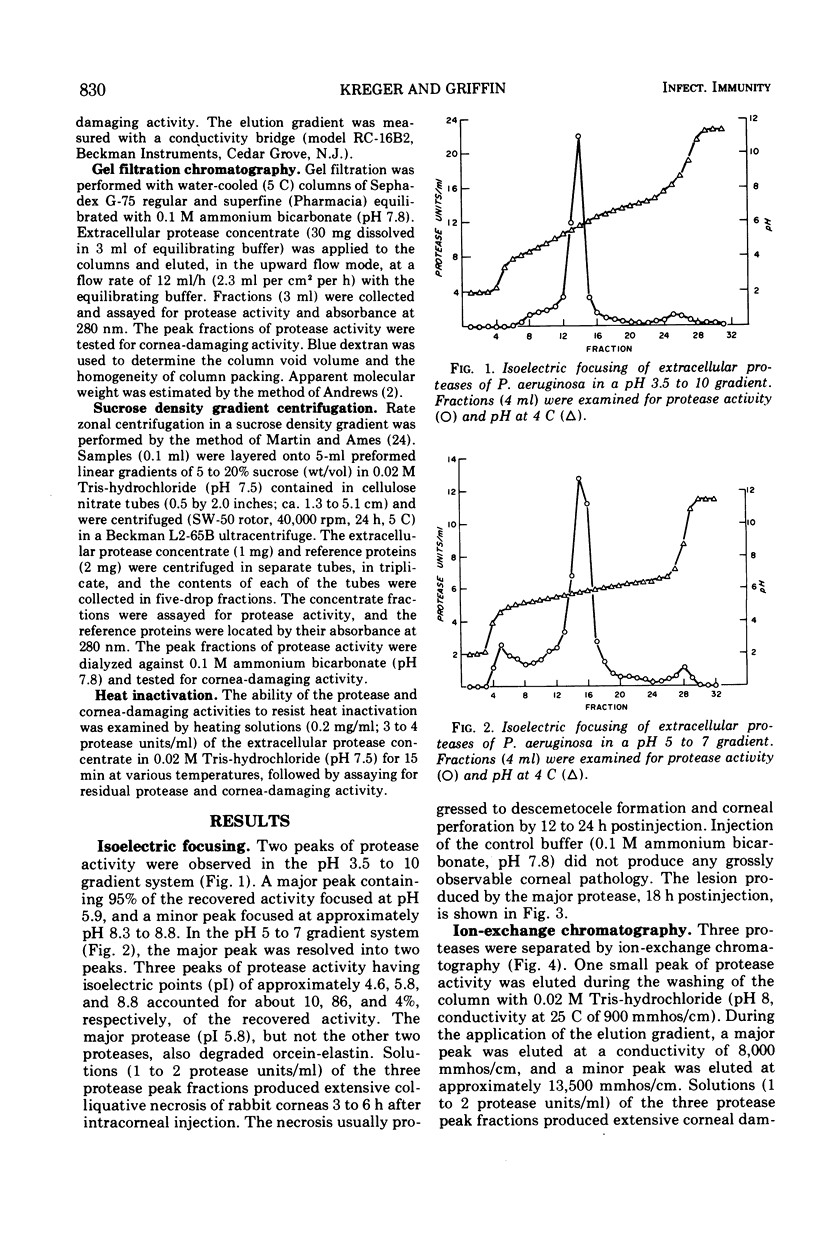
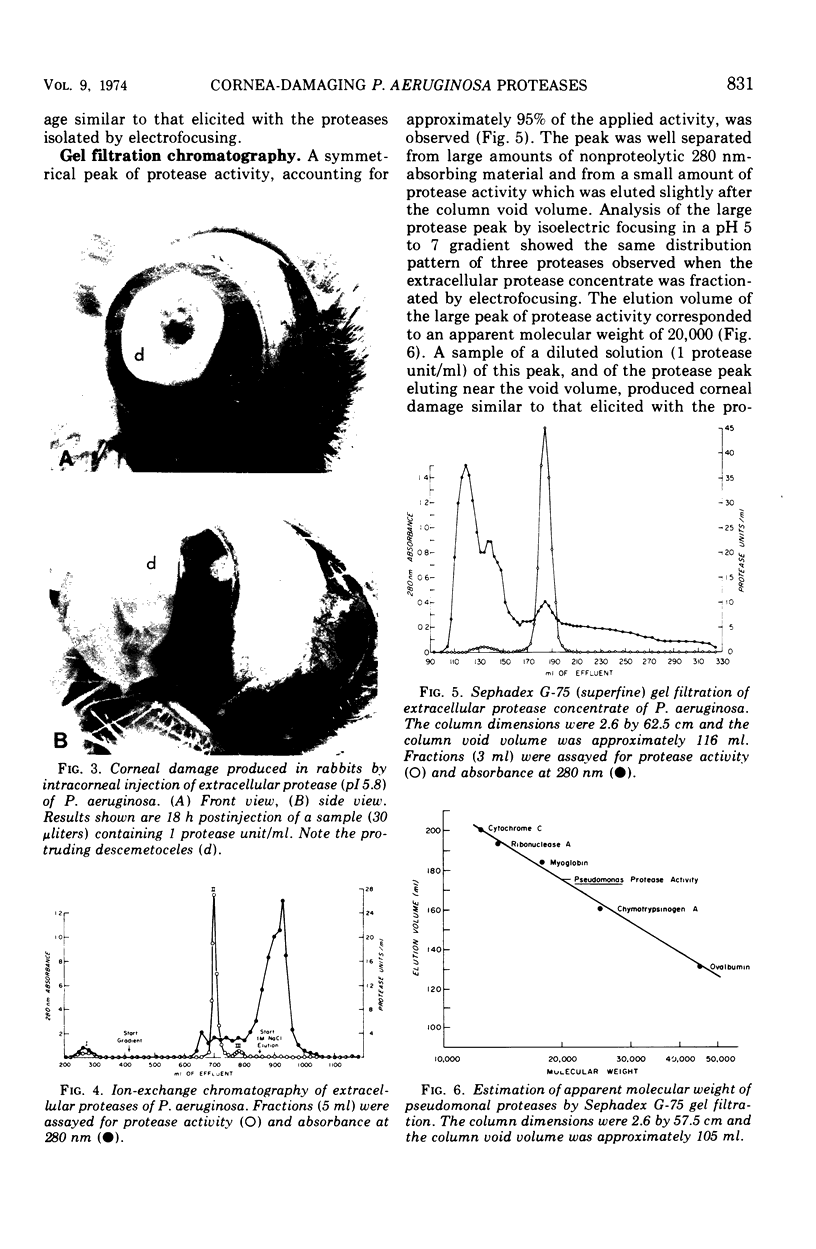
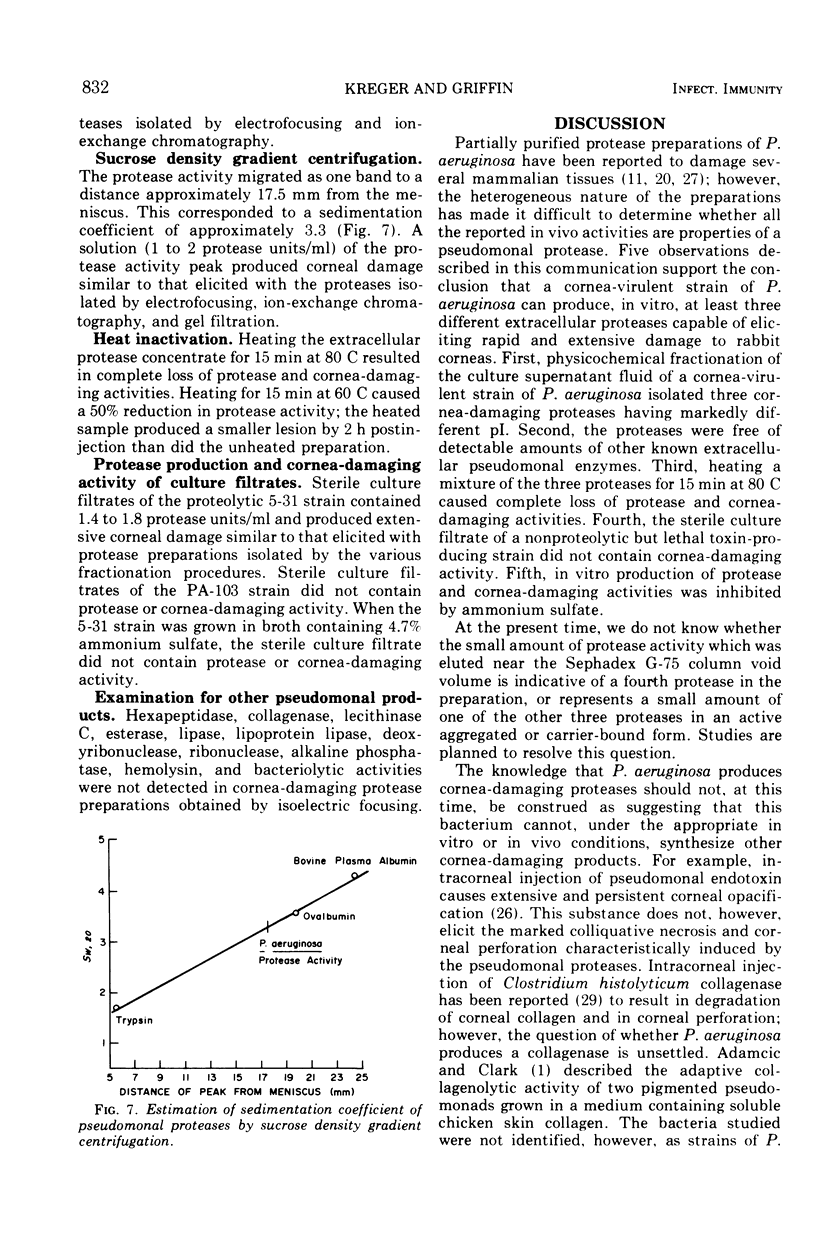
Abstract
Fractionation of the culture supernatant fluids of a cornea-virulent strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by ammonium sulfate precipitation, diafiltration, isoelectric focusing, ion-exchange chromatography, gel filtration, and sucrose density gradient centrifugation failed to separate the rabbit cornea-damaging activity and the in vitro protease activity of the preparations. Three proteases having similar molecular weights (approximately 20,000) and isoelectric points of approximately 4.6, 5.8, and 8.8 were obtained free of detectable amounts of other known extracellular pseudomonal enzymes. Heating a mixture of the three proteases for 15 min at 80 C resulted in complete loss of protease and cornea-damaging activities. The sterile culture filtrate of a nonproteolytic but lethal toxin-producing strain of P. aeruginosa did not contain cornea-damaging activity. Cultivation of the proteolytic strain in broth containing 4.7% ammonium sulfate yielded a culture supernatant fluid free of protease and cornea-damaging activities. The results obtained support the conclusion that a cornea-virulent strain of P. aeruginosa can produce, in vitro, at least three different extracellular proteases capable of eliciting rapid and extensive damage to rabbit corneas.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamcic M., Clark D. S. Callogenolytic activity of pigmented pseudomonads. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Aug;16(8):709–712. doi: 10.1139/m70-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvidson S., Wadström T. Detection of proteolytic activity after isoelectric focusing in polyacrylamide gel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 15;310(2):418–420. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNHEIMER A. W., SCHWARTZ L. L. Isolation and composition of staphylococcal alpha toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:455–468. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURNS R. P., RHODES D. H., Jr Pseudomonas eye infection as a cause of death in premature infants. Arch Ophthalmol. 1961 Apr;65:517–525. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1961.01840020519010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
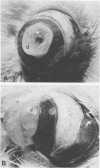
