Abstract
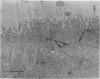
An electron microscope study of infected human louse gut cells and feces was made to determine whether a valid correlation exists between the increased resistance of Rickettsia prowazeki (in the louse feces) to adverse environmental influences and changes in the organism which might be reflected in its ultrastructure. Upon fine structural examination of this intracellular parasite as it passed from the louse midgut cell to the feces, it was apparent that no such morphological changes had occurred.
Full text
PDF

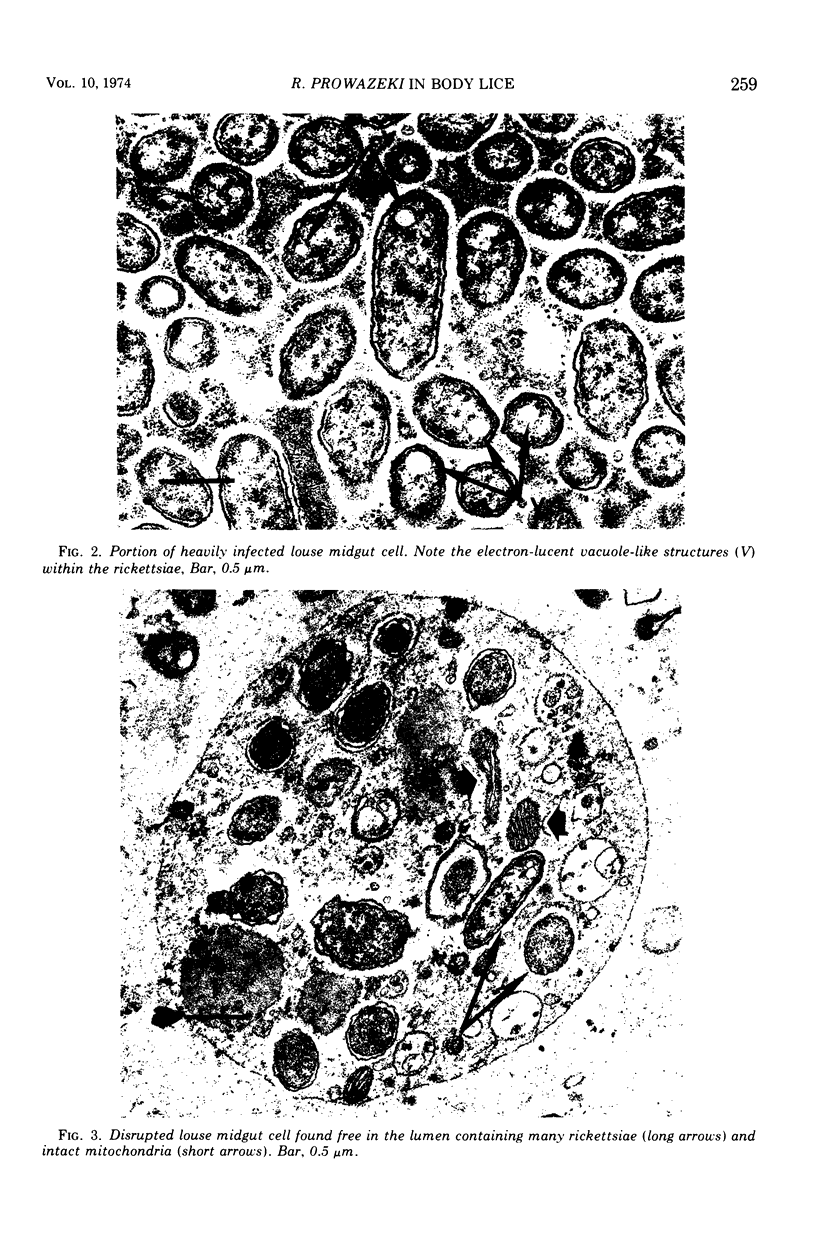
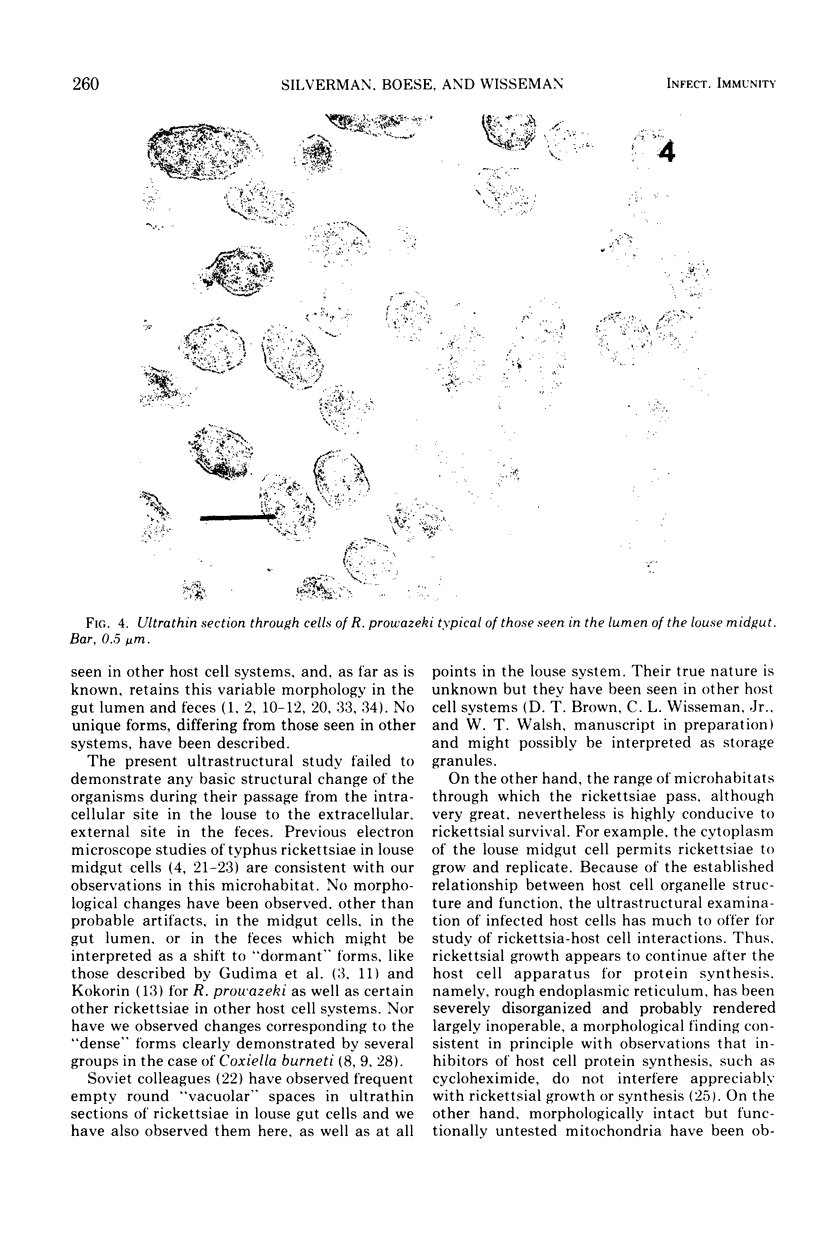
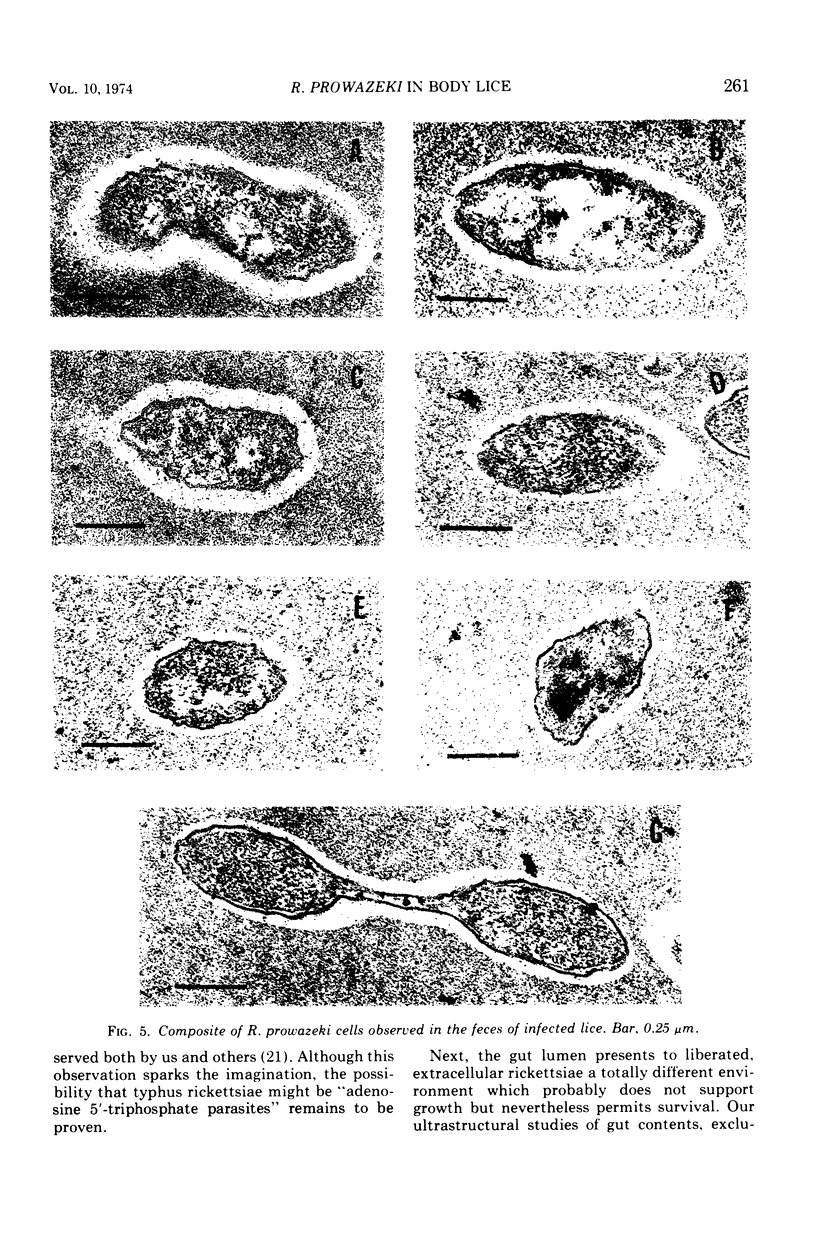


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anacker R. L., Pickens E. G., Lackman D. B. Details of the ultrastructure of Rickettsia prowazekii grown in the chick yolk sac. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):260–262. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.260-262.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. R., Hopps H. E., Barile M. F., Bernheim B. C. Comparison of the ultrastructure of several rickettsiae, ornithosis virus, and Mycoplasma in tissue culture. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1387–1404. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1387-1404.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avakian A. A., Gudima O. S., Alimov Zh A. Elektronnomikroskopicheskoe izuchenie Rickettsia canada v kletkakh kul'tur tkanei. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1973 Mar;50(3):3–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALAEVA N. M. Biologicheskie svoistva rikketsii Muzera pri dlitel'nom kul'tivirovanii ikh v kishechnike platianykh vshei. III. Morfologiia rikketskii Muzera i Provacheka pri issledovanii v elektronnom mikroskope. