Abstract
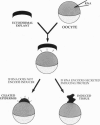
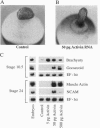
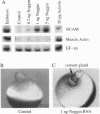
We have developed a paracrine signaling assay capable of mimicking inductive events in the early vertebrate embryo. RNA encoding one or more secreted proteins is microinjected into a Xenopus laevis oocyte. After a brief incubation to allow translation, a piece of embryonic tissue competent to respond to the signaling protein is grafted onto the oocyte. The secreted protein's effect on the grafted explant is then scored by assaying expression of tissue-specific markers. Explants of ectodermal tissue from blastula or gastrula stage embryos were grafted onto oocytes that had been injected with RNA encoding activin or noggin. We found that the paracrine assay faithfully reconstitutes mesoderm induction by activin and neural induction by noggin. Blastula-stage explants grafted onto activin-expressing oocytes expressed the mesodermal marker genes brachyury, goosecoid, and muscle actin. Gastrula-stage explants grafted onto noggin-expressing oocytes expressed neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) and formed cement gland. By injecting pools of RNA synthesized from a cDNA expression library into the oocyte, we also used the assay to screen for secreted neural-inducing proteins. We assayed 20,000 independent transformants of a library constructed from LiCl-dorsalized Xenopus laevis embryos, and we identified two cDNAs that induced neural tissue in ectodermal explants from gastrula-stage embryos. Both cDNAs encode noggin. These results suggest that the paracrine assay will be useful for the cloning of novel signaling proteins as well as for the analysis of known factors.
Full text
PDF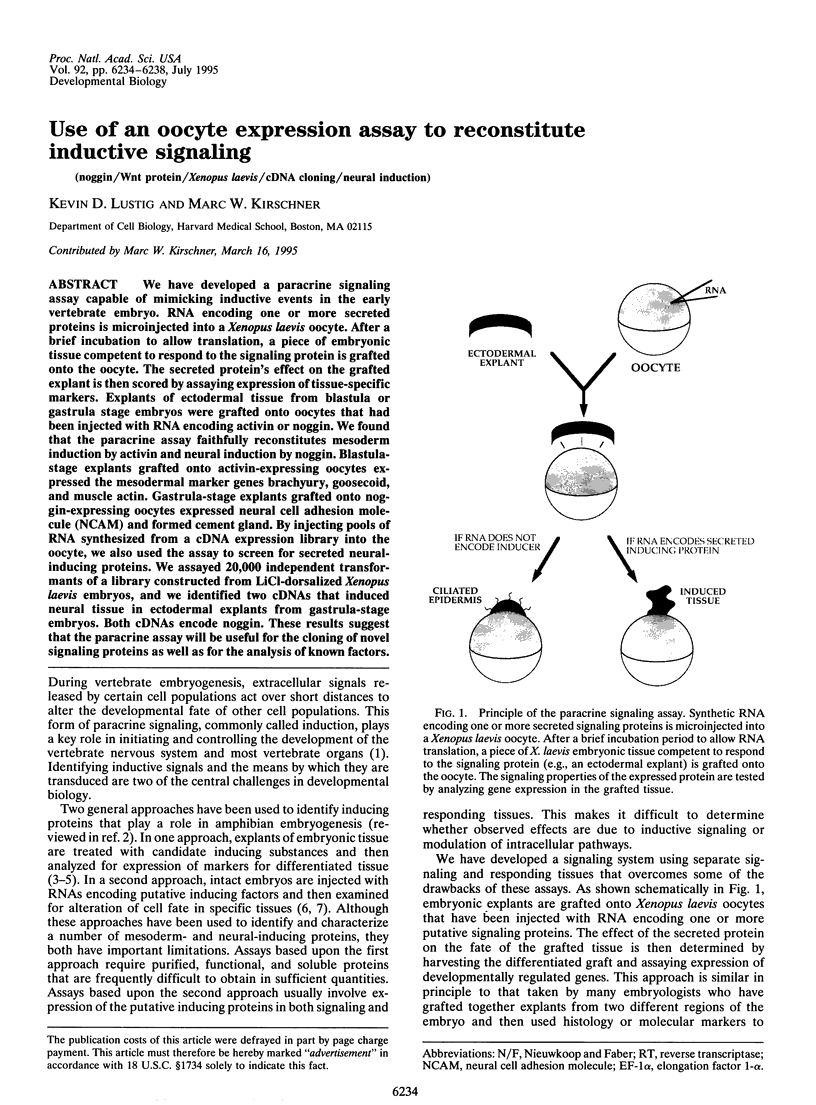



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cho K. W., Blumberg B., Steinbeisser H., De Robertis E. M. Molecular nature of Spemann's organizer: the role of the Xenopus homeobox gene goosecoid. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1111–1120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90288-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian J. L., Moon R. T. Interactions between Xwnt-8 and Spemann organizer signaling pathways generate dorsoventral pattern in the embryonic mesoderm of Xenopus. Genes Dev. 1993 Jan;7(1):13–28. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale L., Smith J. C., Slack J. M. Mesoderm induction in Xenopus laevis: a quantitative study using a cell lineage label and tissue-specific antibodies. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Oct;89:289–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. B., Howes G., Symes K., Cooke J., Smith J. C. The biological effects of XTC-MIF: quantitative comparison with Xenopus bFGF. Development. 1990 Jan;108(1):173–183. doi: 10.1242/dev.108.1.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Fairman S., Mohun T. J., Brennan S. Activation of muscle-specific actin genes in Xenopus development by an induction between animal and vegetal cells of a blastula. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):913–922. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R. M. Neural induction in Xenopus. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Aug;4(4):543–549. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90070-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmati-Brivanlou A., Kelly O. G., Melton D. A. Follistatin, an antagonist of activin, is expressed in the Spemann organizer and displays direct neuralizing activity. Cell. 1994 Apr 22;77(2):283–295. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90320-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmati-Brivanlou A., Melton D. A. Inhibition of activin receptor signaling promotes neuralization in Xenopus. Cell. 1994 Apr 22;77(2):273–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90319-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao K. R., Elinson R. P. The entire mesodermal mantle behaves as Spemann's organizer in dorsoanterior enhanced Xenopus laevis embryos. Dev Biol. 1988 May;127(1):64–77. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90189-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay B. K. Xenopus laevis: Practical uses in cell and molecular biology. Injections of oocytes and embryos. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;36:663–669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelman D., Kirschner M. Synergistic induction of mesoderm by FGF and TGF-beta and the identification of an mRNA coding for FGF in the early Xenopus embryo. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kintner C. R., Melton D. A. Expression of Xenopus N-CAM RNA in ectoderm is an early response to neural induction. Development. 1987 Mar;99(3):311–325. doi: 10.1242/dev.99.3.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P. S., Melton D. A. Hormonal regulation of embryogenesis: the formation of mesoderm in Xenopus laevis. Endocr Rev. 1994 Jun;15(3):326–341. doi: 10.1210/edrv-15-3-326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Varnum S. M., Wormington W. M., Melton D. A. The mRNA encoding elongation factor 1-alpha (EF-1 alpha) is a major transcript at the midblastula transition in Xenopus. Dev Biol. 1989 May;133(1):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90300-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb T. M., Knecht A. K., Smith W. C., Stachel S. E., Economides A. N., Stahl N., Yancopolous G. D., Harland R. M. Neural induction by the secreted polypeptide noggin. Science. 1993 Oct 29;262(5134):713–718. doi: 10.1126/science.8235591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon R. T. In pursuit of the functions of the Wnt family of developmental regulators: insights from Xenopus laevis. Bioessays. 1993 Feb;15(2):91–97. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng H. B. Xenopus laevis: Practical uses in cell and molecular biology. Solutions and protocols. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;36:657–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp R. A., Weintraub H. Ubiquitous MyoD transcription at the midblastula transition precedes induction-dependent MyoD expression in presumptive mesoderm of X. laevis. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):927–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90545-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. M., Darlington B. G., Heath J. K., Godsave S. F. Mesoderm induction in early Xenopus embryos by heparin-binding growth factors. Nature. 1987 Mar 12;326(6109):197–200. doi: 10.1038/326197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. M. Inducing factors in Xenopus early embryos. Curr Biol. 1994 Feb 1;4(2):116–126. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(94)00027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. M., Isaacs H. V., Darlington B. G. Inductive effects of fibroblast growth factor and lithium ion on Xenopus blastula ectoderm. Development. 1988 Jul;103(3):581–590. doi: 10.1242/dev.103.3.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Price B. M., Green J. B., Weigel D., Herrmann B. G. Expression of a Xenopus homolog of Brachyury (T) is an immediate-early response to mesoderm induction. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90573-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Price B. M., Van Nimmen K., Huylebroeck D. Identification of a potent Xenopus mesoderm-inducing factor as a homologue of activin A. Nature. 1990 Jun 21;345(6277):729–731. doi: 10.1038/345729a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. C., Harland R. M. Expression cloning of noggin, a new dorsalizing factor localized to the Spemann organizer in Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):829–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90316-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. C., Knecht A. K., Wu M., Harland R. M. Secreted noggin protein mimics the Spemann organizer in dorsalizing Xenopus mesoderm. Nature. 1993 Feb 11;361(6412):547–549. doi: 10.1038/361547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen G., Woolf T., Whitman M., Sokol S., Vaughan J., Vale W., Melton D. A. Activins are expressed early in Xenopus embryogenesis and can induce axial mesoderm and anterior structures. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):485–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90445-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Melton D. A. Induction of mesoderm by a viral oncogene in early Xenopus embryos. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):803–806. doi: 10.1126/science.2658054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. A., Melton D. A. Mesodermal patterning by an inducer gradient depends on secondary cell-cell communication. Curr Biol. 1994 Aug 1;4(8):676–686. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00152-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodland H. R., Jones E. A. The development of an assay to detect mRNAs that affect early development. Development. 1987 Dec;101(4):925–930. doi: 10.1242/dev.101.4.925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]