- Brown S. I., Bloomfield S. E., Tam W. The cornea-destroying enzyme of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Invest Ophthalmol. 1974 Mar;13(3):174–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke M. E., Pattee P. A. Purification and characterization of a staphylolytic enzyme from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):860–865. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.860-865.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diener B., Carrick L., Jr, Berk R. S. In vivo studies with collagenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):212–217. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.212-217.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER E., Jr, ALLEN J. H. Corneal ulcers produced by cell-free extracts of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am J Ophthalmol. 1958 Jul;46(1 Pt 2):21–27. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(58)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER E., Jr, ALLEN J. H. Mechanism of corneal destruction by pseudomonas proteases. Am J Ophthalmol. 1958 Nov;46(5 Pt 2):249–255. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(58)90804-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold D. S., Goldman J. N., Kuritz H. M. Locus of the lethal event in the serum bactericidal reaction. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2127–2131. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2127-2131.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRASSMANN W., NORDWIG A. [Quantitative colorimetric test for collagenase]. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1960 Dec 31;322:267–272. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1960.322.1.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerke J. R., Magliocco M. V. Experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection of the Mouse Cornea. Infect Immun. 1971 Feb;3(2):209–216. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.2.209-216.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera M., Lysenko O. The mechanism of pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. V. Isolation and properties of the proteinases toxic for larvae of the greater wax moth Galleria mellonella L. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1968;13(4):288–294. doi: 10.1007/BF02909616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurioka S., Liu P. V. Improved assay method for phospholipase C. Appl Microbiol. 