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1958 Jul;29(7):132–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOVARNICK M. R., MILLER J. C., SNYDER J. C. The influence of certain salts, amino acids, sugars, and proteins on the stability of rickettsiae. J Bacteriol. 1950 Apr;59(4):509–522. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.4.509-522.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boese J. L., Wisseman C. L., Jr, Walsh W. T., Fiset P. Antibody and antibiotic action on Rickettsia prowazeki in body lice across the host-vector interface, with observations on strain virulence and retrieval mechanisms. Am J Epidemiol. 1973 Oct;98(4):262–282. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canonico P. G., Van Zwieten M. J., Christmas W. A. Purification of large quantities of coxiella burnetii rickettsia by density gradient zonal centrifugation. Appl Microbiol. 1972 May;23(5):1015–1022. doi: 10.1128/am.23.5.1015-1022.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crăcea E., Voiculescu R., Zarnea G., Ionescu M., Botez D. Electron microscopic study of phase I and II C. burneti in the chick yolk sac by use of ferritin conjugated antibody. Z Immunitatsforsch Allerg Klin Immunol. 1970 Oct;140(4):358–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin C. S., Tyrrell D. A., Head B., Rees R. J. Inhibition of haemaggregation by lepromin and other mycobacterial substances. Nature. 1967 Dec 9;216(5119):1019–1020. doi: 10.1038/2161019a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudima O. S. Osobennosti strukturnoi organizatsii rikketsii. Vestn Akad Med Nauk SSSR. 1969;24(10):35–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulevskaya S. A., Ignatovich V. F. New electron microscopic data on structural formations in the cytoplasm of rickettsia prowazeki. Acta Virol. 