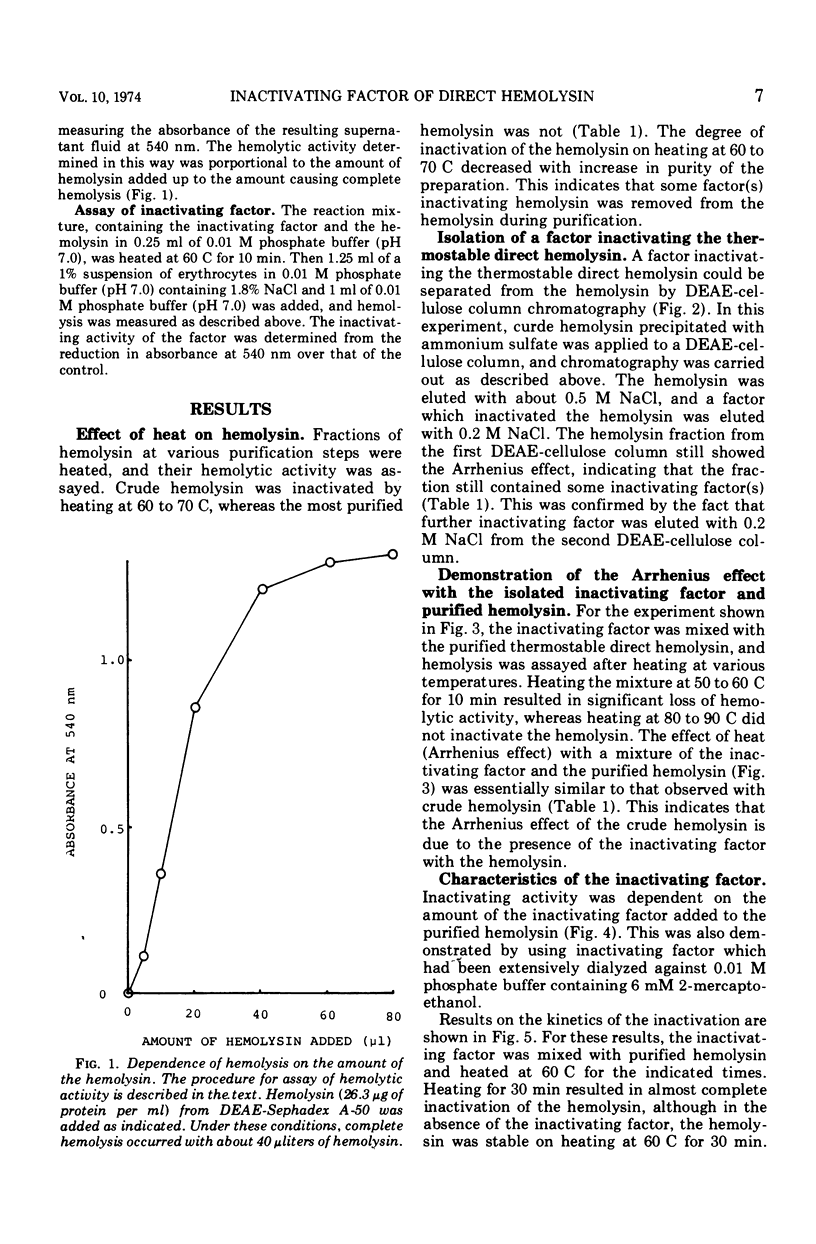
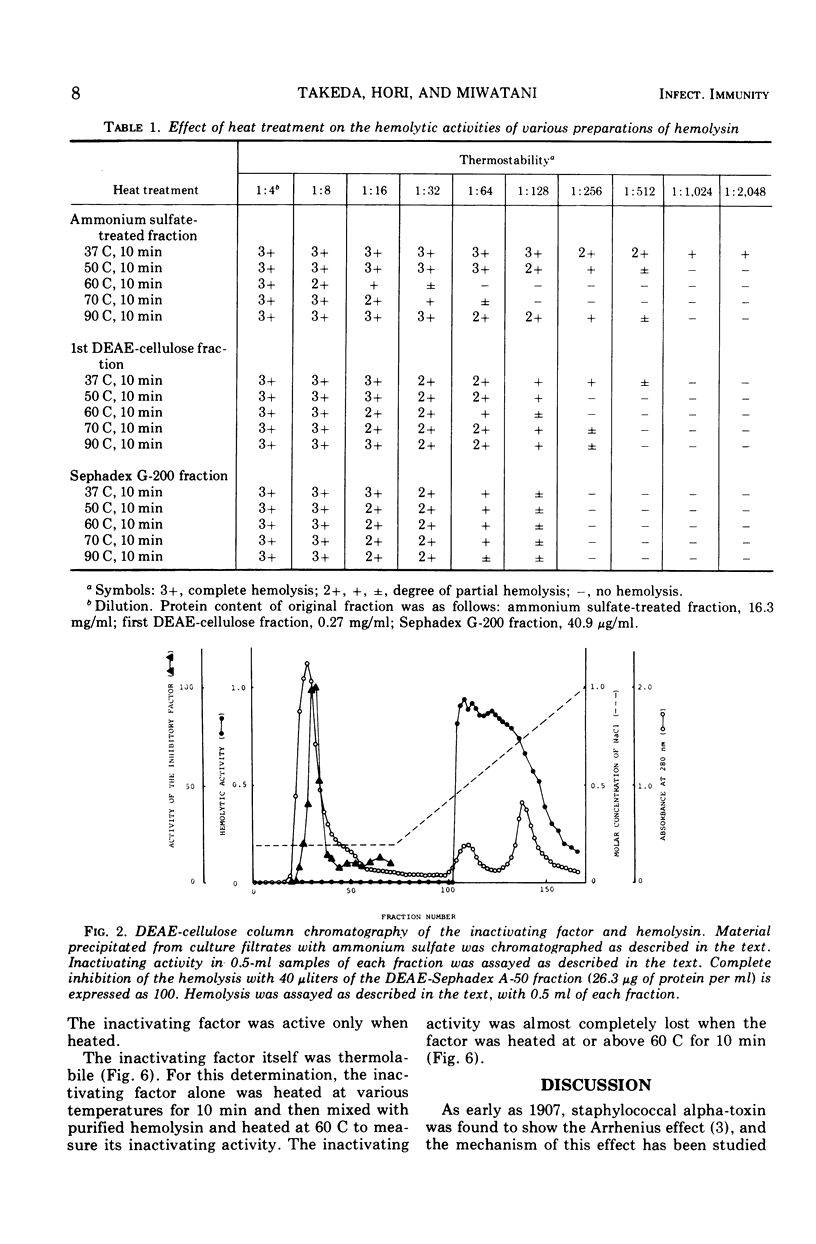
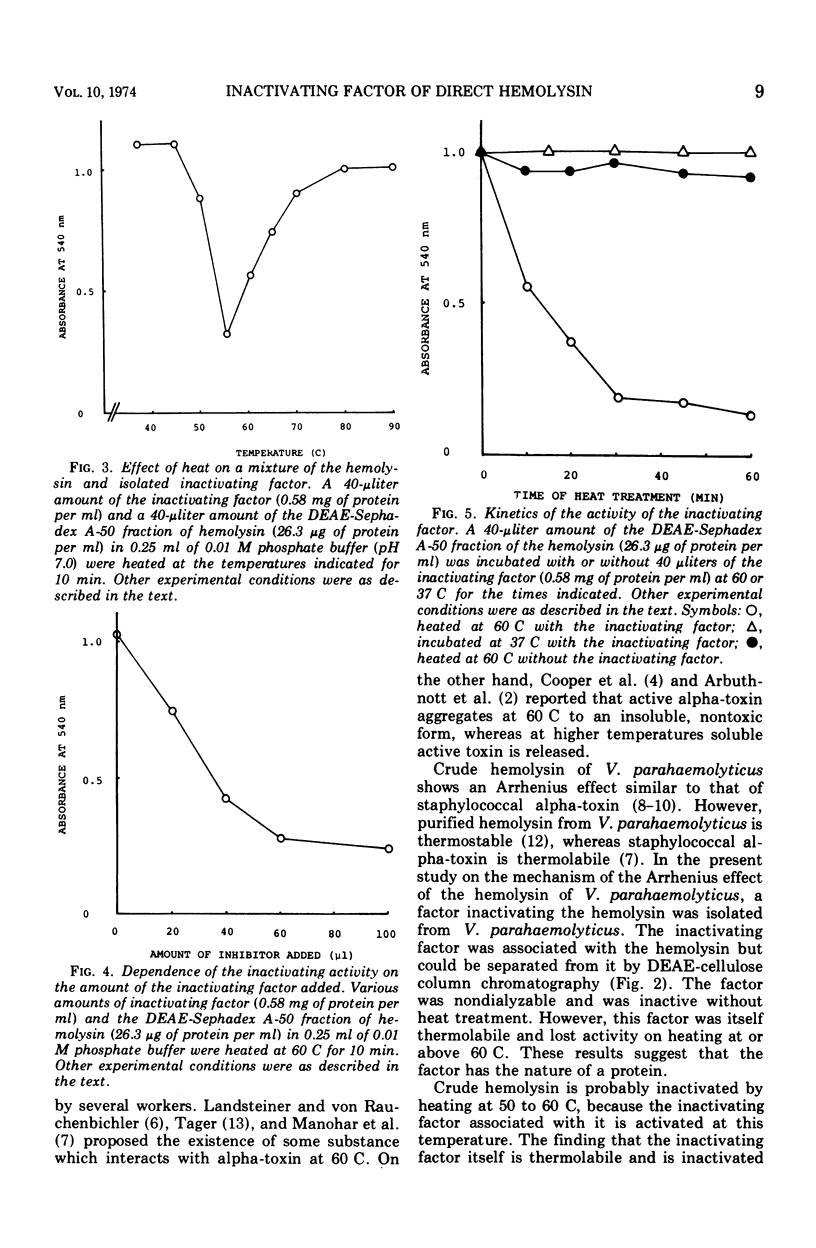
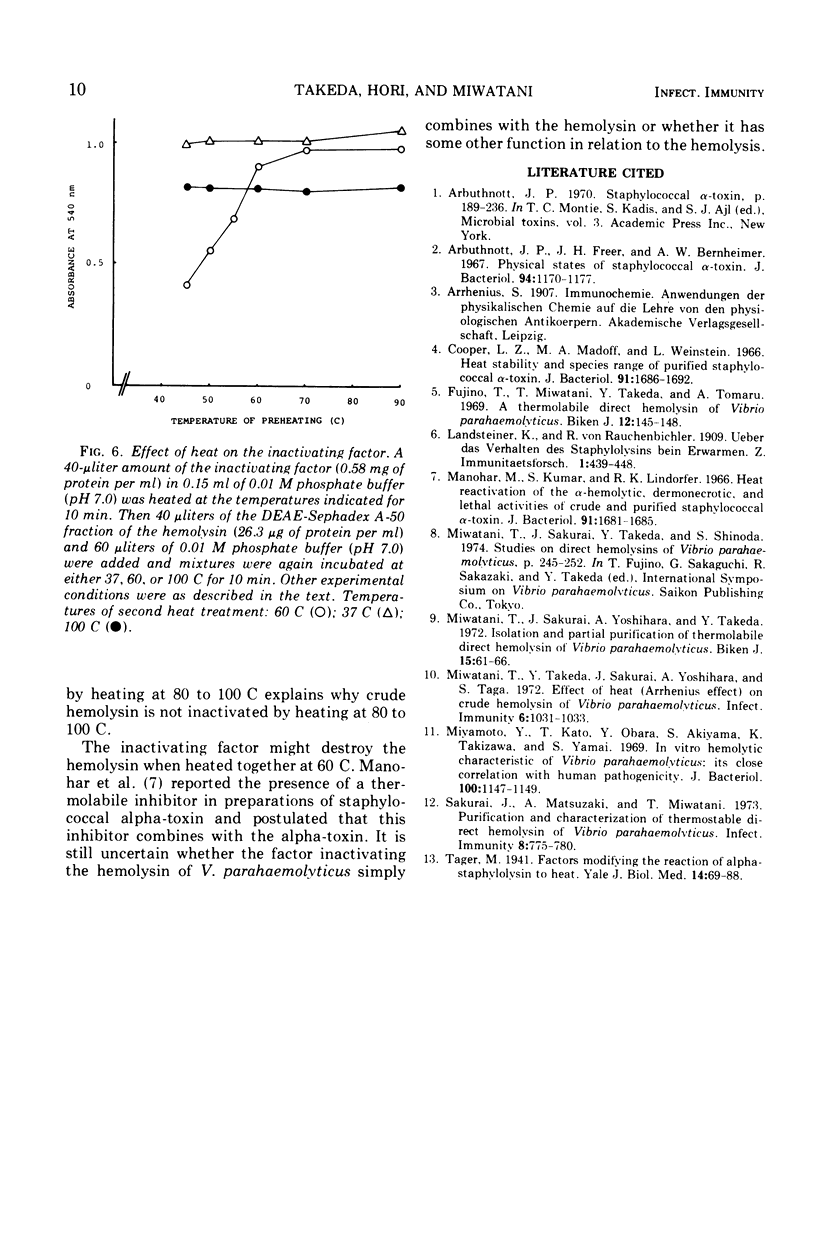
Abstract
A factor was found in Vibrio parahaemolyticus which inactivated the hemolytic activity of a purified, thermostable direct hemolysin. The inactivating factor was associated with the hemolysin but could be separated from it by diethylaminoethyl-cellulose column chromatography. The inactivating factor was activated by heating at 50 to 60 C, but was itself thermolabile and lost activity on heating to 70 to 100 C. The mechanism of the Arrhenius effect, observed with crude hemolysin of V. parahaemolyticus, is as follows. At 50 to 60 C, the temperature-dependent inactivating factor associated with hemolysin inactivates the hemolysin, whereas at 80 to 100 C the crude hemolysin retains activity because at this temperature the factor is inactivated.