Abstract
Staphylococcus cohnii subsp. cohnii belongs to the family Staphylococcaceae in the order Bacillales, class Bacilli and phylum Firmicutes. The increasing relevance of S. cohnii to human health prompted us to determine the genomic sequence of Staphylococcus cohnii subsp. cohnii strain hu-01, a multidrug-resistant isolate from a hospital in China. Here we describe the features of S. cohnii subsp. cohnii strain hu-01, together with the genome sequence and its annotation. This is the first genome sequence of the species Staphylococcus cohnii.
Keywords: Staphylococcus cohnii subsp. cohnii, genome, Hiseq2000
Introduction
Staphylococcus cohnii belongs to the Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci group. It was described by Schleifer and Kloos (1975) and was named for Ferdinand Cohn, a German botanist and bacteriologist [1]. Recently, more cases of Staphylococcus cohnii infection have been reported in the literature. This organism may be responsible for brain abscess, pneumonia, acute cholecystitis, endocarditis, bacteremia, urinary tract infection and septic arthritis [2]. S. cohnii is comprised of two subspecies that are defined on the basis of their phenotypic characteristics: Staphylococcus cohnii subsp. cohnii and Staphylococcus cohnii subsp. urealyticus [3]. S. cohnii subsp. cohnii is a Gram-positive coccus, coagulase negative and catalase positive, that behaves like a commensal mucocutaneous bacterium [4]. It has more frequently been isolated in hospital than in non-hospital environments [2]. Here we report this draft genome of S. cohnii subsp. cohnii strain hu-01, the first genome of this species to be sequenced.
Classification and features
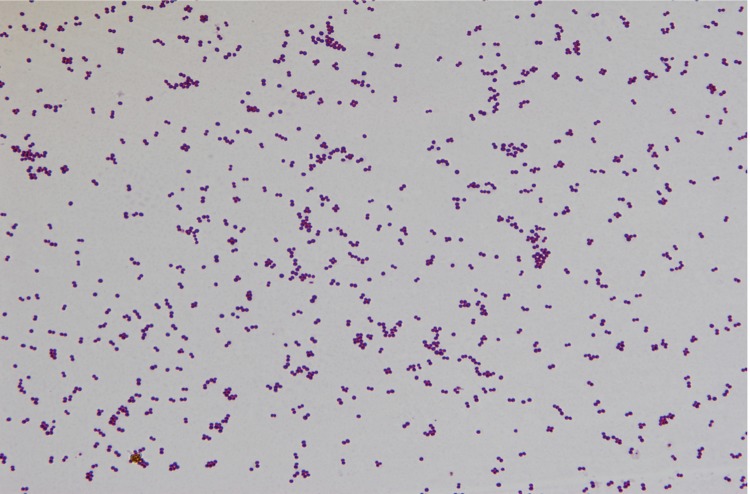
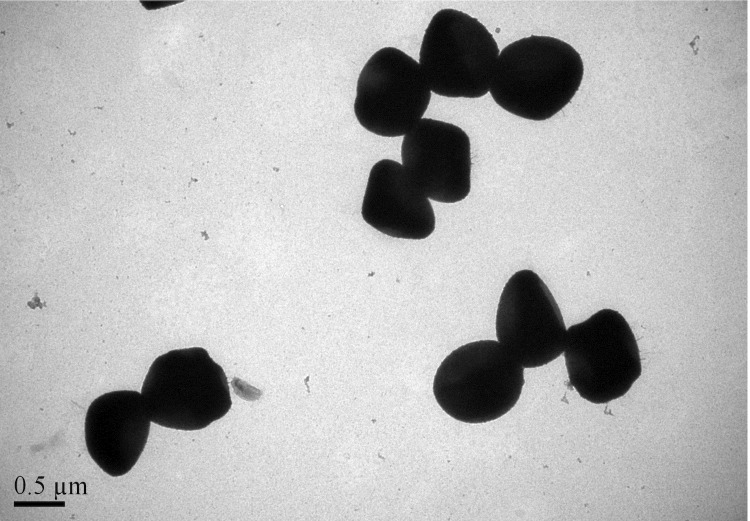
Strain hu-01 was isolated from a hospital environment in Zhejiang province, China, in October 2012. It is a Gram-positive, coccus-shaped bacterium that can grow on 5% sheep blood enriched Columbia agar (BioMérieux, Marcyl’Etoile, France) at 37°C. Growth occurs under either aerobic or anaerobic conditions. The optimum temperature for growth is 37 ºC, with a temperature range of 15-45 ºC (Table 1). Cell morphology, motility and sporulation were examined by using transmission electron (H-600, Hitachi) microscopy. Cells of strain hu-01 are coccoidal, 0.6 to 1.2 μm in diameter, occurring predominantly singly or in pairs (Figure 1 and Figure 2).
