Abstract
Background
Iris L. s.l. is one of the most diverse and well-known genera in the Asparagales, with approximately 250–300 circumscribed species and significant economic impact. The taxonomy of the genus has suffered dramatic changes in the last century, particularly in the last decades after the application of molecular techniques. As a result several contrasting systematic arrangements are currently available to taxonomists. Many genera that were split from Iris s.str. in the past, on the basis of morphology (e.g., Hermodactylus, Iridodictyum, Juno, Pardanthopsis, and Xiphion, among others), are now a priori re-included in a very widely circumscribed Iris s.l. (incl. Belamcanda). This resulted in a more heterogeneous genus that is more difficult to define on morphological grounds. Testing congruence between taxonomic treatments and the results of recent molecular studies of Iris has never been performed, mostly due to the lack of proper taxonomic context.
Results
We generated several conventional phylogenies for Iris & outgroups using extensive sampling of taxa (187) and characters (10 plastid loci). We demonstrate that the natural history of Iris, written either as conventional molecular phylogenies or, if viewing in the context of the comparative approach, as a nested most parsimonious hierarchy of patterns, appear to be fully congruent with the narrow taxonomical treatment of the genus, restricted to the rhizomatous “bearded” taxa. The resulting topologies place Belamcanda, Pardanthopsis, and Gattenhofia as sisters to Iris s.str. and genus Siphonostylis as sister to Iris s.l.
Conclusion
The present study clearly justifies the splitting of Iris s.l. into at least 23 genera, 18 of which have already been accepted in the past by numerous authorities. These genera are characterized by unique combinations of partly overlapping morphological characters and biogeography. Moreover, nearly the same entities, which we here recognize at a generic rank, were for centuries frequently referred to by horticulturists as “working-name” groups.
Introduction
With approximately 250–300 species in circumscribtion, Iris s.l. is one of the most diverse and well-known genera in the Asparagales. The genus also includes a few outstanding model systems in evolutionary biology, particularly those used for studying hybridization and speciation in plants (e.g., [1], [2]). Due to its popularity in the horticultural trade, Iris has significant economic impact. However the taxonomy of Iris s.l. remains complicated. Based on morphology, many genera were split from Iris s.str. and were widely accepted in the past (e.g. Hermodactylus, Iridodictyum, Juno, or Xiphion, among others. They are now a priori re-included in a widely circumscribed Iris s.l., which renders it more heterogeneous and difficult to define on morphological grounds.
The test for congruence of Iris’s taxonomy, with the results of recent molecular studies of Iris, seems to be critical, but it has never been performed in a proper way, mostly due to the lack of correct taxonomic context. Here, we present the phylogenies for the Iris s.l. & outgroups by using extensive sampling of taxa (187) and characters (10 plastid loci), establishing the largest molecular matrix yet assembled for the group.
We also paired conventional phylogenetic analyses with the three-taxon analysis (3TA) [3], [4], [5] of binary representations of DNA matrices of the Iris s.l. & outgroups.
We compare the obtained conventional molecular phylogenies of Iris and the most parsimonious hierarchy of patterns yielded by the three-taxon analyses, with the different taxonomical treatments of the genus, and propose a new taxonomic arrangement of Iris s.l.
Results
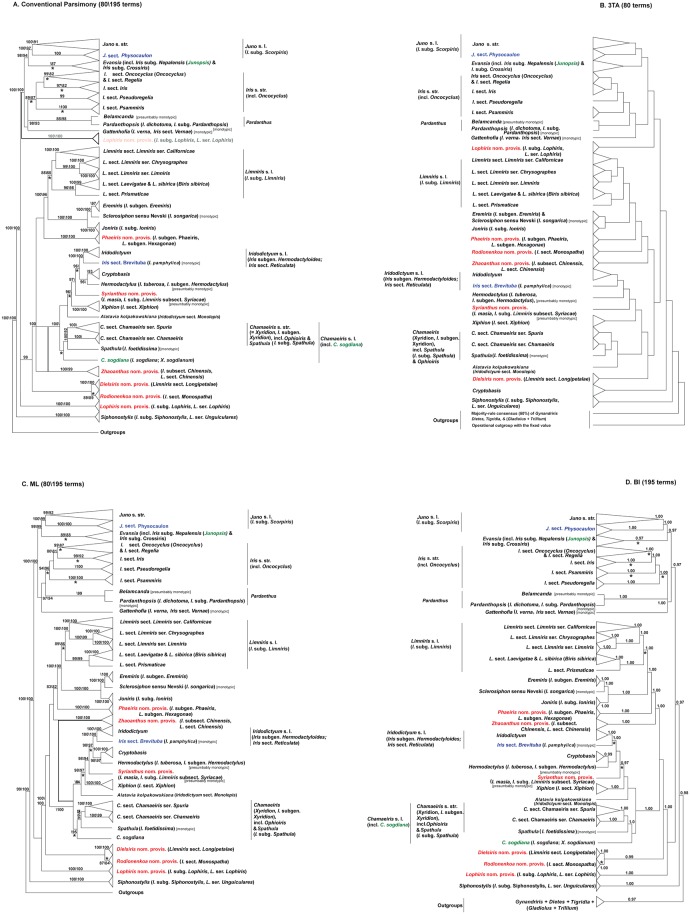
Figure 1 provides the detailed summary of the results. The names of the clades are given in italics due to the strong congruence with various taxonomic entities. The phylogenetic analyses of either the complete or modified supermatrix and the three-taxon statements (3TSs) binary matrices yielded similar topologies with all of the traditional infrageneric taxa of Iris s.l., resolved as well or strongly supported monophyletic groups or lineages (Figures 1–2, Figures S1–S6).
Figure 1. The summary of analyses.
A. The summary of strict consensus of 24\160 (80\195 terms) most parsimonious topologies recovered from a MP analysis (PAUP*) of conventional Iris s.l. & outgroups plastid supermatrix. Bold branches show the positions of Lophiris nom. provis. (Iris subg. Lophiris) and Zhaoanthus nom. provis. (I. subsect. Chinensis) within the 80-term topology. See Figure S1 and Figure S2A for the details. B. The summary of the single most parsimonious topology recovered from a MP analysis (PAUP*) of WS representation of conventional Iris s.l. & outgroups plastid supermatrix (81 terms, 80 taxa (79 of Iris s.l. +1 outgroup) + operational outgroup). See Figure S3 for the details. C. Summary of the two most probable topologies (80\195 terms) recovered from a ML analysis (RAxML) of conventional Iris s.l. & outgroups plastid supermatrix. ML BS values for nodes receiving >80% supports are indicated above and below the branches. Bold branches show the position of Zhaoanthus nom. provis. (I. subsect. Chinensis) within 80-term topology. See Figure 2A and Figure S2B for the details. D. Consensus topology recovered from a Bayesian analysis (MrBayes) of conventional Iris s.l. & outgroups plastid supermatrix (195 terms). Numbers above and below branches indicate posterior probabilities >0.95. See Figure S4 for the details. Taxa, proposed to be accepted at the generic rank for the first time are indicated in red; taxa potentially recognizable at generic rank are indicated in blue, critical taxa are indicated in green. Selected synonyms of accepted or proposed genera are indicated in curved brackets. Asterisks indicate the branches with a minor conflict of support levels. The widely used name “Limniris (Tausch) Rchb.” must be conserved against “Biris Medik.” (Iris sibirica L.), as it was already conserved against “Pseudo-iris Medik.” [42].
Figure 2. Conventional plastid phylogeny and nested most parsimonious hierarchy of patterns.
