Abstract
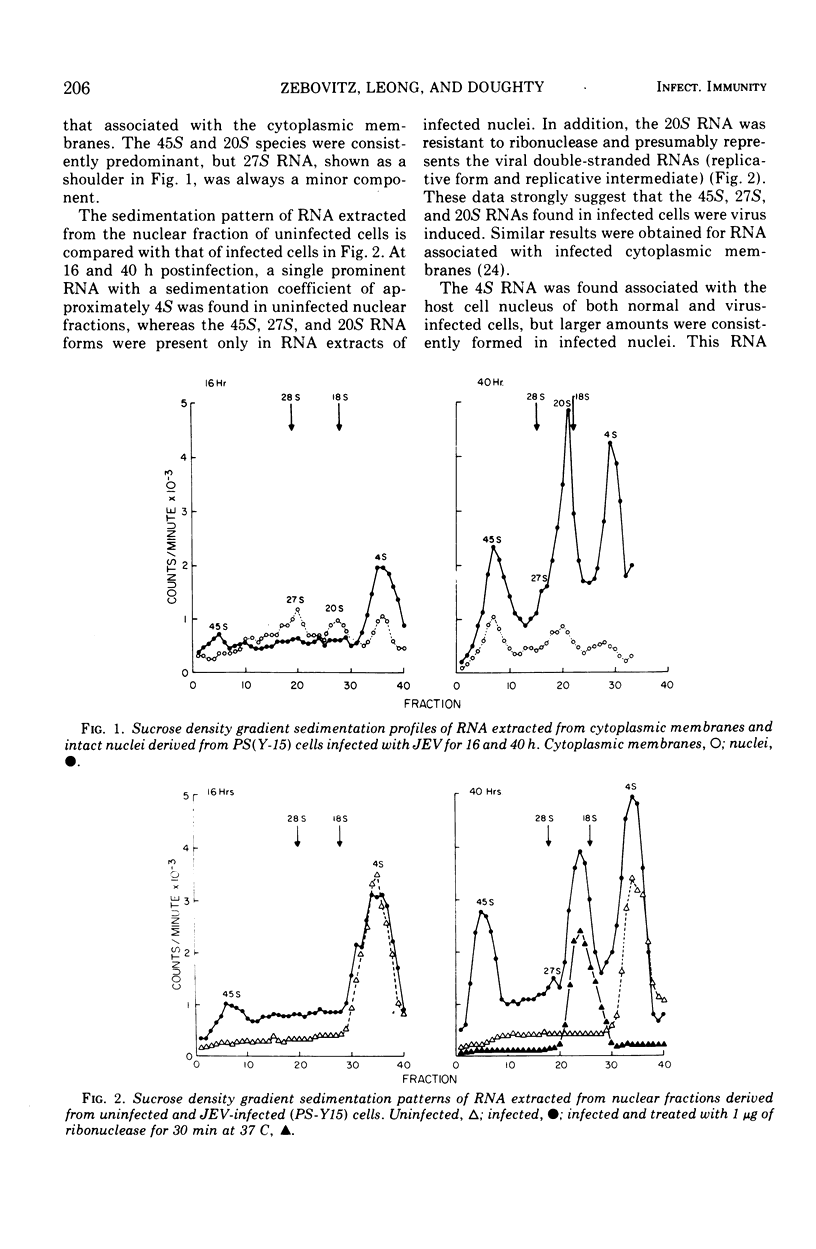
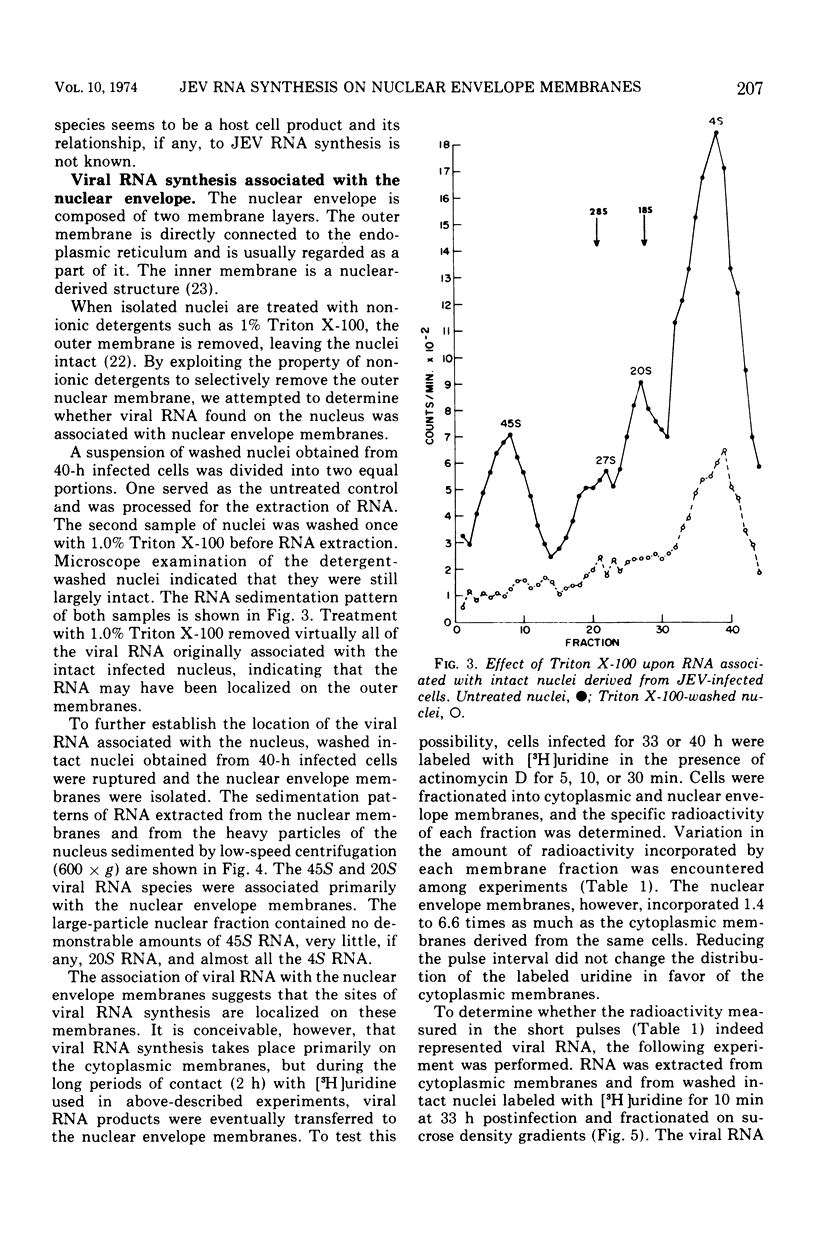
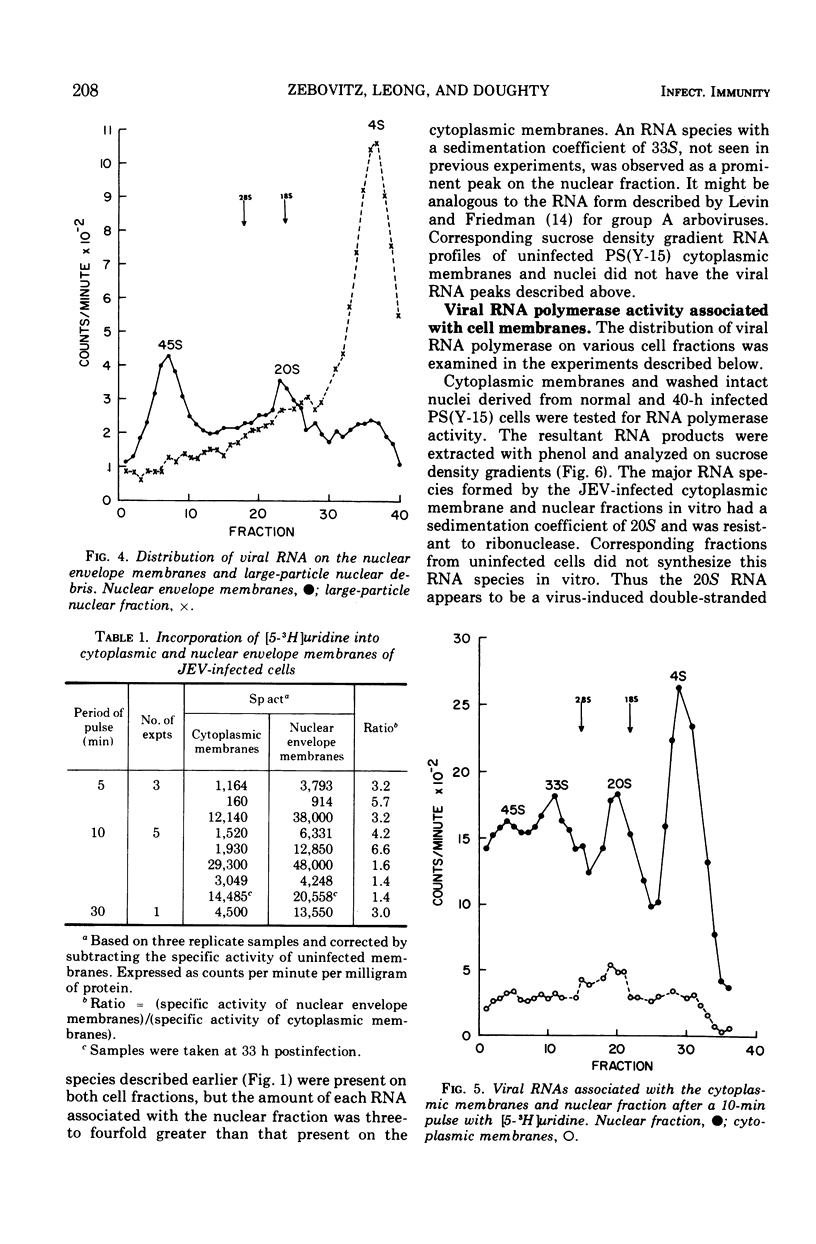
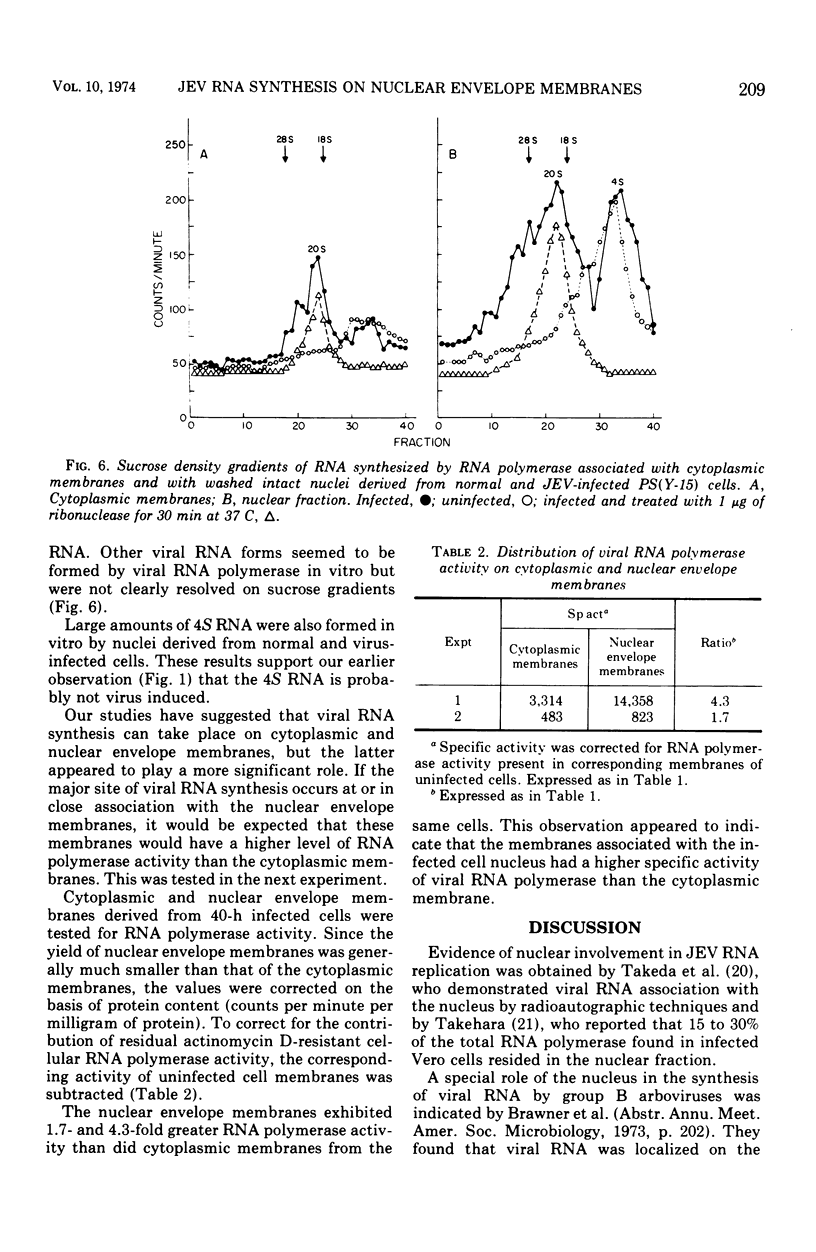
The distribution of viral ribonucleic acid (RNA) on various cell membrane fractions derived from a porcine kidney cell line infected with Japanese encephalitis virus was investigated. At 40 h postinfection, after virus growth had reached its peak, three viral RNAs, 45S, 27S, and 20S, were associated with the cytoplasmic membranes and intact nuclei. The amount of each RNA associated with the nucleus was two- to fivefold greater than that present with the cytoplasmic membranes. Treatment of washed infected nuclei with 1.0% Triton X-100, which removed the outer nuclear envelope membrane, also removed the viral RNA. When the nucleus was fractionated into nuclear envelope membranes and a large particle fraction which sedimented at 600 × g, nearly all of the viral RNA remained associated with the envelope membranes. The nuclear envelope membranes contained higher viral RNA polymerase activity than the cytoplasmic membranes derived from the same cells. These data suggest that major sites for Japanese encephalitis virus RNA synthesis may be localized on or in very close association with the nuclear envelope membranes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amako K., Dales S. Cytopathology of Mengovirus infection. II. Proliferation of membranous cisternae. Virology. 1967 Jun;32(2):201–215. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90270-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALTIMORE D., EGGERS H. J., FRANKLIN R. M., TAMM I. Poliovirus-induced RNA polymerase and the effects of virus-specific inhibitors on its production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jun;49:843–849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.6.