Table1. Classification and general features of S. cohnii subsp. cohnii strain hu-01 according to the MIGS recommendations [9].
| MIGS ID | Property | Term | Evidence codea |
|---|---|---|---|
| Domain Bacteria | TAS [20] | ||
| Phylum Firmicutes | TAS [21-23] | ||
| Class Bacilli | TAS [24,25] | ||
| Current classification | Order Bacillales | TAS [26,27] | |
| Family Staphylococcaceae | TAS [24,28] | ||
| Genus Staphylococcus | TAS [26,29-31] | ||
| Species Staphylococcus cohnii subsp. cohnii | TAS [1,3] | ||
| Strain hu-01 | IDA | ||
| Gram stain | Positive | IDA | |
| Cell shape | coccus | IDA | |
| Motility | Nonmotile | IDA | |
| Sporulation | Nonsporulating | IDA | |
| Temperature range | 15-45°C | IDA | |
| Optimum temperature | 37°C | IDA | |
| MIGS-6.3 | Salinity | Tolerates 10% NaCl | IDA |
| MIGS-22 | Oxygen | Facultatively anaerobic | IDA |
| Carbon source | D-mannitol, fructose, trehalose | IDA | |
| Energy source | fructose, trehalose | IDA | |
| MIGS-6 | Habitat | Hospital environment | IDA |
| MIGS-15 | Biotic relationship | Free living | IDA |
| MIGS-14 | Pathogenicity | Opportunistic pathogen | IDA |
| Isolation | Hospital | IDA | |
| MIGS-4 | Geographic location | Hangzhou, China | IDA |
| MIGS-5 | Sample collection time | October, 2012 | IDA |
| MIGS-4.1 | Latitude | 30°16’N | IDA |
| MIGS-4.2 | Longitude | 120°12’E | IDA |
| MIGS-4.3 | Depth | unknown | IDA |
| MIGS-4.4 | Altitude | 50 (meters) | IDA |
aEvidence codes-IDA: Inferred from Direct Assay; TAS: Traceable Author Statement (i.e., a direct report exists in the literature); NAS: Non-traceable Author Statement (i.e., not directly observed for the living, isolated sample, but based on a generally accepted property for the species, or anecdotal evidence). These evidence codes are from the Gene Ontology project [32]. If the evidence code is IDA, then the property should have been directly observed, for the purpose of this specific publication, for a live isolate by one of the authors, or an expert or reputable institution mentioned in the acknowledgements.
Figure1.
Gram staining of S. cohnii subsp. cohnii strain hu-01
Figure 2.