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arbuthnott J. P., Freer J. H., Bernheimer A. W. Physical states of staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1170–1177. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1170-1177.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper L. Z., Madoff M. A., Weinstein L. Heat stability and species range of purified staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1686–1692. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1686-1692.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujino T., Miwatani T., Takeda Y., Tomaru A. A thermolabile direct hemolysin of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Biken J. 1969 Jun;12(2):145–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manohar M., Kumar S., Lindorfer R. K. Heat reactivation of the alpha-hemolytic, dermonecrotic, lethal activities of crude and purified staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1681–1685. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1681-1685.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwatani T., Sakurai J., Yoshihara A., Takeda Y. Isolation and partial purification of thermolabile direct hemolysin of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Biken J. 1972 Jun;15(2):61–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwatani T., Takeda Y., Sakurai J., Yoshihara A., Taga S. Effect of heat (Arrhenius effect) on crude hemolysin of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Infect Immun. 1972 Dec;6(6):1031–1033. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.6.1031-1033.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto Y., Kato T., Obara Y., Akiyama S., Takizawa K., Yamai S. In vitro hemolytic characteristic of Vibrio parahaemolyticus: its close correlation with human pathogenicity. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):1147–1149. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.1147-1149.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai J., Matsuzaki A., Miwatani T. Purification and characterization of thermostable direct hemolysin of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):775–780. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.775-780.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