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELLETT A. J., HARRIS R. G., SANDERS F. K. SITES OF SYNTHESIS OF ENCEPHALOMYOCARDITIS VIRUS COMPONENTS IN INFECTED L-CELLS. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Mar;38:299–307. doi: 10.1099/00221287-38-3-299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Tamm I. Membranous structures associated with translation and transcription of poliovirus RNA. Science. 1969 Nov 14;166(3907):885–886. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3907.885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Tamm I. The role of cytoplasmic membranes in poliovirus biosynthesis. Virology. 1970 Sep;42(1):100–111. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Levin J. G., Grimley P. M., Berezesky I. K. Membrane-associated replication complex in arbovirus infection. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):504–515. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.504-515.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINZBURG-TIETZ Y., KAUFMANN E., TRAUB A. STUDIES ON NUCLEAR RIBOSOMES. II. TRANSFER OF RIBOSOMES FROM NUCLEUS TO CYTOPLASM IN THE EARLY STAGES OF VIRAL INFECTION. Exp Cell Res. 1964 Apr;34:384–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(64)90373-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimley P. M., Berezesky I. K., Friedman R. M. Cytoplasmic structures associated with an arbovirus infection: loci of viral ribonucleic acid synthesis. J Virol. 1968 Nov;2(11):1326–1338. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.11.1326-1338.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimley P. M., Levin J. G., Berezesky I. K., Friedman R. M. Specific membranous structures associated with the replication of group A arboviruses. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):492–503. