Abstract
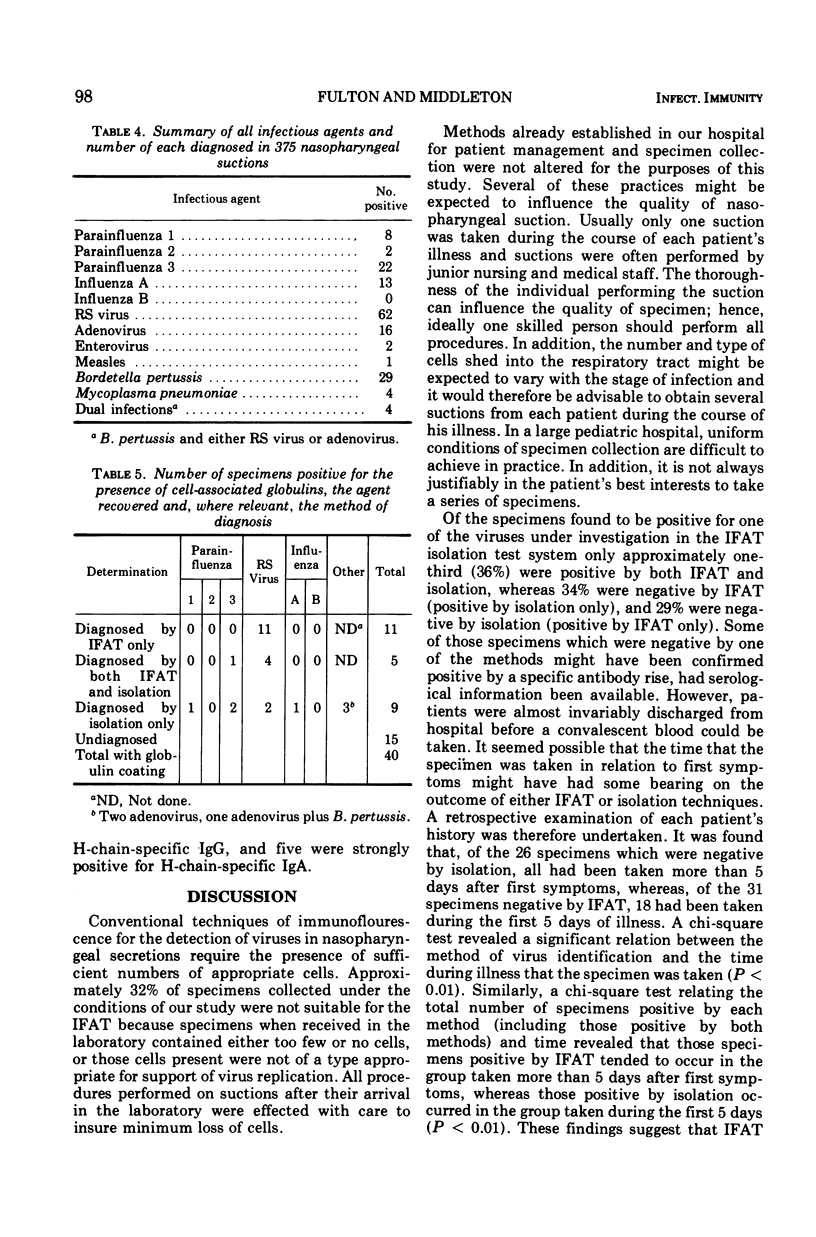
The immunoflourescent antibody technique (IFAT) and cell culture isolation procedures were compared for their efficiency in the etiological diagnosis of viral respiratory illness in children. Before the IFAT was incorporated as a routine procedure, antisera used in the test were carefully calibrated to insure specificity. A study was then conducted in which 375 nasopharyngeal suctions were investigated by both IFAT and isolation for the presence of parainfluenza virus types 1, 2, and 3, respiratory syncytial, influenza A, and influenza B viruses. Methods already established in our hospital for patient management and specimen collection were not altered for the purposes of the study. The IFAT, as conventionally practiced in the detection of respiratory virus antigens, requires adequate numbers of ciliated epithelial cells. There were 68.5% specimens which contained cells suitable for IFAT, whereas 31.5% had either an insufficient number or inappropriate types of cells and could be used only for virus isolation. Cell-associated immunoglobulins were detected in 16% of those specimens with adequate cells. When all specimens were considered regardless of their cell population, IFAT was inferior to isolation in diagnostic efficiency. However, isolation complemented by IFAT resulted in a statistically significant increase in number of positive virus identifications. Under routine working conditions in a large pediatric hospital, it was found that IFAT could not replace isolation techniques but could, if used in conjunction with isolation, provide a significant overall increase in number of positive diagnoses. The time that the specimen was taken in relation to first symptoms was found to be an important variable with respect to the method most likely to succeed in virus identification.
