of dihydrostreptomycin on phagocytosis of mouse-peritoneal macrophages in vitro. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):537–541. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.537-541.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett W. E., Cohn Z. A. The isolation and selected properties of blood monocytes. J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 1;123(1):145–160. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline M. J. Drug potentiation of macrophage function. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):601–605. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.601-605.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn Z. A. The structure and function of monocytes and macrophages. Adv Immunol. 1968;9:163–214. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60443-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber H., Fudenberg H. H. The interaction of monocytes and macrophages with immunoglobulins and complement. Ser Haematol. 1970;3(2):160–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B., Blanden R. V. Cellular immunity. Prog Allergy. 1967;11:89–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REBUCK J. W., CROWLEY J. H. A method of studying leukocytic functions in vivo. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1955 Mar 24;59(5):757–805. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1955.tb45983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M. Attachment of modified erythrocytes to phagocytic cells in absence of serum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Feb;124(2):396–399. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M. The dissociation of the attachment and ingestion phases of phagocytosis by macrophages. Exp Cell Res. 1967 Apr;46(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(67)90405-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley D. Phagocytosis and immunity. The central role of phagocytosis in immune reactions. Experientia. 1966 Jan 15;22(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley D., Turner K. J. Number of molecules of antibody required to promote phagocytosis of one bacterium. Nature. 1966 Apr 30;210(5035):496–498. doi: 10.1038/210496a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton J. S., Weiss L. Transformation of monocytes in tissue culture into macrophages, epithelioid cells, and multinucleated giant cells. An electron microscope study. J Cell Biol. 1966 Feb;28(2):303–332. doi: 10.1083/jcb.28.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