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.492-503.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS H. BREAKDOWN OF NUCLEAR RIBONUCLEIC ACID IN THE PRESENCE OF ACTINOMYCIN D. Nature. 1964 Jun 27;202:1301–1303. doi: 10.1038/2021301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRAI T., HIRAI A. TOBACCO MOSAIC VIRUS: CYTOLOGICAL EVIDENCE OF THE SYNTHESIS IN THE NUCLEUS. Science. 1964 Aug 7;145(3632):589–591. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3632.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue Y. K., Yamada M. A. Clonal line of porcine kidney stable cells for assay of Japanese encephalitis virus. J Bacteriol. 1964 May;87(5):1239–1240. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.5.1239-1240.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krug R. M. Cytoplasmic and nucleoplasmic viral RNPs in influenza virus-infected MDCK cells. Virology. 1972 Oct;50(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90350-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. G., Friedman R. M. Analysis of arbovirus ribonucleic acid forms by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1971 Apr;7(4):504–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.4.504-514.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN E. M., WORK T. S. Studies on protein and nucleic acid metabolism in virus-infected mammalian cells. IV. The localization of metabolic changes within subcellular fractions of Krebs II mouse-ascites-tumour cells infected with encephalomyocarditis virus. Biochem J. 1961 Dec;81:514–520. doi: 10.1042/bj0810514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A. The morphogenesis of poliovirus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1972;58:157–174. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65357-5_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G., Swim H. E. Replication of mengovirus. I. Effect on synthesis of macromolecules by host cell. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2317–2326. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2317-2326.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalla T. A., Amici A. The distribution of viral antigen in cells infected with tobacco mosaic virus as revealed by electron microscopy. Virology. 1967 Jan;31(1):78–91. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEDA H., YAMADA M. A., AOYAMA Y. DEMONSTRATION OF RNA SYNTHESIS CAUSED BY JAPANESE ENCEPHALITIS VIRUS INFECTION IN PS(Y-15) CELLS WITH THE AID OF CHROMOMYCIN A-3. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1965 Apr;18:111–120. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.18.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takehara M. Comparative studies on nucleic acid synthesis and virus-induced RNA polymerase activity in mammalian cells infected with certain arboviruses. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1971;34(4):266–277. doi: 10.1007/BF01242972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R., Hamilton M. J., Cole R. D. Membrane phospholipids associated with nuclei and chromatin: melting profile, template activity and stability of chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 20;67(2):231–246. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90238-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zebovitz E., Leong J. K., Doughty S. C. Japanese encephalitis virus replication: a procedure for the selective isolation and characterization of viral RNA species. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972;38(4):319–327. doi: 10.1007/BF01262822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