1971 Nov;15(6):510–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOOSER H. Die Wandlungen der Auffassungen über die Epidemiologie des epidemischen Fleckfiebers in den letzten 50 Jahren. Schweiz Z Pathol Bakteriol. 1953;16(5):802–820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers W. F., Osterman J. V., Wisseman C. L., Jr Nutritional studies of Rickettsia guintana: nature of the hematin requirement. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):89–95. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.89-95.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shkolnik L. Y., Zatulovsky B. G. Electron microscopy of vaccine and Breinl strains of Rickettsia prowazeki in louse gut cells. Acta Virol. 1971 Jan;15(1):102–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISSEMAN C. L., Jr, JACKSON E. B., HAHN F. E., LEY A. C., SMADEL J. E. Metabolic studies of rickettsiae. I. The effects of antimicrobial substances and enzyme inhibitors on the oxidation of glutamate by purified rickettsiae. J Immunol. 1951 Aug;67(2):123–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Newman L. W., Grays R., Green A. E. Metabolism of Rickettsia typhi and Rickettsia akari in irradiated L cells. Infect Immun. 1972 Jul;6(1):50–57. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.1.50-57.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebe M. E., Burton P. R., Shankel D. M. Isolation and characterization of two cell types of Coxiella burneti phase I. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):368–377. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.368-377.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wike D. A., Ormsbee R. A., Tallent G., Peacock M. G. Effects of various suspending media on plaque formation by rickettsiae in tissue culture. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):550–556. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.550-556.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]