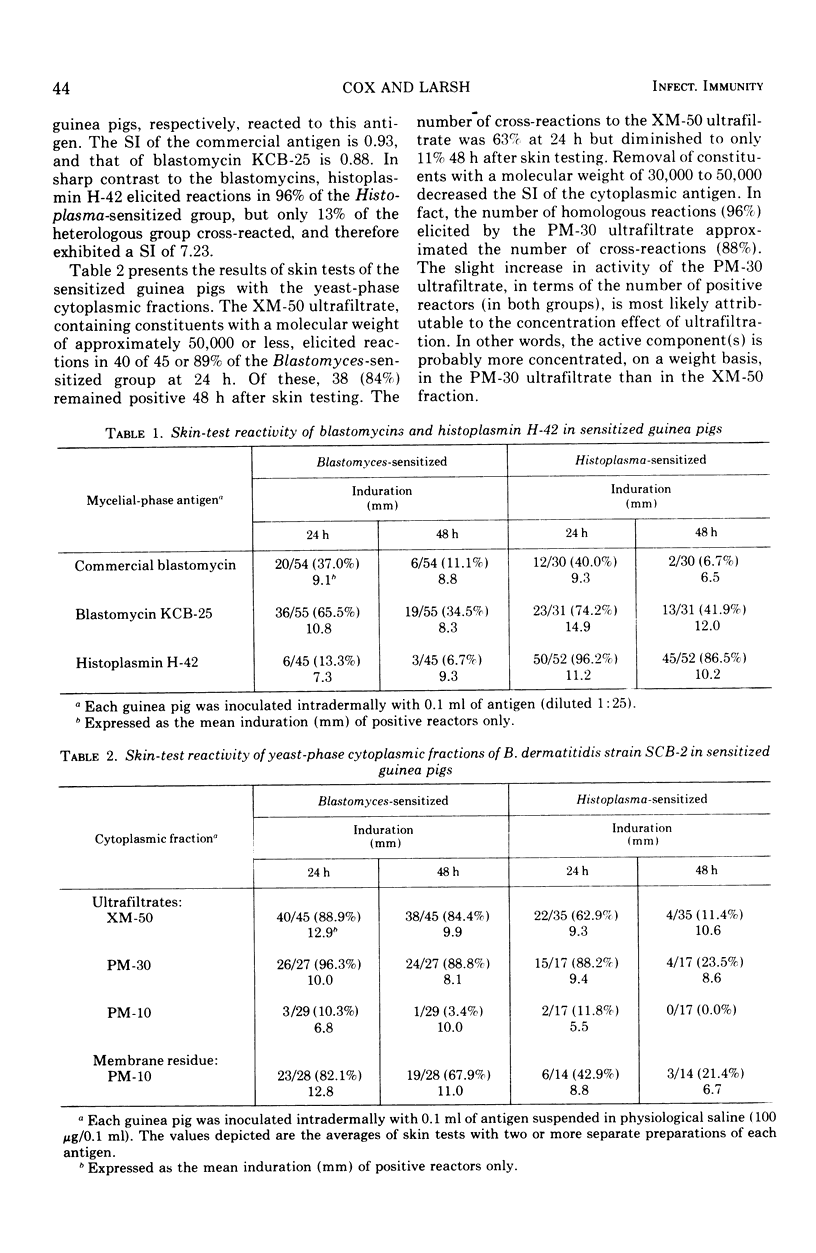
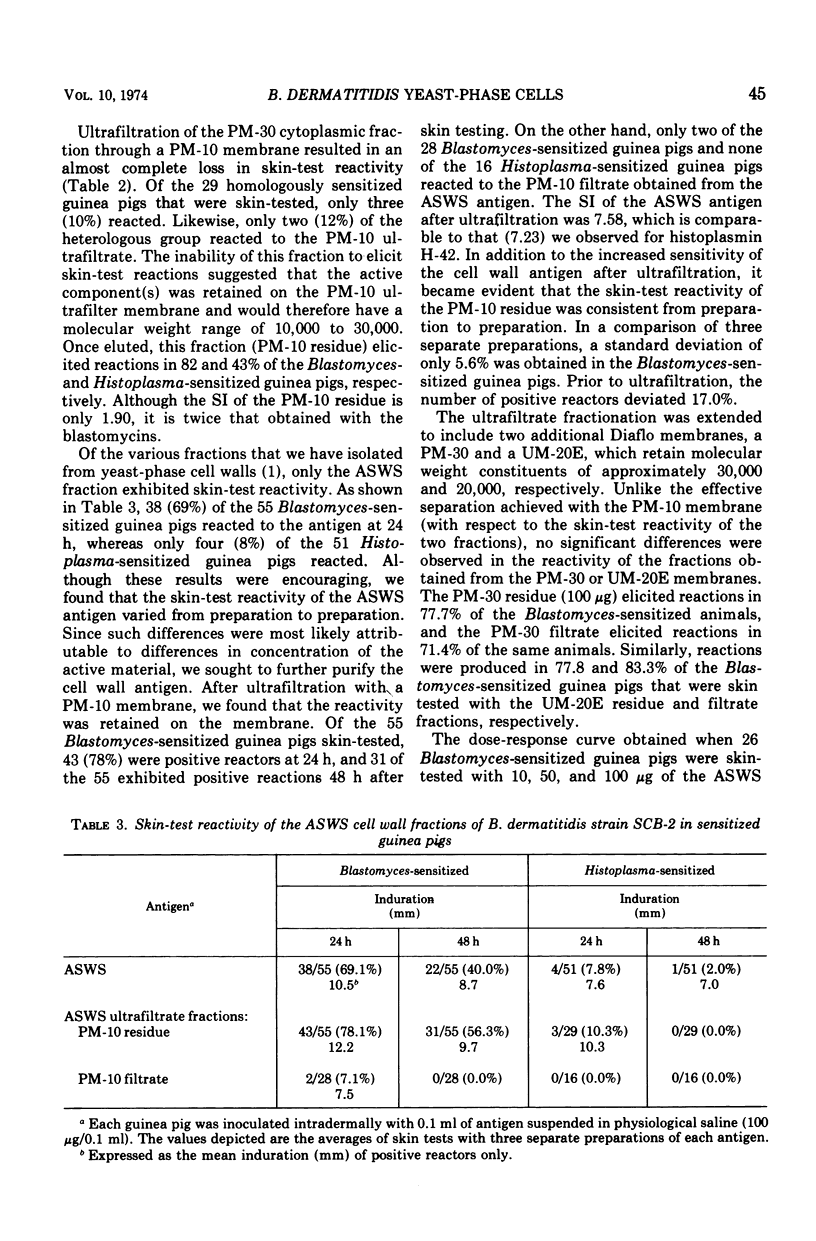
Abstract
Cell wall and cytoplasmic fractions were isolated from mechanically disrupted yeast-phase cells of Blastomyces dermatitidis in an effort to obtain a reliable skin-test antigen. The biological activities of these fractions were compared with those of two blastomycin preparations. The cytoplasmic antigens exhibited a low index of specificity yet exceeded the specificities of the blastomycins. The skin test-active component(s) of the cytoplasmic material had a molecular weight between 10,000 and 30,000 and could easily be concentrated by ultrafiltration on a PM-10 membrane. Unlike the cytoplasmic antigens and blastomycins, an alkali-soluble, water-soluble cell wall antigen effectively distinguished guinea pigs that were sensitized to B. dermatitidis from those sensitized to Histoplasma capsulatum. The biological activity of the yeast-phase antigen could be quantitated, on a weight basis, after purification by ultrafiltration (PM-10 membrane).
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cox R. A., Best G. K. Cell wall composition of two strains of Blastomyces dermatitidis exhibiting differences in virulence for mice. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):449–453. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.449-453.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DYSON J. E., Jr, EVANS E. E. Delayed hypersensitivity in experimental fungus infections: the skin reactivity of antigens from the yeast phase of Blastomyces dermatitidis. J Invest Dermatol. 1955 Apr;24(4):447–454. doi: 10.1038/jid.1955.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNIGHT R. A., MARCUS S. Polysaccharide skin test antigens derived from Histoplasma capsulatum and Blastomyces dermatitidis. Am Rev Tuberc. 1958 Jun;77(6):983–989. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1958.77.6.983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]