Transmission electron micrograph of cells of strain hu-01. Bar: 0.5 µm
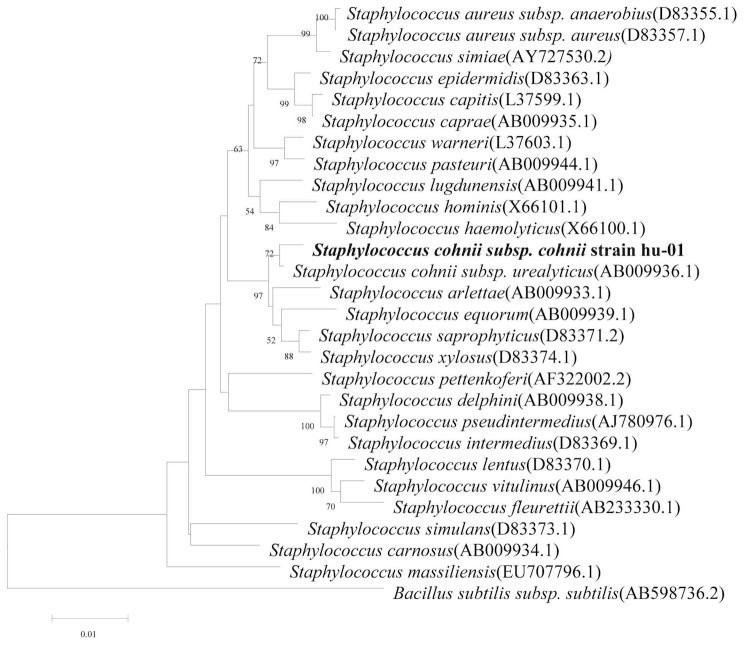
Comparative 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis by BLASTN [5,6] using the NCBI-NR/NT database revealed 94-99% sequence similarity to members of genus Staphylococcus. Neighbor-Joining phylogenetic analysis based on Kimura 2-parameter model indicated the strain hu-01 is most closely related the strain Staphylococcus cohnii subsp. urealyticus (AB009936.1) (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic tree depicting the relationship between S. cohnii subsp. cohnii strain hu-01 and other members of the genus Staphylococcus. The strains and their corresponding Genbank accession numbers are shown following the organism name and indicated in parentheses. The phylogenetic tree uses 16S rRNA gene sequences aligned by the CLUSTALW [7], and phylogenetic inferences were made using Neighbor-joining method based on Kimura 2-parameter model within the MEGA5 software [8] and rooted with Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis. Bootstrap consensus trees were inferred from 100 replicates, only bootstrap values > 50% were indicated.
Biochemical features were tested by using two automated systems, the Vitek2 Compact (bioMérieux, Marcy l'Etoile, France) and Phoenix 100 ID/AST system (Becton Dickinson Company [BD], Sparks, Maryland, USA). Positive reactions were obtained for D-fructose, trehalose, D-gluconic acid and D-mannitol. Negative reactions were observed for glucose, D-trehalose, D-sucrose, maltose, urea, cellobiose, glucoside, D-tagatose and maltotriose. This strain was susceptible to gentamicin, ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin, quinupristin, linezolid, vancomycin, tetracycline, tigecycline, nitrofurantoin, rifampicin, trimethoprim and resistant to cefoxitin, benzylpenicillin, oxacillin, erythromycin, clindamycin.
Genome sequencing information
Genome project history
S. conhii subsp. cohnii strain hu-01 was selected for sequencing because of its increasing relevance to human health. The strain was isolated from a hospital environment in China. This whole genome shotgun project of S. conhii subsp. cohnii strain hu-01 was deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank under the accession AYOS00000000. Table 2 presents the project information and its association with MIGS version 2.0 compliance [9].
Table 2. Project information.
| MIGS ID | Property | Term |
|---|---|---|
| MIGS-31 | Finishing quality | High-quality draft |
| MIGS-28 | Libraries used | One pair-end 500 bp library |
| MIGS-29 | Sequencing platforms | Illumina HiSeq 2000 |
| MIGS-31.2 | Fold coverage | 150×(based on 500 bp library) |
| MIGS-30 | Assemblers | Velvet 1.2.07 |
| MIGS-32 | Gene calling method | Glimmer 3.0 |
| Genbank ID | AYOS00000000 | |
| Genbank Date of Release | Jan 06, 2014 | |
| GOLD ID | Gi0062613 | |
| MIGS-13 | Project relevance | Biotechnology, Pathway, Pathogenic |
Growth conditions and DNA isolation
S. conhii subsp .cohnii strain hu-01 was grown aerobically on Columbia blood agar base, at 37°C for 24h. Genomic DNA was extracted using the DNeasy blood and tissue kit (Qiagen, Germany), according to the manufacturer’s recommended protocol. The quantity of DNA was measured by the NanoDrop Spectrophotometer and Cubit. Then 10μg of DNA was sent to the State Key Laboratory for Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Disease at Zhejiang University for sequencing on a Hiseq2000 (Illumina, CA) sequencer.