A. Most probable topology (-ln likelihood = 45410.319704) recovered from a ML analysis (RAxML) of conventional Iris s.l. & outgroups plastid supermatrix (195 terms). ML BS values for nodes receiving >80% supports are indicated above and below the branches. B. Robinson-Foulds 3TA topology (RFS) of score 7 combined the results of all 3TA analyses (Figure S3 (single MP topology), Figure S5A (single MP topology), and Figures S5B–E (RF median consensus of the even numbers of MP topologies)). See Figure S3 and Figure S5 for the details. Taxa proposed to be accepted at the generic rank for the first time are indicated in red; taxa potentially recognizable at generic rank are indicated in blue, critical taxa are indicated in green. Selected synonyms of accepted or proposed genera are indicated in curved brackets.
Positions of monophyletic Cryptobasis Nevski (I. subsect. Tenuifoliae Diels), I. sect. Psammiris (Spach) J.J.Taylor (I. subgen. Psammiris Spach), I. sect. Pseudoregelia Dykes (I. subgen. Pseudoevansia Baker), Lophiris nom. provis. (Iris subg. Lophiris (Tausch) C.A. Wilson), I. subgen. Crossiris Spach (I. watti Baker ex Hook.f. + I. japonica Thunb.), Juno sect. Acanthospora Rodion., J. sect. Wendelboa Rodion., Rodionenkoa nom. provis. (I. sect. Monospatha Rodion.), Spathula (Tausch) Fourr. (I. foetidissima L., I. subg. Spathula (Tausch) Spach), and Zhaoanthus nom. provis. (I. subsect. Chinensis Diels, Limniris sect. Chinensis (Diels) Rodion.) depend on the chosen method of the analysis (Figures 1–2, Figures S1–S6).
Clade {Pardanthus (Belamcanda Adans. (B. chinensis (L.) Redouté, I. domestica (L.) Goldblatt & Mabb.) + Pardanthopsis (Hance) L.W. Lenz (Pardanthopsis dichotoma (Pall.) L.W. Lenz, Iris dichotoma Pall., Pardanthus dichotomus (Pall.) Ledeb.)} and Gattenhofia Medik. (I. subsect. Vernae Diels) are sister groups of the well or strongly supported Iris s.str. (Figures 1–2, Figure S1). Siphonostylis Wern. Schulze (I. subg. Siphonostylis (Wern. Schulze) C.A. Wilson (I. ser. Unguiculares (Diels) G.H.M. Lawr. = Limniris sect. Unguiculares (Diels) Rodion.)), was confirmed as the sister group to the rest of Iris s.l. (Figure 1, Figures S1–S2).
Evansia Salisb. (incl. Junopsis Wern.Schulze (I. subg. Nepalensis (Dykes) G.H.M. Lawr.)) is sister to Juno Tratt. (I. subgen. Scorpiris Spach), and {Juno + Evansia} + {Iris s.str. + Gattenhofia + Belamcanda + Pardanthopsis} are strongly supported sister clades.
The monotypic genus Sclerosiphon Nevski (Iris songarica Schrenk) is a strongly supported sister to Eremiris (Spach) Rodion. (I. subgen. Eremiris Spach) and both latter groups form a a strongly supported sister clade to Joniris (Spach) Klatt (I. subg. Ioniris Spach). Clade {Sclerosiphon + Eremiris + Joniris} is a strongly supported sister of Limniris (Tausch) Rchb. s.l.
Iridodictyum Rodion (Iris subgen. Hermodactyloides Spach; I. sect. Reticulata Dykes) (incl. Iris sect. Brevituba B. Mathew (I. pamphylica Hedge)), (Cryptobasis Nevski (conventional phylogenies only) + Hermodactylus Mill. (I. subgen. Hermodactylus (Tourn.) Sweet (I. tuberosa L.)), Syrianthus nom. provis. (I. masia Dykes, I. subg. Limniris (Tausch) Spach subsect. Syriacae Diels), Xiphion Mill. (I. sect. Xiphion (Mill.) Tausch), Alatavia kolpakowskiana (Regel) Rodion. (Iridodictyum sect. Monolepis Rodion., Iris kolpakowskiana Regel), and Chamaeiris Medik. (Xyridion (Tausch) Fourr., I. subgen. Xyridion Spach (incl. Spathula)) formed a grade with the partly conflict levels of support (Figure 1–2, Figures S1–S6).
Juno sect. Physocaulon Rodion. is a strongly supported sister clade to the rest of the Juno, I. sect. Brevituba (I. pamphylica) is strongly supported sister to Iridodictyum, and Chamaeiris sogdiana (Bunge) M.B.Crespo (Iris sogdiana Bunge, Xyridion sogdianum (Bunge) Nevski) is a sister to the rest of the Chamaeiris (Figure 1–2, Figures S1–S6).
Several species sampled in more than one infraspecific taxa, appeared to be non-monophyletic (I. caucasica Hoffm., I. hartwegii Baker, I. potaninii Maxim. and others) (Figure 2).
Analyses
We sampled 173 broadly defined species of Iris s.l. and five out-group taxa: Dietes Salisb. (D. robinsoniana Klatt), Gladiolus L. (G. caucasicus Herb.), Gynandriris Parl. (G. pritzeliana (Diels) Goldblatt and G. sisyrinchium Parl.), Tigridia Juss. (T. pavonia (L.f.) DC.), and Trillium L. (T. ovatum Pursh) (Appendix S1). For seven species (Iris anguifuga Y.T. Zhao & X.J. Xue, I. foetidissima L., I. domestica (L.) Goldblatt & Mabb., I. japonica Thunb., I. forrestii Dykes, I. setosa Pall. ex Link, and I. subdecolorata Vved.) (Appendix S1) two or three accessions were included in the analyses. For 10 species (I. caucasica, I. collettii Hook.f., I. hartwegii s.l. (incl. I. pinetorum Eastw.), I. histrio Rchb.f., I. hymenospatha B. Mathew & Wendelbo, I. potaninii, I. proantha Diels, I. stenophylla Hausskn. ex Baker, I. tenuissima Dykes, and I. virginica L. s.l. (incl. I. shrevei Small) infraspecific taxa (either subspecies or varieties) were included in the analyses (Appendix S1). With the exclusion of Alatavia, all Iris-segregated genera, as well as a vast majority of the infrageneric groups of the broadly defined Iris, were sampled in two or more taxa (if not monotypic) (Appendix S1). The total number of taxa sampled for Iris s.l. & outgroups was 187 (182 for Iris s.l.).
The sequence data (10 plastid loci: 5′ trnK, matK, 3′ trnK, trnL intron, trnL-F IGS, ndhF, rpl14-rps8 IGS, rps8 gene, rps8-rpL36 IGS, and trnE-trnT spacer) was taken from the GenBank/EMBL databases (Appendix S1). Sequences were generated mostly by [6], [7], [8], [9], [10], [11], [12], [13], [14], [15], [16], [17], [18], [19] (Appendix S1), and in the majority during the long-term comprehensive studies of Wilson [15], [16], [17] and Ikinci et al. [18]. Iris domestica, I. anguifuga, I. falcifolia Bunge, I. foetidissima, I. loczyi Kanitz, I. pallasii Fisch. ex Trevir., I. tenuifolia Pall., and I. ventricosa Pall. were sampled, additionally sampled or re-sampled from [7], [12], [13], [18], [19] (Appendix S1) (see also [18] for the brief discussion on I. falcifolia). Following [20] and [21], the sequence data for trnE-trnT and rpl14-rps8 spacers of Trillium ovatum [14] were combined with the sequence data of the most distant Iris’s s.l. outgroup (Gladiolus).
All sequences were aligned using MAFFT [22], [23], and then were concatenated and analyzed as a single contiguous dataset (supermatrix). The number of terms in the final supermatrix was 195. We followed MAFFT’s FFT-NS-i, E-INS-i, L-INS-i, and G-INS-i alignment strategies [22], [23], with the default settings for gap opening penalty and offset value. Including gaps, the total G-INS-i alignment used for the final analyses consisted of 8464 bp.