1967 May;15(3):551–555. doi: 10.1128/am.15.3.551-555.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laibson P. R. Cornea and sclera. Arch Ophthalmol. 1972 Nov;88(5):553–574. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1972.01000030555018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. Exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. Factors that influence the production of exotoxin A. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):506–513. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V., Hsieh H. C. Inhibition of protease production of various bacteria by ammonium salts: its effect on toxin production and virulence. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):406–413. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.406-413.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. The roles of various fractions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in its pathogenesis. II. Effects of lecithinase and protease. J Infect Dis. 1966 Feb;116(1):112–116. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.1.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKS J. Recognition of pathogenic staphylococci: with notes on non-specific staphylococcal haemolysin. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1952 Jan;64(1):175–186. doi: 10.1002/path.1700640118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORIHARA K. PRODUCTION OF ELASTASE AND PROTEINASE BY PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:745–757. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.745-757.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORIHARA K., TSUZUKI H., OKA T., INOUE H., EBATA M. PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA ELASTASE. ISOLATION, CRYSTALLIZATION, AND PRELIMINARY CHARACTERIZATION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Aug;240:3295–3304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORIHARA K., YOSHIDA N., KURIYAMA K. PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA PEPTIDE PEPTIDOHYDROLASE. IV. OPTICAL ROTATORY DISPERSION AND AMINO ACID COMPOSITION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Nov 22;92:361–366. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90194-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. J., Ewing W. H. The deoxyribonuclease test as applied to certain gram-negative bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1967 May;13(5):616–618. doi: 10.1139/m67-080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinke G., Barum J., Rosenberg B., Berk R. In Vivo Studies with the Partially Purified Protease (Elastase) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):583–589. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.583-589.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A., 3rd, Sandine W. E., Elliker P. R. Extracellular nuclease in the genus Lactobacillus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):604–606. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.604-606.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohos S. C., Wagner B. M. Damage to collagen in corneal immune injury. Observation of connective tissue structure. Arch Pathol. 1969 Jul;88(1):3–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Lapiere C. M., Gross J. Tadpole collagenase. Preparation and purification. Biochemistry. 1966 Oct;5(10):3123–3130. doi: 10.1021/bi00874a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIERRA G. A simple method for the detection of lipolytic activity of micro-organisms and some observations on the influence of the contact between cells and fatty substrates. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1957;23(1):15–22. doi: 10.1007/BF02545855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uss R. H., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Muraschi T. F., Miller K. D. Two distinct elastases from different strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Sep 30;191(1):179–181. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90332-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldvogel F. A., Swartz M. N. Collagenolytic activity of bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):662–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.662-667.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L. A. Chelation in experimental Pseudomonas keratitis. Br J Ophthalmol. 1970 Sep;54(9):587–593. doi: 10.1136/bjo.54.9.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wretlind B., Hedén L., Sjöberg L., Wadström T. Production of enzymes and toxins by hospital strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in relation to serotype and phage-typing pattern. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Feb;6(1):91–100. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]