Genome sequencing and assembly
One DNA library was generated (500 bp insert size, with the Illumina adapter at both ends, detected by Agilent DNA analyzer 2100), then sequencing was performed by using an Illumina Hieseq 2000 genomic sequencer, with a 2×100 pair end sequencing strategy. A total of 1,103 M bp of sequence data was produced which was assessed for quality by the following criteria: 1) Reads linked to adapters at both end were considered as sequencing artifacts then removed. 2) Bases with a quality index lower than Q20 at both ends were trimmed. 3) Reads with ambiguous bases (N) were removed. 4) Single qualified reads were discarded (In this situation, one read is qualified but its mate is not). A total of 867.94 M clean filtered reads were assembled into scaffolds using the Velvet version 1.2.07 with parameters "-scaffolds no" [10], then we used a PAGIT flow [11] to prolong the initial contigs and correct sequencing errors. to arrive at a set of improved scaffolds.
Genome annotation
Predict genes were identified using Glimmer version 3.0 [12],tRNAscan-SE version 1.21 [13] was used to find tRNA genes, whereas ribosomal RNAs were found by using RNAmmer version 1.2 [14]. To annotate predicted genes, we used HMMER version 3.0 [15], with parameters 'hmmscan -E 0.01 -domainE 0.01' to align genes against Pfam version 27.0 [16] (only pfam-A was used) to find genes with conserved domains. The KAAS server [17] was used to assign translated amino acids (with genetic code table 11) into KEGG Orthology with SBH (single-directional best hit) method. Translated genes were aligned with the COG database using NCBI blastp (hits should have scores no less than 60, e-value is no more than 1e-6). To find genes with hypothetical or putative function, we aligned genes against NCBI nucleotide sequence database (nt database was downloaded at Sep 20, 2013) by using NCBI blastn, only if hits have an identity of no less than 0.95, coverage no less than 0.9, and the reference gene had an annotation of putative or hypothetical. To define genes with signal peptide, we use signalp version 4.1 [18] to identify genes with signal peptide with default parameters except " -t gram+ ". TMHMM2.0 [19] was used to identify genes with transmembrane helices.
Genome properties
The draft genome sequence of S. conhii subsp. cohnii strain hu-01 revealed a genome size of 5,761,489 bp and a G+C content of 34.85% (521 scaffolds with N50 is 39,926 bp). These scaffolds contain 5,820 coding sequences (CDSs), 61 tRNAs (excluding 6 Pseudo tRNAs) and incomplete rRNA operons (10 small subunit rRNA and 3 large subunit rRNAs). A total of 1,840 protein-coding genes were assigned as putative function or hypothetical proteins. 3,734 genes were categorized into COGs functional groups. The properties and the statistics of the genome are summarized in Table 3 and Table 4.
Table 3. Genome statistics of S. cohnii subsp. cohnii strain hu-01.
| Attribute | Value | % of totala |
|---|---|---|
| Genome size (bp) | 5,761,489 | -- |
| DNA coding region (bp) | 4,751,472 | 82.469 |
| DNA G+C content (bp) | 1,697,984 | 29.471 |
| Total genes | 5,833 | -- |
| RNA genes | 13 | 0.221 |
| Protein-coding genes | 5,820 | 99.777 |
| Genes with function prediction | 1,840 | 31.544 |
| Genes assigned to COGs | 3,734 | 64.015 |
| Genes assigned to Pfam domains | 4,943 | 84.741 |
| Genes with signal peptides | 431 | 7.388 |
| Genes with transmembrane helices | 1,629 | 27.927 |
a) The total is based on either the size of the genome in base pairs or the total number of genes in the annotated genome.
Table 4. Number of genes associated with the general COG functional categories.