Five analytical approaches were used:
Bayesian analyses (BI) of the 195 term supermatrix were conducted with the MrBayes (v. 3.1.2) [24]. Two runs with four chains each (three heated and one cold) were run for 40 million generations; the chains were sampled every 1000 generations with default parameters.
We analyzed the 80 and 195 term supermatrces by the maximum likelihood (ML) approach, as implemented in RAxML v. 7.4.2 [25], [26] with 2000 rapid bootstrap (BS) replicates, integrated with 200 searches for the optimal tree.
The 195 term supermatrix was also analyzed by PhyML v. 3.1 [27], as implemented in SeaView v. 4.5.1 [28], with estimated proportion of invariable sites and empirical nucleotide equilibrium frequencies. We took a BioNJ tree as a starting tree, and defined the strategy of the tree topology search as “best of NNIs and SPRs” [27]. Instead of the ML BS, branch supports were calculated with the approximate likelihood-ratio test (aLRT) [29].
In the cases of parametric approaches, the GTR + G model was assumed to be the best choice.
Conventional maximum parsimony (MP) analysis of both the 80 and 195 term supermatrices, was performed with PAUP* v. 4.0b10 and 4.0a134 [30], using heuristic searches with 1000 random addition replicates, with no more than 100 trees saved per replicate, and tree-bisection-reconnection (TBR) branch swapping with the MulTrees option in effect. MP Jackknife (JK) values of clade support are estimated using 2500 replicates and 10 random addition sequences (saving no more than 1000 trees per replicate), with the TBR branch swapping/MulTrees option in effect with the deletion of 37.0% of the characters in each replicate.
The three-taxon analysis (3TA) of the DNA matrices was established after their three-taxon Williams-Siebert (WS) representation [31], [32] using TAXODIUM v. 1.2 [32]. The value of the operational outgroup was fixed as a consensus sequence of the matrix [Dietes + Gynandriris + Tigridia + (Gladiolus + Trillium)], or, in some cases, as a consensus of matrices [Iris japonica 1, 2 + I. watti] (Figure S5B) or [Belamcanda (I. domestica) + Pardanthopsis (I. dichotoma) + Gattenhofia (I. verna)] (Figure S5C). The majority rule consensus (50%) was used for the calculation of the consensus sequences (only modal values, shown with the minimum frequency among applicable states, required to include the state in consensus equal to 0.5).
The WS or binary representation of the DNA matrix is, in fact, the 3TS matrix [32]. Therefore below, we use the term “WS representation” as a synonym of the term “3TS matrix”.
Due to the computational limitations for the MP search, before WS representation, the conventional matrix of Iris s.l. & outgroups was reduced down to 80 taxa (79 species + single outgroup), but retained the sampling of all major taxonomic entities (Figure 1B, Figure S3). Based on the relationships obtained after the MP analysis of this 3TS matrix, five additional “local” [33] 3TAs were performed, each within [33] one of the fully sampled major clades of the obtained 3TA topology (Figure S5).
With the exclusion of a single most parsimonious topology, which was recovered after the MP analysis of the 3TS matrix of Evansia (Figure 5SB), the even number of the most parsimonious trees was obtained after each local MP search (Figure 5S). In all cases, the topology of strict consensus was not minimal. Therefore, additionally to the strict consensus [4], [5], we calculated the median consensus tree (reviewed in [5], [34]), based on Robinson-Foulds (RF) distance [34]. Calculations were performed by using RFS v. 2.0 [34] (Figures S5A, C–E).
Eventually all six minimal 3TA topologies (two single, most parsimonious trees (Figure S3, S5A) and four RF median consensus, each represented one of the minimal trees (Figures S5A, C–E)) were combined to the single median RF Supertree [34] (Figure 2B), and additionally to the almost identical, single, median Supertriplets-based supertree [35] (not shown).
In cases of all 3TAs, we used the uniform weighing (reviewed in [4], [5]) of the statements. The results of the 3TAs were accepted as preliminary, but sufficient to the comparison with conventional phylogenies (Figures 1–2).
Trees and matrices were handled using Se-Al v. 2.0a11 [36], Mesquite v. 2. 75 [37], SeaView v. 4.5.1 [28], and FigTree v. 1.4 [38]. Resources of bioinformatics portal CIPRES (https://www.phylo.org/) and RCC of University of Florida (http://researchcomputing.ufl.edu/), were used for the several MP and BI analyses.
Discussion
Linnaeus [39] accepted a broadly defined genus Iris, contrary to previous authors such as Bauhin and Cherler [40], Dodoens [41], Tournefort [42] among others. However, almost at the same time, Miller [43], [44], and later Adanson [45], Fourreau [46], Medikus [47], Parlatore [48], Reichenbach [49], and Trattinnick [50] among others, challenged Linnaeus’s treatment, by accepting segregation of additional genera [39], [40], [41]. Linnaean’s “Iris s.l.”, however, appeared to be normative for most experts until today, despite the fact that a broad definition of Iris, as currently circumscribed, makes that group too heterogeneous, and therefore difficult to define [51], [52], [53].
Molecular contributions of Tille et al. [54] and Wilson [15], [16], [17] have demonstrated that Belamcanda chinensis is deeply nested within the Iris s.l. clade. Thus, in case of recognition of Belamcanda as an independent genus, Iris s.l. appears to be clearly non-monophyletic [15], [16], [17], [54]. Therefore, in the light of the recent molecular data [15], [16], [17], [18], to make Iris s.l. monophyletic, all bulbous genera, namely the frequently recognized Alatavia, Iridodictyum, Juno, and Xiphion, plus the rhizomatous or tuberous Chamaeiris, Hermodactylus or Junopsis, must be circumscribed within Iris. The presumably monotypic, polypoid genera Belamcanda and Pardanthopsis must also be circumscribed within Iris, but this matter seems to be very problematic [55]. For example, Lenz [56], [57], [58] and Schulze [59] listed about a dozen morphological, anatomical and biological features, which clearly separate Pardanthopsis and Belamcanda from Iris s.l., as well as from each other. These authors also showed that both genera do not form hybrids with other species of Iris s.l., but can mutually interbreed to produce × Pardancanda norrisii L.W. Lenz (I. × norrisii (L.W. Lenz) C. Whitehouse) [56], [58]. Attention must also be paid to the fact that the basionym of Belamcanda chinensis is Ixia chinensis L., a name applied to plants with an actinomorphic open flower, which is clearly different from the typical 3-merianthic, closed Iris-flower structure.
Strong morphological evidence has been used to argue in favor for separating several genera from Iris s.str., such as Alatavia [60], Chamaeiris (Xyridion) [51], [61], Cryptobasis [62], [63], [64], [65], [66], Eremiris [67], Iridodictyum [68], Juno [68], [69], Limniris [70], Sclerosiphon [66], Siphonostylis [71], [72], [73], and Xiphion [68], [74]. They all constitute independent lineages, which are easy to define on morphological grounds. Among these, natural hybridization is almost unknown to occur, aside from one to a few potentially credible cases (e. g., Iris × neumayeri Janch. ex Holub (I. graminea L. × I. sibirica L.)).
Our data are essentially congruent with the results of Shneer’s [75] (see also [76] and [77]), who showed that serologically Hermodactylus, Gynandriris, Iris, Xiphion, Juno, Pardanthopsis, Iridodictyum, and Belamcanda are nested into two groups: (a.) Hermodactylus + Gynandriris on one side, and (b.) the rest of the genera on the other. Within group (b.), the “beardless” irises (Limniris s.l.) are sharply different from the “bearded” irises (Iris s.str.), which are serologically closer to Juno, Pardanthopsis, and Belamcanda. In contrast, Chamaeiris (Xyridion), Iridodictyum, and Xiphion, appeared to be more closely related to the “beardless” irises (Limniris s.l.), not to Iris s.str. [75].