Full text
PDF

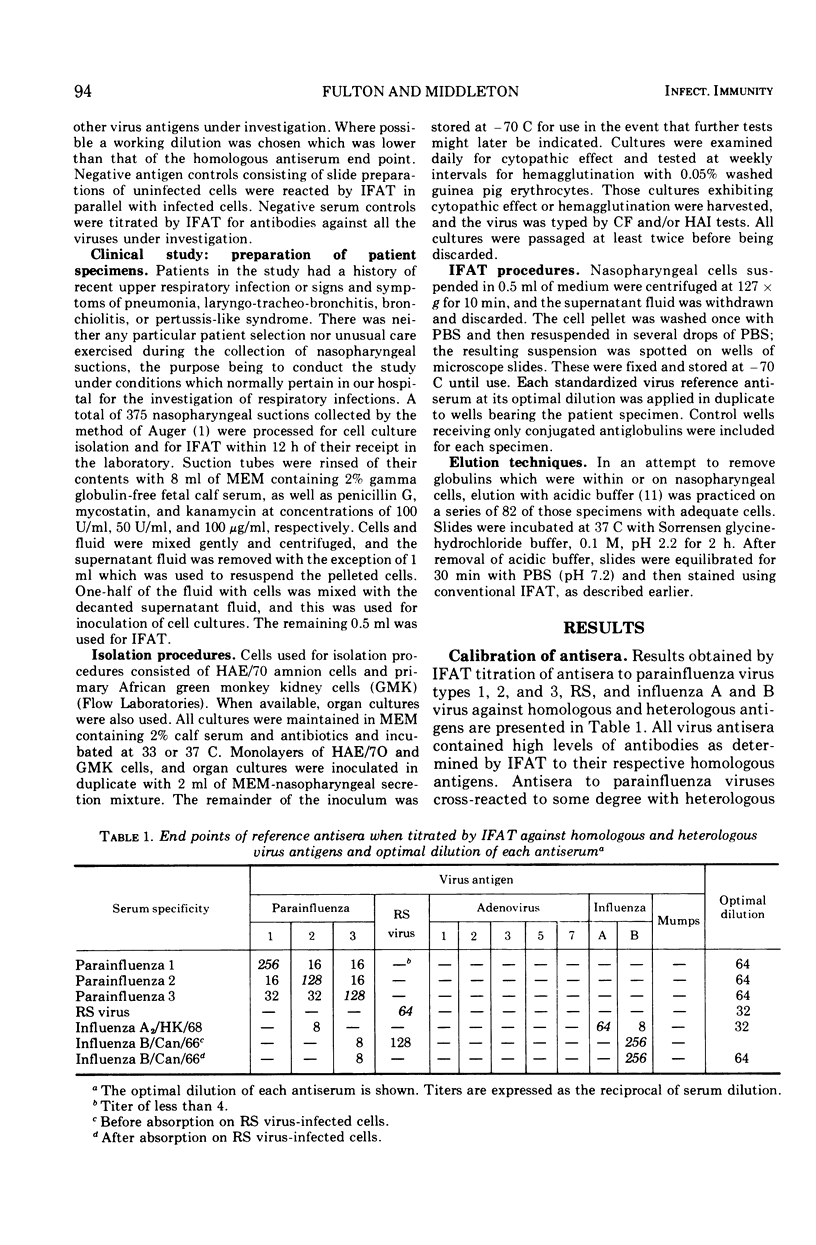

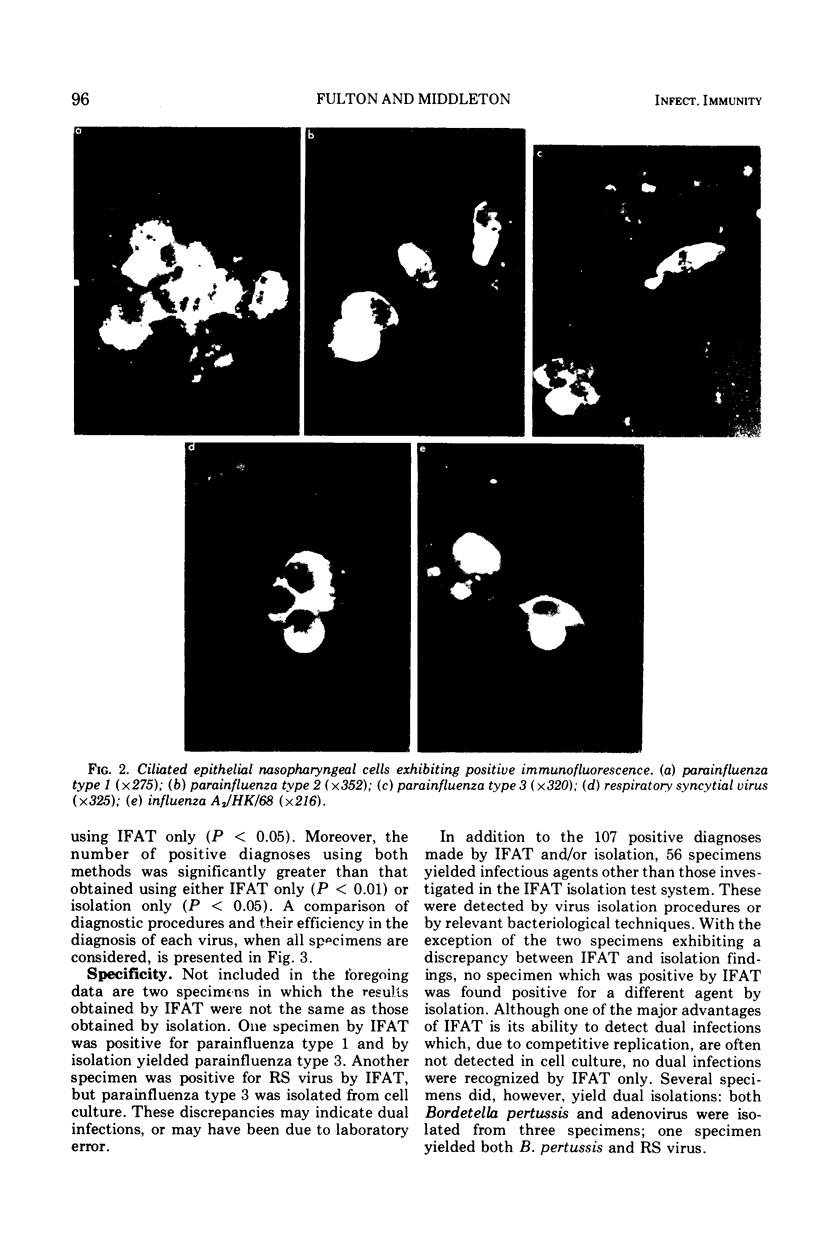
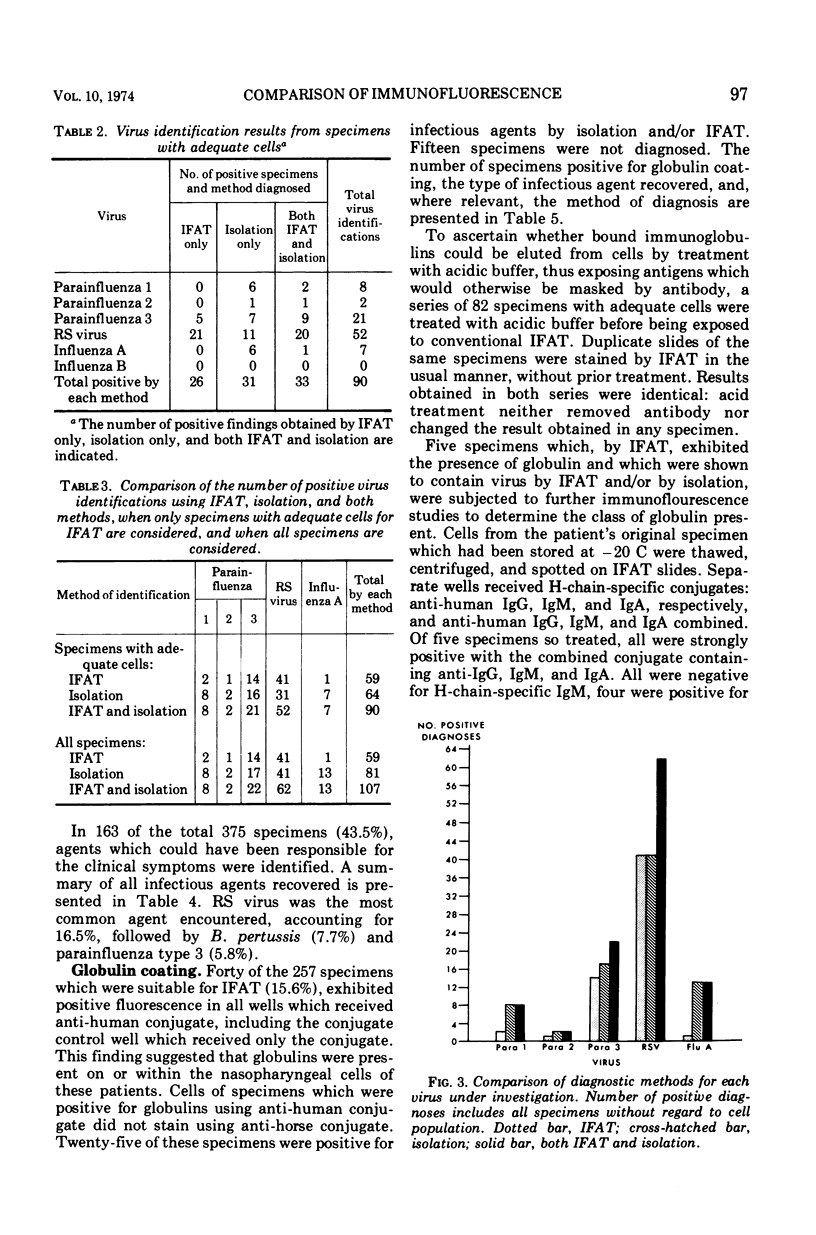



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BELLANTI J. A., ARTENSTEIN M. S., BUESCHER E. L. CHARACTERIZATION OF VIRUS NEUTRALIZING ANTIBODIES IN HUMAN SERUM AND NASAL SECRETIONS. J Immunol. 1965 Mar;94:344–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brocklebank J. T., Court S. D., McQuillin J., Gardner P. S. Influenza-A infection in children. Lancet. 1972 Sep 9;2(7776):497–500. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91902-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cate T. R., Rossen R. D., Douglas R. G., Jr, Butler W. T., Couch R. B. The role of nasal secretion and serum antibody in the rhinovirus common cold. Am J Epidemiol. 1966 Sep;84(2):352–363. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cradock-Watson J. E., McQuillin J., Gardner P. S. Rapid diagnosis of respiratory syncytial virus infection in children by the immunofluorescent technique. J Clin Pathol. 1971 May;24(4):308–312. doi: 10.1136/jcp.24.4.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cradock-Watson J. E., Ridehalgh M. K., Bourne M. S., Vandervelde E. M. Nasal immunoglobulin responses in acute rubella determined by the immunofluorescent technique. J Hyg (Lond) 1973 Sep;71(3):603–617. doi: 10.1017/s002217240004660x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas R. G., Jr, Rossen R. D., Butler W. T., Couch R. B. Rhinovirus neutralizing antibody in tears, parotid saliva, nasal secretions and serum. J Immunol. 1967 Aug;99(2):297–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEDOVA D., ZELENKOVA L. THE USE OF THE FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY METHOD FOR THE RAPID IDENTIFICATION OF THE A2 INFLUENZA VIRUS. II. THE IDENTIFICATION OF INFLUENZA VIRUS IN NASAL SMEARS BY THE FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY TECHNIQUE. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1965;9:135–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEDMAN P., PETERS J. H., KARK R. M. Localization of gamma-globulin in the diseased kidney. Arch Intern Med. 1960 Apr;105:524–535. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1960.00270160022005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner P. S., McQuillin J. Application of immunofluorescent antibody technique in rapid diagnosis of respiratory syncytial virus infection. Br Med J. 1968 Aug 10;3(5614):340–343. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5614.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner P. S., McQuillin J., McGuckin R., Ditchburn R. K. Observations on clinical and immunofluorescent diagnosis of parainfluenza virus infections. Br Med J. 1971 Apr 3;2(5752):7–12. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5752.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner P. S., McQuillin J., McGuckin R. The late detection of respiratory syncytial virus in cells of respiratory tract by immunofluorescence. J Hyg (Lond) 1970 Dec;68(4):575–580. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400042509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray K. G., MacFarlane D. E., Sommerville R. G. Direct immunofluorescent identification of respiratory syncytial virus in throat swabs from children with respiratory illness. Lancet. 1968 Mar 2;1(7540):446–448. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92779-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hers J. F., van der Kuip L., Masurel N. Rapid diagnosis of influenza. Lancet. 1968 Mar 9;1(7541):510–511. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91470-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. W., Bellanti J. A., Arrobio J. O., Mills J., Brandt C. D., Chanock R. M., Parrott R. H. Respiratory syncytial virus neutralizing activity in nasal secretions following natural infection. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jun;131(2):658–661. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU C. Rapid diagnosis of human influenza infection from nasal smears by means of fluorescein-labeled antibody. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Aug-Sep;92(4):883–887. doi: 10.3181/00379727-92-22642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQuillin J., Gardner P. S., McGuckin R. Rapid diagnosis of influenza by immunofluorescent techniques. Lancet. 1970 Oct 3;2(7675):690–695. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91961-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQuillin J., Gardner P. S., Sturdy P. M. The use of cough-nasal swabs in the rapid diagnosis of respiratory syncytial virus infection by the fluorescent antibody technique. J Hyg (Lond) 1970 Jun;68(2):283–292. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400028746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REMINGTON J. S., VOSTI K. L., LIETZE A., ZIMMERMAN A. L. SERUM PROTEINS AND ANTIBODY ACTIVITY IN HUMAN NASAL SECRETIONS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Aug;43:1613–1624. doi: 10.1172/JCI105037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODRIGUEZ J., DEINHARDT F. Preparation of a semipermanent mounting medium for fluorescent antibody studies. Virology. 1960 Oct;12:316–317. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossen R. D., Douglas G., Jr, Cate T. R., Couch R. B., Butler W. T. The sedimentation behavior of rhinovirus neutralizing activity in nasal secretion and serum following the rhinovirus common cold. J Immunol. 1966 Oct;97(4):532–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossen R. D., Schade A. L., Butler W. T., Kasel J. A. The proteins in nasal secretion: a longitudinal study of the gammaA-globulin, gammaG-globulin, albumin, siderophilin, and total protein concentrations in nasal washings from adult male volunteers. J Clin Invest. 1966 May;45(5):768–776. doi: 10.1172/JCI105391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R., Gardner P. S. Respiratory syncytial virus neutralizing activity in nasopharyngeal secretions. J Hyg (Lond) 1970 Dec;68(4):581–588. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400042510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. B., Bellanti J. A., Chanock R. M. Immunoglobulins in serum and nasal secretions following infection with type 1 parainfluenza virus and injection of inactivated vaccines. J Immunol. 1967 Jul;99(1):133–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturdy P. M., McQuillin J., Gardner P. S. A comparative study of methods for the diagnosis of respiratory virus infections in childhood. J Hyg (Lond) 1969 Dec;67(4):659–670. doi: 10.1017/s002217240004211x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateno I., Kitamoto O., Kawamura A., Jr Diverse immunocytologic findings of nasal smears in influenza. N Engl J Med. 1966 Feb 3;274(5):237–242. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196602032740502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson D., Stanford C. F., Connolly J. H. Fluorescent-antibody diagnosis of influenza-A infection. Lancet. 1972 Oct 14;2(7781):826–826. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92189-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremonti L. P., Lin J. S., Jackson G. G. Neutralizing activity in nasal secretions and serum in resistance of volunteers to parainfluenza virus type 2. J Immunol. 1968 Sep;101(3):572–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urquhart G. E., Walker G. H. Immunofluorescence for routine diagnosis of respiratory syncytial virus infection. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Oct;25(10):843–845. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.10.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman R. H., Mann J. J., Kasel J. A. Influenza virus neutralizing antibody in human respiratory secretions. J Immunol. 1968 Jan;100(1):80–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman R. H., Wigley FM Small P. A., Jr Specificity of respiratory secretion antibody against influenza virus. J Immunol. 1970 Dec;105(6):1477–1483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]