| Code | Valuea | %ageb | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| J | 230 | 3.95 | Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis |
| K | 452 | 7.77 | Transcription |
| L | 184 | 3.16 | Replication, recombination and repair |
| B | 3 | 0.05 | Chromatin structure and dynamics |
| D | 72 | 1.24 | Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning |
| V | 187 | 3.21 | Defense mechanisms |
| T | 238 | 4.09 | Signal transduction mechanisms |
| M | 254 | 4.36 | Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis |
| N | 70 | 1.20 | Cell motility |
| Z | 1 | 0.02 | Cytoskeleton |
| W | 1 | 0.02 | Extracellular structures |
| U | 57 | 0.98 | Intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport |
| O | 147 | 2.53 | Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones |
| C | 292 | 5.02 | Energy production and conversion |
| G | 384 | 6.60 | Carbohydrate transport and metabolism |
| E | 640 | 11.0 | Amino acid transport and metabolism |
| F | 140 | 2.41 | Nucleotide transport and metabolism |
| H | 234 | 4.02 | Coenzyme transport and metabolism |
| I | 165 | 2.84 | Lipid transport and metabolism |
| P | 389 | 6.68 | Inorganic ion transport and metabolism |
| Q | 197 | 3.38 | Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism |
| R | 841 | 14.45 | General function prediction only |
| S | 403 | 6.92 | Function unknown |
| --c | 483 | 8.30 | Not archived in COGs |
| --d | 1603 | 27.54 | No hits |
a) For some genes, qualified alignments can occur with several genes belonging to different COG categories. In such cases only the best match to a single COG category is considered. b) The total is based on the total number of protein coding genes(5,820) in the annotated genome. c) These genes have alignments with reference genes archived in COG, but these reference genes do not have COG categories. d) Genes without a qualified hit to a reference genes.
Conclusion
Staphylococcus cohnii ssp. cohnii are part of the normal flora of human skin and mucous membranes which, in particular conditions, may become opportunistic pathogens [4]. The genome sequence of Staphylococcus cohnii subsp. cohnii strain hu-01 will provide the basis to elucidate the molecular principles of host colonization and insight into the genetic background of this organism’s pathogenesis.
Acknowledgement
We thank Qiang Ye and Li Liang, Chinese Center of Medical Culture Collections /National Institutes for Food and Drug Control for providing the Biochemical features. This study was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 program) (No. 2013CB531401) and the key Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81330011).
References
- 1.Schleifer KH, Kloos WE. Isolation and Characterization of Staphylococci from Human Skin I. Amended Descriptions of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus saprophyticus and Descriptions of Three New Species: Staphylococcus cohnii, Staphylococcus haemolyticus, and Staphylococcus xylosus. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1975; 25:50-61 10.1099/00207713-25-1-50 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Soldera J, Nedel WL, Cardoso PR, d'Azevedo PA. Bacteremia due to I ssp. urealyticus caused by infected pressure ulcer: case report and review of the literature. Sao Paulo Med J 2013; 131:59-61 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kloos WE, Wolfshohl JF. Staphylococcus cohnii subspecies: Staphylococcus cohnii subsp. cohnii subsp. nov. and Staphylococcus cohnii subsp. urealyticum subsp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1991; 41:284-289 10.1099/00207713-41-2-284 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Stefano M, Del Rosso A, Saldutto P, Paradiso Galatioto G, Vicentini C. Intrascrotal Abscess, Propionibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus cohnii ssp. cohnii: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Case Rep Urol 2012;2012:313694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 5.Johnson M, Zaretskaya I, Raytselis Y, Merezhuk Y, McGinnis S, Madden TL. NCBI BLAST: a better web interface. Nucleic Acids Res 2008;36(Web Server issue):W5-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 6.McGinnis S, Madden TL. BLAST: at the core of a powerful and diverse set of sequence analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 2004;32(Web Server issue):W20-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 7.Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG. Multiple sequence alignment using ClustalW and ClustalX. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics 2002;Chapter 2:Unit 2 3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 2011; 28:2731-2739 10.1093/molbev/msr121 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Field D, Garrity G, Gray T, Morrison N, Selengut J, Sterk P, Tatusova T, Thomson N, Allen MJ, Angiuoli SV, et al. The minimum information about a genome sequence (MIGS) specification. Nat Biotechnol 2008; 26:541-547 10.1038/nbt1360 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zerbino DR, Birney E. Velvet: algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res 2008; 18:821-829 10.1101/gr.074492.107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Swain MT, Tsai IJ, Assefa SA, Newbold C, Berriman M, Otto TD. A post-assembly genome-improvement toolkit (PAGIT) to obtain annotated genomes from contigs. Nat Protoc 2012; 7:1260-1284 10.1038/nprot.2012.068 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Delcher AL, Bratke KA, Powers EC, Salzberg SL. Identifying bacterial genes and endosymbiont DNA with Glimmer. Bioinformatics 2007; 23:673-679 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lowe TM, Eddy SR. tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 1997; 25:0955-964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 14.Lagesen K, Hallin P, Rodland EA, Staerfeldt HH, Rognes T, Ussery DW. RNAmmer: consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 2007; 35:3100-3108 10.1093/nar/gkm160 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Eddy SR. Accelerated Profile HMM Searches. PLOS Comput Biol 2011; 7:e1002195 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002195 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Punta M, Coggill PC, Eberhardt RY, Mistry J, Tate J, Boursnell C, Pang N, Forslund K, Ceric G, Clements J, et al. The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 2012; 40:D290-D301 10.1093/nar/gkr1065 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Moriya Y, Itoh M, Okuda S, Yoshizawa AC, Kanehisa M. KAAS: an automatic genome annotation and pathway reconstruction server. Nucleic Acids Res 2007;35(Web Server issue):W182-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 18.Petersen TN, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H. SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat Methods 2011; 8:785-786 10.1038/nmeth.1701 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Krogh A, Larsson B, von Heijne G, Sonnhammer EL. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol 2001; 305:567-580 10.1006/jmbi.2000.4315 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Woese CR, Kandler O, Wheelis ML. Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1990; 87:4576-4579 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gibbons NE, Murray RGE. Proposals Concerning the Higher Taxa of Bacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1978; 28:1-6 10.1099/00207713-28-1-1 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Garrity GM, Holt JG. The Road Map to the Manual. In: Garrity GM, Boone DR, Castenholz RW (eds), Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriolo-gy, Second Edition, Volume 1, Springer, New York, 2001, p. 119-169. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Murray RGE. The Higher Taxa, or, a Place for Everything...? In: Holt JG (ed), Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, First Edition, Volume 1, The Williams and Wilkins Co., Baltimore, 1984, p. 31-34. [Google Scholar]
- 24.List of new names and new combinations previ-ously effectively, but not validly, published. List no. 132. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2010; 60:469-472 10.1099/ijs.0.022855-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ludwig W, Schleifer KH, Whitman WB. Class I. Bacilli class nov. In: De Vos P, Garrity G, Jones D, Krieg NR, Ludwig W, Rainey FA, Schleifer KH, Whitman WB (eds), Bergey's Manual of Systemat-ic Bacteriology, Second Edition, Volume 3, Springer-Verlag, New York, 2009, p. 19-20. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Skerman VBD, McGowan V, Sneath PHA. Approved Lists of Bacterial Names. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1980; 30:225-420 10.1099/00207713-30-1-225 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Prévot AR. In: Hauderoy P, Ehringer G, Guillot G, Magrou. J., Prévot AR, Rosset D, Urbain A (eds), Dictionnaire des Bactéries Pathogènes, Second Edition, Masson et Cie, Paris, 1953, p. 1-692. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Schleifer KH, Bell JA. Family VIII. Staphylococcaceae fam. nov. In: De Vos P, Garrity G, Jones D, Krieg NR, Ludwig W, Rainey FA, Schleifer KH, Whitman WB (eds), Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Second Edi-tion, Volume 3, Springer-Verlag, New York, 2009, p. 392. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rosenbach FJ. In: Bergmann JF (ed), Microorganismen bei den Wund Infections Krankheiten des Menschen., Wiesbaden, 1884, p. 1-122. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Baird-Parker AC. Genus II. Staphylococcus Rosenbach 1884, 18. In: Buchanan RE, Gibbons NE (eds), Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, Eighth Edition, The Williams and Wil-kins Co., Baltimore, 1974, p. 483-489. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Judicial Commission Opinion 17. Conservation of the Generic name Staphylococcus Rosenbach, Designation of Staphylococcus aureus Rosenbach as the Nomenclatural Type of the Genus Staphylococcus Rosenbach, and Designation of the Neotype culture of Staphylococcus aureus Rosenbach. Int Bull Bacteriol Nomencl Taxon 1958; 8:153-154 [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, et al. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet 2000; 25:25-29 10.1038/75556 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]