Later Shneer [78] and Rodionenko [66], [71] also argued that the Iris sect. Unguiculares is a separate genus, Siphonostylis [72], [73]. According to Shneer [78] and Rodionenko [66], [71], Siphonostylis displayed features closer to those present in presumably primitive irises. Accordingly, in our analyses, this later genus is the sister group to the rest of the broadly defined Iris s.l. clade (Figure 1, Figures S1–S3, see also [16], [17], [55] for similar results). Also, Shneer [78] confirmed that serologically Iris s.str. and the “beardless” taxa (I. subg. Limniris and I. subg. Xyridion, both accepted here at the generic rank as Limniris and Chamaeiris respectively) are very dissimilar, and she also showed [78] that the members of the relatively homogeneous “Iris s.str.”, appear to be similar to irises of I. subg. Crossiris, the genus Evansia (incl. Junopsis [79]) of our topologies (Figure 1, Figures S1–S2A).
Belamcanda and Pardanthopsis are sister taxa to each other, and therefore may be treated as either one or two genera. Due to the agreement that Belamcanda and Pardanthopsis must both be accepted at the generic rank [56], [58], [80], we tend to agree with the morphologically diverse genus × Pardancanda W. Lenz which results from the artificial crossing of the closely related Belamcanda and Pardanthopsis [56], [58].
Our findings do not mean, however, that all Iris - segregated genera, are congruent to our topologies. Due to the recent sampling of sequence data, we did not find enough evidence to accept genera such as Biris Medik, Junopsis, Neubeckia Alef., Oncocyclus Siemssen, Regelia Hort. ex H. Wendl., Spathula, and Ophioiris (Y.T. Zhao) Rodion. [81], but at least the case of Junopsis [82] clearly requires further investigation.
The re-treated results of recent comprehensive molecular studies of Iris s.l. [15], [16], [17], [18], if placed in a proper taxonomic context, provide unique opportunity to show that a rainbow cannot consist of a single color, and a broadly defined Iris is better treated as a tribe rather than a single genus. The natural history of Iris, written either as conventional molecular phylogenies (Figure 1–2, Figures S1, 2S, S4, S6) or, if viewing in the context of the comparative approach, as a nested most parsimonious hierarchy of patterns [4], [83] implying the “fourth parallelism” [84] (Figure 1–2, Figures S3, S5), appear to be fully congruent with the narrow taxonomical treatment of the genus, restricted to the rhizomatous “bearded” taxa. This leads to a new taxonomic arrangement of the whole aggregate, with at least 23 previously recognized infrageneric groups needing to be accepted at the generic rank (Figures 1–2). At least 18 of these groups have already been treated as independent genera by different authorities in the past (Figure 1–2, Figures S1–S6, Table S1), and many of them are still in current use. Our multi-generic proposal for Iris s.l. (Crespo et al., in prep.) is mostly concurrent with the distinction of groups, which have traditionally been used (and are still currently used) as “working-names” by horticulturists [85] within the last two centuries. It renders a more simple and practical nomenclatural system, than an alternative complex treatment of an expanded Iris with numerous infrageneric taxa. Unique combinations of partly overlapped morphological characters can be successfully used as a diagnostic for taxonomic recognition of such smaller and then more homogeneous and intuitively clear genera (Figures 1–2, Table S1).
In his early classification of the Old World Iridoideae, Goldblatt [86] suggested that the genera Dietes, Iris s.l., Hermodactylus, and Belamcanda should be grouped into one subtribe Iridinae Pax. This is generally supported in our present study.
Our multi-generic solution of Iris s.l. parallels the new recently proposed classifications of Hyacinthaceae subfam. Ornithogaloideae (Asparagaceae subfam. Scilloideae tribe Ornithogaleae) [87], Typha L. (Typhaceae) [88], [89], Chenopodium L. (Chenopodiaceae-Amaranthaceae) [90], Aloe L. (Xanthorrhoeaceae subfam. Asphodeloideae) [91], Nothofagus Blume [92] (Nothofagaceae), or or Centaurium Hill [93] (Gentianaceae), which simplify the taxonomy of the whole aggregate, and makes all segregate genera more homogeneous and easy to work with.
A broadly defined Iris seems to be semantically equivalent to tribe Hordeeae Kunth ex Spenn. & Martynov (former Triticeae Dumort.) with its sometimes cryptic, sometimes clear morphological diversity, wide range of chromosome numbers, and polyploid complexes (Table S1). The inclusion of Belamcanda, as well as of numerous other Iris-segregated genera in the circumscription of Iris s.l, may therefore be similar to the recognition of the tribe Hordeeae, at the rank of single genus - for example, the genus Hordeum L. s.l. It is hard to imagine, however, that such a decision will not be challenged, even if the pro-arguments will be nominated as practical expediency, problems with the nomenclature, and as other third-party considerations.
Supporting Information
Conventional plastid phylogeny (MP). Strict consensus of 160 most parsimonious topologies (length = 5268, CI = 0.6137, RI = 0.8365) recovered from a MP analysis (PAUP*) of conventional of Iris s.l. & outgroups plastid supermatrix (195 terms, 8464 characters in total, 1559 are parsimony-informative). All characters were treated as “unordered” (Fitch parsimony). MP JK values for nodes with greater than 80% support are indicated above or below the branches.
(EPS)
Conventional plastid phylogenies (reduced supermatrix). A. Strict consensus of 24 most parsimonious topologies (length = 3512, CI = 0.6723, RI = 0.7695) recovered from a MP analysis (PAUP*) of conventional of Iris s.l. & outgroups plastid supermatrix (80 terms, 8237 characters in total, 1045 characters are parsimony-informative). All characters were treated as “unordered” (Fitch parsimony). MP JK values for nodes with greater than 80% support are indicated above or below the branches. B. Most probable topology (−ln likelihood = 33243.302540) recovered from a ML analysis (RAxML) of conventional Iris s.l. & outgroups plastid supermatrix (80 terms, 8237 characters). ML BS values for nodes receiving >80% supports are indicated above and below the branches. Taxa proposed to be accepted at the generic rank for the first time are indicated in red; taxa potentially recognizable at generic rank are indicated in blue; critical taxa are indicated in green.
(EPS)
Nested most parsimonious hierarchy of patterns (reduced supermatrix). Single most parsimonious topology (length = 2558783; RI = 0.7858) recovered from the MP analysis (PAUP*) of WS representation of conventional Iris s.l. & outgroups plastid supermatrix (81 terms, 80 taxa (79 taxa of Iris s.l. + outgroup ( = majority-rule consensus (50%) of the matrix [Gynandriris + Dietes + Tigridia + (Gladiolus + Trillium)]) + operational outgroup). All 2 023 963 binary characters (3TSs) are parsimony-informative, all weighted uniformly and all treated as “ordered” (Wagner parsimony). The value of operational outgroup fixed as a value of majority-rule consensus (50%) of the matrix [Gynandriris + Dietes + Tigridia + (Gladiolus + Trillium)].
(EPS)
Conventional plastid phylogeny (BI). Consensus topology recovered from a Bayesian analysis (MrBayes) of conventional Iris s.l. & outgroups plastid supermatrix (195 terms, 8464 characters in total). The first 3000 trees were discarded as burn-in, and posterior probabilities were calculated from the majority-rule consensus of the remaining trees sampled in both runs. At the end of the runs, the standard deviation of split frequencies between the two runs had fallen to 0.0070. Numbers above and below the branches indicate posterior probabilities >0.95. Taxa, proposed to be accepted at the generic rank for the first time are indicated in red; taxa potentially recognizable at generic rank are indicated in blue; critical taxa are indicated in green.
(EPS)
Nested most parsimonious hierarchies of patterns. A. 1. Strict consensus of the four most parsimonious topologies (length = 700315; RI = 0.8943; the length of the strict consensus equals to 700319) recovered from the MP analysis (PAUP*) of the WS representation of conventional plastid supermatrix Juno (57 terms). All 633358 binary characters (3TSs) are parsimony-informative, all are weighted uniformly and all are treated as “ordered” (Wagner parsimony). The value of the operational outgroup is fixed as a value of the majority-rule consensus (50%) of the matrix [Gynandriris + Dietes + Tigridia + (Gladiolus + Trillium)]; 2. RF median consensus (RFS) of the same most parsimonious topologies (RF distance score = 46; length = 700315; RI = 0.8943). B. Single most parsimonious topology (length = 1279; RI = 0.9412) recovered from the MP analysis (PAUP*) of WS representation of the conventional, plastid supermatrix of Evansia (10 terms). All 1208 binary characters (3TSs) are parsimony-informative, all are weighted uniformly and all are treated as “ordered” (Wagner parsimony). Based on the patterns of the relationships recovered from a MP analysis of the 81 terms 3TA matrix (Figure S3), the value of the operational outgroup is fixed as a value of the majority-rule consensus of the matrix [Iris japonica 1, 2 + I. wattii]. C. 1. Strict consensus of the 90 most parsimonious topologies (length = 72792; RI = 0.9363; the length of the strict consensus equal to 72884) recovered from the MP analysis of WS representation of conventional plastid supermatrix of the core Iris (37 terms). All 68435 characters (3TSs) are parsimony-informative, all are weighted uniformly and all are treated as “ordered” (Wagner parsimony). Based on the patterns of the relationships recovered from a MP analysis of the 81 term 3TA matrix (Figure S3), the value of the operational outgroup is fixed as a value of the majority-rule consensus of the matrix [Belamcanda (I. domestica) + Pardanthopsis (I. dichotoma) + Gattenhofia (I. verna)]; 2. RF median consensus (RFS) of the same most parsimonious topologies (RF distance score = 824; length = 72792; RI = 0.9363). D. 1. Strict consensus of the two most parsimonious topologies (length = 364930; RI = 0.8704; the length of the strict consensus equal to 364936) recovered from the MP analysis (PAUP*) of WS representation of conventional plastid supermatrix of Limniris s.l. + Phaeiris nom. provis. (L. subgen. Hexagonae, I. subgen. Phaeiris) + Eremiris (I. subgen. Eremiris) + Joniris (L. subgen. Ioniris; sect. Ioniris) + Sclerosiphon (I. songarica) (41 terms). All 323073 characters (3TSs) are parsimony-informative, all are weighted uniformly and all are treated as “ordered” (Wagner parsimony). The value of the operational outgroup is fixed as a value of the majority-rule consensus (50%) of the matrix [Gynandriris + Dietes + Tigridia + (Gladiolus + Trillium)]; 2. RF median consensus (RFS) of the same most parsimonious topologies (RF distance score = 7; length = 364930; RI = 0.8704). E. 1. Strict consensus of the 18 most parsimonious topologies (length = 87337; RI = 0.8526; the length of the strict consensus equals to 87347) recovered from the MP analysis (PAUP*) of WS representation of the conventional plastid supermatrix of Iridodictyum s.l. (Iris subgen. Hermodactyloides; Iris sect. Reticulata) + Hermodactylus (I. subgen. Hermodactylus) + Syrianthus (I. subg. Limniris subsect. Syriacae) + Xiphion (I. subg. Xiphion) + Alatavia (Iridodictyum sect. Monolepis) + Chamaeiris (Xyridion; I. sect. Xyridion) (28 terms). All 76118 characters (3TSs) are parsimony-informative, all are weighted uniformly and all are treated as “ordered” (Wagner parsimony). The value of the operational outgroup is fixed as a value of the majority-rule consensus (50%) of the matrix [Gynandriris + Dietes + Tigridia + (Gladiolus + Trillium)]; 2. RF median consensus (RFS) of the same most parsimonious topologies (RF distance score = 0; length = 87337; RI = 0.8526).
(EPS)
Conventional plastid phylogeny (ML). Most probable topology (-ln likelihood = 45051.530110) recovered from a ML analysis (PhyML) of the conventional Iris s.l. & outgroups plastid supermatrix (195 terms, 8464 characters in total). The aLRT support values of 0.9 or higher are indicated above and below the branches. Taxa proposed to be accepted at the generic rank for the first time are indicated in red; taxa potentially recognizable at generic rank are indicated in blue; critical taxa are indicated in green.
(EPS)
Summary of morphological characters and chromosomal counts for the accepted genera.
(EPS)
List of taxa with GenBank-EMBL accession numbers used in the analyses.
(PDF)
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. V. S. Shneer (Komarov Botanical institute RAS, Russia), Dr. M. Chester (University of Cambridge, UK), Dr. A. P. Sukhorukov, Dr. D. D. Sokoloff (M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Russia), Dr. M. A. Gitzendanner (University of Florida, USA), and two anonymous reviewers for various helpful suggestions. We also thank Dr. D. Williams (London Museum of Natural History, UK) and Dr. M. C. Ebach (University of New South Wales and the Sydney’s Australian Museum, AU) for general discussion regarding 3TA, appeared with no relation to the content or conclusions of this ms. We thank Dr. M. A. Gitzendanner and Dr. O. Moskalenko (University of Florida, USA) for assistance with UF Research Computing Center (http://researchcomputing.ufl.edu/). Mr. A. P. Dold (Rhodes University, SA) acknowledged for his final linguist review. We also thank Dr. D. L. Swofford (Duke University, USA) for the executable of 4.0a134 version of PAUP* he kindly shared with us. We thank Dr. D. E. Soltis (University of Florida, USA) and Dr. P. S. Soltis (University of Florida, USA) for various supports.
Disclaimer: No agreements with methodology and conclusions are implied from the behalf of any person acknowledged in this section.
Ms dedicated to the memory of Georgi I. Rodionenko (1913–2014), Sergei A. Nevski (1908–1938), and Sergei S. Ikonnikov (1931–2005).
Funding Statement
The authors have no support or funding to report.
References
- 1.Anderson E (1949) Introgressive hybridization. London, New York: John Wiley and Sons Inc. in association with Chapman and Hall. 109 p.
- 2. Arnold ML, Ballerini ES, Brothers AN (2012) Hybrid fitness, adaptation and evolutionary diversification: lessons learned from Louisiana irises. Heredity 108: 159–166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Nelson G, Platnick NI (1991) Three-taxon statements - a more precise use of parsimony? Cladistics 7: 351–366. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Williams DM, Ebach MC (2008) Foundations of systematics and biogeography. New York, United States: Springer. 306 p.
- 5.Kitching IJ, Forey PL, Humphries CJ, Williams DM (1998) Cladistics. The theory and practice of parsimony analysis. Second edition. Systematics Association Publication 11: i–xiii, 1–228.
- 6.Bruni I, De Mattia F, Martellos S, Galimberti A, Savadori P, et al. (2012) DNA barcoding as an effective tool in improving a digital plant identification system: a case study for the area of mt. Valerio, Trieste (NE Italy). Plos One 7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 7.de Vere N, Rich TCG, Ford CR, Trinder SA, Long C, et al. (2012) DNA barcoding the native flowering plants and conifers of Wales. Plos One 7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 8. Givnish TJ, Pires JC, Graham SW, McPherson MA, Prince LM, et al. (2005) Repeated evolution of net venation and fleshy fruits among monocots in shaded habitats confirms a priori predictions: evidence from an ndhF phylogeny. Proceedings of the Royal Society B-Biological Sciences 272: 1481–1490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Givnish TJ, Ames M, McNeal JR, McKain MR, Steele PR, et al. (2010) Assembling the tree of the Monocotyledons: plastome sequence phylogeny and evolution of Poales. Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden 97: 584–616. [Google Scholar]
- 10. Goldblatt P, Savolainen V, Porteous O, Sostaric I, Powell M, et al. (2002) Radiation in the Cape flora and the phylogeny of peacock irises Moraea (Iridaceae) based on four plastid DNA regions. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 25: 341–360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Goldblatt P, Rodriguez A, Powell MP, Davies TJ, Manning JC, et al. (2008) Iridaceae ‘out of Australasia’? Phylogeny, biogeography, and divergence time based on plastid DNA sequences. Systematic Botany 33: 495–508. [Google Scholar]
- 12. Li D-Z, Gao L-M, Li H-T, Wang H, Ge X-J, et al. (2011) Comparative analysis of a large dataset indicates that internal transcribed spacer (ITS) should be incorporated into the core barcode for seed plants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 108: 19641–19646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Makarevitch I, Golvonina K, Scherbik S, Blinov A (2003) Phylogenetic relationships of the siberian Iris species inferred from noncoding chloroplast DNA sequences. International Journal of Plant Sciences 164: 229–237. [Google Scholar]
- 14. Shaw J, Lickey EB, Beck JT, Farmer SB, Liu WS, et al. (2005) The tortoise and the hare II: Relative utility of 21 noncoding chloroplast DNA sequences for phylogenetic analysis. American Journal of Botany 92: 142–166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Wilson CA (2004) Phylogeny of Iris based on chloroplast matK gene and trnK intron sequence data. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 33: 402–412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Wilson CA (2009) Phylogenetic relationships among the recognized series in Iris section Limniris . Systematic Botany 34: 277–284. [Google Scholar]
- 17. Wilson CA (2011) Subgeneric classification in Iris re-examined using chloroplast sequence data. Taxon 60: 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- 18. Ikinci N, Hall T, Lledo MD, Clarkson JJ, Tillie N, et al. (2011) Molecular phylogenetics of the juno irises, Iris subgenus Scorpiris (Iridaceae), based on six plastid markers. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society 167: 281–300. [Google Scholar]
- 19. Davies TJ, Savolainen V, Chase MW, Moat J, Barraclough TG (2004) Environmental energy and evolutionary rates in flowering plants. Proceedings of the Royal Society B-Biological Sciences 271: 2195–2200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Graham SW, Olmstead RG, Barrett SCH (2002) Rooting phylogenetic trees with distant outgroups: a case study from the commelinoid monocots. Molecular Biology and Evolution 19: 1769–1781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Murdock AG (2008) Phylogeny of marattioid ferns (Marattiaceae): inferring a root in the absence of a closely related outgroup. American Journal of Botany 95: 626–641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Katoh K, Misawa K, Kuma K, Miyata T (2002) MAFFT: a novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Research 30: 3059–3066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Katoh K, Standley DM (2013) MAFFT: multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Molecular Biology and Evolution 30: 772–780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19: 1572–1574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Stamatakis A (2006) RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 22: 2688–2690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Silvestro D, Michalak I (2012) RaxmlGUI: a graphical front-end for RAxML. Organisms Diversity & Evolution 12: 335–337. [Google Scholar]
- 27. Guindon S, Dufayard JF, Lefort V, Anisimova M, Hordijk W, et al. (2010) A new algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Systematic Biology 59: 307–321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Gouy M, Guindon S, Gascuel O (2010) SeaView version 4: a multiplatform graphical user interface for sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree building. Molecular Biology and Evolution 27: 221–224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Anisimova M, Gascuel O (2006) Approximate likelihood-ratio test for branches: a fast, accurate, and powerful alternative. Systematic Biology 55: 539–552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Swofford DL (2002) PAUP*. Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and other methods). Sunderland, Massachusetts: Sinauer Associates.
- 31.Williams DM, Siebert DJ (2000) Characters, homology and three-item analysis. In: Scotland RW, R.T P, editors. Homology and systematics: coding characters for phylogenetic analysis. London, New York: Chapman and Hall. 183–208.
- 32.Mavrodiev EV, Madorsky A (2012) TAXODIUM Version 1.0: a simple way to generate uniform and fractionally weighted three-item matrices from various kinds of biological data. Plos One 7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 33. Mishler BD (1994) Cladistic analysis of molecular and morphological data. American Journal of Physical Anthropology 94: 143–156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bansal MS, Burleigh JG, Eulenstein O, Fernández -Baca D (2010) Robinson-Foulds Supertrees. Algorithms for Molecular Biology 5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 35. Ranwez V, Criscuolo A, Douzery EJP (2010) SuperTriplets: a triplet-based supertree approach to phylogenomics. Bioinformatics 26: i115–i123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Rambaut A (2008) Se-Al v. 2.0a11. Molecular evolution, phylogenetics and epidemiology. Edinburgh, UK: University of Edinburgh, Institute of Evolutionary Biology.
- 37.Maddison WP, Maddison DR (2011) Mesquite: a modular system for evolutionary analysis. Version 2.75.
- 38.Rambaut A (2012) FigTree v. 1.4. Molecular evolution, phylogenetics and epidemiology. Edinburgh, UK: University of Edinburgh, Institute of Evolutionary Biology.
- 39.Linnaeus C (1753) Species Plantarum. Stockholm: Laurentius Salvius.
- 40.Bauhin J, Cherler JH (1651) Historia plantarum universalis: Edobruni: Typographia Caldoriana.
- 41.Dodoens R (1583) Stirpium Historiae Pemptades Sex sive libri XXX. Antuerpiae: Ch. Plantini.
- 42.Tournefort JP (1719) Institutiones rei herbariae. 3, 1 ed. Paris: Typographia Regia.
- 43.Miller P (1754) Gardeners dictionary. London: J. & J. Rivington.
- 44.Miller P (1768) Gardeners dictionary. 8 ed. London: J. & F. Rivington.
- 45.Adanson M (1763) Familles des Plantes. Paris: Vincent.
- 46. Fourreau M (1869) Catalogue des plantes du cours du Rhône (suite). Annales de la Société Linnéenne de Lyon 17: 89–200. [Google Scholar]
- 47. Medikus FC (1790) Ueber den verschiedenen Blüthenbau, vorzüglich in Rücksicht der Blumen. Hist & Commentat Acad Elect Sci Theod-Palat 6: 414–443. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Parlatore F (1860) Flora italiana. Firenze: Le Monnier.
- 49.Reichenbach HGL (1841) Der deutsche Botaniker. Erster Band. Das Herbarienbuch. Dresden and Leipzig: Ch. Arnold.
- 50.Trattinnick L (1817) Auswahl vorzüglich schöner, seltener, berühmter, und sonst sehr merkwürdiger Gartenpflanzen, in getreuen Abbildungen Wien: A. Strauss.
- 51. Crespo MB (2011) Chamaeiris, an earlier name for Xyridion (Iridoideae, Iridaceae). Flora Montiberica 49: 60–71. [Google Scholar]
- 52. Crespo MB (2012) Nomenclatural types of Iberian irises (Iris and related genera, Iridaceae). Flora Montiberica 53: 49–62. [Google Scholar]
- 53. Crespo MB, Alonso M (2012) (2073) Proposal to conserve the name Pseudiris Chukr & A. Gil against Pseudo-iris Medik. (Iridaceae), or to conserve Limniris against Pseudo-iris. Taxon 61: 684–685. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Tillie N, Chase MW, Hall T (2001) Molecular studies in the genus Iris L.: a preliminary study. Annali di Botanica (Roma) 105–112.
- 55.Mavrodiev EV (2010) Is there an alternative treatment of including genus Belamcanda to the genus Iris (Iridaceae)? In: Shmakov AI, editor. Problems of botany of south Siberia and Mongolia, 9. Barnaul.
- 56. Lenz LW (1972) An intergeneric hybrid between Belamcanda chinensis and Pardanthopsis dichotoma equals Iris dichotoma . Aliso 7: 405–407. [Google Scholar]
- 57. Lenz LW (1972) The status of Pardanthopsis (Iridaceae). Aliso 7: 401–403. [Google Scholar]
- 58. Lenz LW (1972) × Pardancanda × norrisii - intergeneric hybrid between Belamcanda chinensis and Pardanthopsis dichotoma (Iris dichotoma). American Horticulturist 51: 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- 59. Schulze W (1971) Systematic position of genus Belamcanda Adans. (Iridaceae).. Feddes Repertorium 81: 519–526. [Google Scholar]
- 60. Rodioneko GI (1999) Alatavia, the new genus of the family Iridaceae. Botanicheskii Zhurnal (St Petersburg) 84: 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- 61. Rodionenko GI (2005) On the independence of the genus Xyridion (Iridaceae). Botanicheskii Zhurnal (St Petersburg) 90: 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Nevskii SA (1937) The flora of the Kuhitang-tau and its foothills. Trudy Botanicheskogo Instituta Akademii Nauk SSSR. Ser. 1. Flora i Sistematika Vyssikh Rastenii: 199–346.
- 63. Mavrodiev EV (2002) Typha tichomirovii and Criptobasis mariae: new species from South-East European Russia and Middle Asia. Byulleten’ Moskovskogo Obshchestva Ispytatelei Prirody Otdel Biologicheskii 107: 77–79. [Google Scholar]
- 64. Ikonnikov SS (1972) Notes on floras of Badakhshan and Pamir. Novosti Sistematiki Vysshikh Rastenii 9: 300–304. [Google Scholar]
- 65. Mavrodiev EV, Alexeev YE (2003) Morphological and biological feautures of the genus Cryptobasis (Iridaceae) in the context of its taxonomy. Botanicheskii Zhurnal (St Petersburg) 88: 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- 66. Rodionenko GI (2006) On the independence of the genus Sclerosiphon (Iridaceae). Botanicheskii Zhurnal (St Petersburg) 91: 1895–1898. [Google Scholar]
- 67. Rodionenko GI (2006) Eremiris – new genus of Iridaceae. Botanicheskii Zhurnal (St Petersburg) 91: 1707–1712. [Google Scholar]
- 68.Rodionenko GI (1987) The genus Iris L. (questions of morphology, biology, evolution and systematics). London: British Iris Society 222 p. (first Russian edition published in 1961).
- 69. Rodionenko GI (1994) Genus Juno (Iridaceae). Botanicheskii Zhurnal (St Petersburg) 79: 100–108. [Google Scholar]
- 70. Rodionenko GI (2007) On the independence of genus Limniris (Iridaceae). Botanicheskii Zhurnal (St Petersburg) 92: 547–554. [Google Scholar]
- 71. Rodionenko GI (2008) On systematics and phylogeny of “beardless irises” (Iridaceae). Botanicheskii Zhurnal 93: 321–329. [Google Scholar]
- 72. Schulze W (1964) Contributions to the taxonomic application of the pollen morphology. I. The genus Iris L. Grana 5: 40–79. [Google Scholar]
- 73. Schulze W (1965) Siphonostylis: a new genus of the Iridaceae. Oesterreichische Botanische Zeitschrift 112: 331–343. [Google Scholar]
- 74. Martinez Rodriguez J, Crespo MB (2013) Xiphion heracleanum sp. nov. (Iridaceae) from Morocco. Nordic Journal of Botany 31: 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- 75. Shneer VS (1990) Serotaxonomic study of the genus Iris s.l. (Iridaceae). Botanicheskii Zhurnal (St Petersburg) 75: 804–810. [Google Scholar]
- 76. Antonov AS, Valiejoroman KM, Pimenov MG, Beridze NA (1988) Non-equivalency of genera in Angiospermae - evidence from DNA hybridization studies. Plant Systematics and Evolution 161: 155–168. [Google Scholar]
- 77. Shneer VS, Antonov AS (1975) Homologies in DNA of species of genus Iris L. Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR. 222: 247–250. [Google Scholar]
- 78. Shneer VS (1999) Serotaxonomic study of the genus Iris s.str. (Iridaceae). Botanicheskii Zhurnal (St Petersburg) 84: 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- 79. Schulze W (1969) Junopsis, eine neue Gattung der Iridaceae. Oesterreichische Botanische Zeitschrift 117: 327–331. [Google Scholar]
- 80.Mathew B (1989) The Iris. Portland: Timber Press.
- 81. Rodionenko GI (2004) Ophioiris, a new genus of the family Iridaceae. Botanicheskii Zhurnal (St Petersburg) 89: 1359–1361. [Google Scholar]
- 82. Guo J, Wilson CA (2013) Molecular phylogeny of Crested Iris based on five plastid markers (Iridaceae). Systematic Botany 38: 987–995. [Google Scholar]
- 83. de Queiroz K, Donoghue JM (1990) Phylogenetic systematics or Nelson’s version of cladistics? Cladistics 6: 61–75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Williams DM, Ebach MC (2004) The reform of palaeontology and the rise of biogeography - 25 years after ‘ontogeny, phylogeny, paleontology and the biogenetic law’ (Nelson, 1978). Journal of Biogeography 31: 685–712. [Google Scholar]
- 85.SGBIS (1997) A guide to species irises: their identification and cultivation Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- 86. Goldblatt P (1981) Systematics, phylogeny and evolution of Dietes (Iridaceae). Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden 68: 132–153. [Google Scholar]
- 87. Martínez-Azorín M, Crespo MB, Juan A, Fay MF (2011) Molecular phylogenetics of subfamily Ornithogaloideae (Hyacinthaceae) based on nuclear and plastid DNA regions, including a new taxonomic arrangement. Annals of Botany 107: 1–37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88. Mavrodiev EV (2001) Rohrbachia, a new genus of the Typhaceae. Botanicheskii Zhurnal (St Petersburg) 86: 120–124. [Google Scholar]
- 89. Mavrodiev EV, Soltis PS, Soltis DE (2010) Plastid sequence data suggest that the genus Rohrbachia (Typhaceae) is sister to Typha s.str. (Typhaceae). Byulleten’ Moskovskogo Obshchestva Ispytatelei Prirody Otdel Biologicheskii 115: 72–74. [Google Scholar]
- 90. Fuentes-Bazan S, Uotila P, Borsch T (2012) A novel phylogeny-based generic classification for Chenopodium sensu lato, and a tribal rearrangement of Chenopodioideae (Chenopodiaceae). Willdenowia 42: 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- 91. Grace OM, Klopper RR, Smith GF, Crouch NR, Figueiredo E, et al. (2013) A revised generic classification for Aloe (Xanthorrhoeaceae subfam. Asphodeloideae). Phytotaxa 76: 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- 92. Heenan PB, Smissen RD (2013) Revised circumscription of Nothofagus and recognition of the segregate genera Fuscospora, Lophozonia, and Trisyngyne (Nothofagaceae). Phytotaxa 146: 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- 93. Mansion G (2004) A new classification of the polyphyletic genus Centaurium Hill (Chironiinae, Gentianaceae): description of the New World endemic Zeltnera, and reinstatement of Gyrandra Griseb. and Schenkia Griseb. Taxon 53: 719–740. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Conventional plastid phylogeny (MP). Strict consensus of 160 most parsimonious topologies (length = 5268, CI = 0.6137, RI = 0.8365) recovered from a MP analysis (PAUP*) of conventional of Iris s.l. & outgroups plastid supermatrix (195 terms, 8464 characters in total, 1559 are parsimony-informative). All characters were treated as “unordered” (Fitch parsimony). MP JK values for nodes with greater than 80% support are indicated above or below the branches.
(EPS)
Conventional plastid phylogenies (reduced supermatrix). A. Strict consensus of 24 most parsimonious topologies (length = 3512, CI = 0.6723, RI = 0.7695) recovered from a MP analysis (PAUP*) of conventional of Iris s.l. & outgroups plastid supermatrix (80 terms, 8237 characters in total, 1045 characters are parsimony-informative). All characters were treated as “unordered” (Fitch parsimony). MP JK values for nodes with greater than 80% support are indicated above or below the branches. B. Most probable topology (−ln likelihood = 33243.302540) recovered from a ML analysis (RAxML) of conventional Iris s.l. & outgroups plastid supermatrix (80 terms, 8237 characters). ML BS values for nodes receiving >80% supports are indicated above and below the branches. Taxa proposed to be accepted at the generic rank for the first time are indicated in red; taxa potentially recognizable at generic rank are indicated in blue; critical taxa are indicated in green.
(EPS)
Nested most parsimonious hierarchy of patterns (reduced supermatrix). Single most parsimonious topology (length = 2558783; RI = 0.7858) recovered from the MP analysis (PAUP*) of WS representation of conventional Iris s.l. & outgroups plastid supermatrix (81 terms, 80 taxa (79 taxa of Iris s.l. + outgroup ( = majority-rule consensus (50%) of the matrix [Gynandriris + Dietes + Tigridia + (Gladiolus + Trillium)]) + operational outgroup). All 2 023 963 binary characters (3TSs) are parsimony-informative, all weighted uniformly and all treated as “ordered” (Wagner parsimony). The value of operational outgroup fixed as a value of majority-rule consensus (50%) of the matrix [Gynandriris + Dietes + Tigridia + (Gladiolus + Trillium)].
(EPS)
Conventional plastid phylogeny (BI). Consensus topology recovered from a Bayesian analysis (MrBayes) of conventional Iris s.l. & outgroups plastid supermatrix (195 terms, 8464 characters in total). The first 3000 trees were discarded as burn-in, and posterior probabilities were calculated from the majority-rule consensus of the remaining trees sampled in both runs. At the end of the runs, the standard deviation of split frequencies between the two runs had fallen to 0.0070. Numbers above and below the branches indicate posterior probabilities >0.95. Taxa, proposed to be accepted at the generic rank for the first time are indicated in red; taxa potentially recognizable at generic rank are indicated in blue; critical taxa are indicated in green.
(EPS)
Nested most parsimonious hierarchies of patterns. A. 1. Strict consensus of the four most parsimonious topologies (length = 700315; RI = 0.8943; the length of the strict consensus equals to 700319) recovered from the MP analysis (PAUP*) of the WS representation of conventional plastid supermatrix Juno (57 terms). All 633358 binary characters (3TSs) are parsimony-informative, all are weighted uniformly and all are treated as “ordered” (Wagner parsimony). The value of the operational outgroup is fixed as a value of the majority-rule consensus (50%) of the matrix [Gynandriris + Dietes + Tigridia + (Gladiolus + Trillium)]; 2. RF median consensus (RFS) of the same most parsimonious topologies (RF distance score = 46; length = 700315; RI = 0.8943). B. Single most parsimonious topology (length = 1279; RI = 0.9412) recovered from the MP analysis (PAUP*) of WS representation of the conventional, plastid supermatrix of Evansia (10 terms). All 1208 binary characters (3TSs) are parsimony-informative, all are weighted uniformly and all are treated as “ordered” (Wagner parsimony). Based on the patterns of the relationships recovered from a MP analysis of the 81 terms 3TA matrix (Figure S3), the value of the operational outgroup is fixed as a value of the majority-rule consensus of the matrix [Iris japonica 1, 2 + I. wattii]. C. 1. Strict consensus of the 90 most parsimonious topologies (length = 72792; RI = 0.9363; the length of the strict consensus equal to 72884) recovered from the MP analysis of WS representation of conventional plastid supermatrix of the core Iris (37 terms). All 68435 characters (3TSs) are parsimony-informative, all are weighted uniformly and all are treated as “ordered” (Wagner parsimony). Based on the patterns of the relationships recovered from a MP analysis of the 81 term 3TA matrix (Figure S3), the value of the operational outgroup is fixed as a value of the majority-rule consensus of the matrix [Belamcanda (I. domestica) + Pardanthopsis (I. dichotoma) + Gattenhofia (I. verna)]; 2. RF median consensus (RFS) of the same most parsimonious topologies (RF distance score = 824; length = 72792; RI = 0.9363). D. 1. Strict consensus of the two most parsimonious topologies (length = 364930; RI = 0.8704; the length of the strict consensus equal to 364936) recovered from the MP analysis (PAUP*) of WS representation of conventional plastid supermatrix of Limniris s.l. + Phaeiris nom. provis. (L. subgen. Hexagonae, I. subgen. Phaeiris) + Eremiris (I. subgen. Eremiris) + Joniris (L. subgen. Ioniris; sect. Ioniris) + Sclerosiphon (I. songarica) (41 terms). All 323073 characters (3TSs) are parsimony-informative, all are weighted uniformly and all are treated as “ordered” (Wagner parsimony). The value of the operational outgroup is fixed as a value of the majority-rule consensus (50%) of the matrix [Gynandriris + Dietes + Tigridia + (Gladiolus + Trillium)]; 2. RF median consensus (RFS) of the same most parsimonious topologies (RF distance score = 7; length = 364930; RI = 0.8704). E. 1. Strict consensus of the 18 most parsimonious topologies (length = 87337; RI = 0.8526; the length of the strict consensus equals to 87347) recovered from the MP analysis (PAUP*) of WS representation of the conventional plastid supermatrix of Iridodictyum s.l. (Iris subgen. Hermodactyloides; Iris sect. Reticulata) + Hermodactylus (I. subgen. Hermodactylus) + Syrianthus (I. subg. Limniris subsect. Syriacae) + Xiphion (I. subg. Xiphion) + Alatavia (Iridodictyum sect. Monolepis) + Chamaeiris (Xyridion; I. sect. Xyridion) (28 terms). All 76118 characters (3TSs) are parsimony-informative, all are weighted uniformly and all are treated as “ordered” (Wagner parsimony). The value of the operational outgroup is fixed as a value of the majority-rule consensus (50%) of the matrix [Gynandriris + Dietes + Tigridia + (Gladiolus + Trillium)]; 2. RF median consensus (RFS) of the same most parsimonious topologies (RF distance score = 0; length = 87337; RI = 0.8526).
(EPS)
Conventional plastid phylogeny (ML). Most probable topology (-ln likelihood = 45051.530110) recovered from a ML analysis (PhyML) of the conventional Iris s.l. & outgroups plastid supermatrix (195 terms, 8464 characters in total). The aLRT support values of 0.9 or higher are indicated above and below the branches. Taxa proposed to be accepted at the generic rank for the first time are indicated in red; taxa potentially recognizable at generic rank are indicated in blue; critical taxa are indicated in green.
(EPS)
Summary of morphological characters and chromosomal counts for the accepted genera.
(EPS)
List of taxa with GenBank-EMBL accession numbers used in the analyses.
(PDF)