Abstract
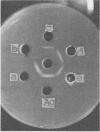
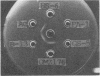
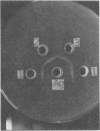
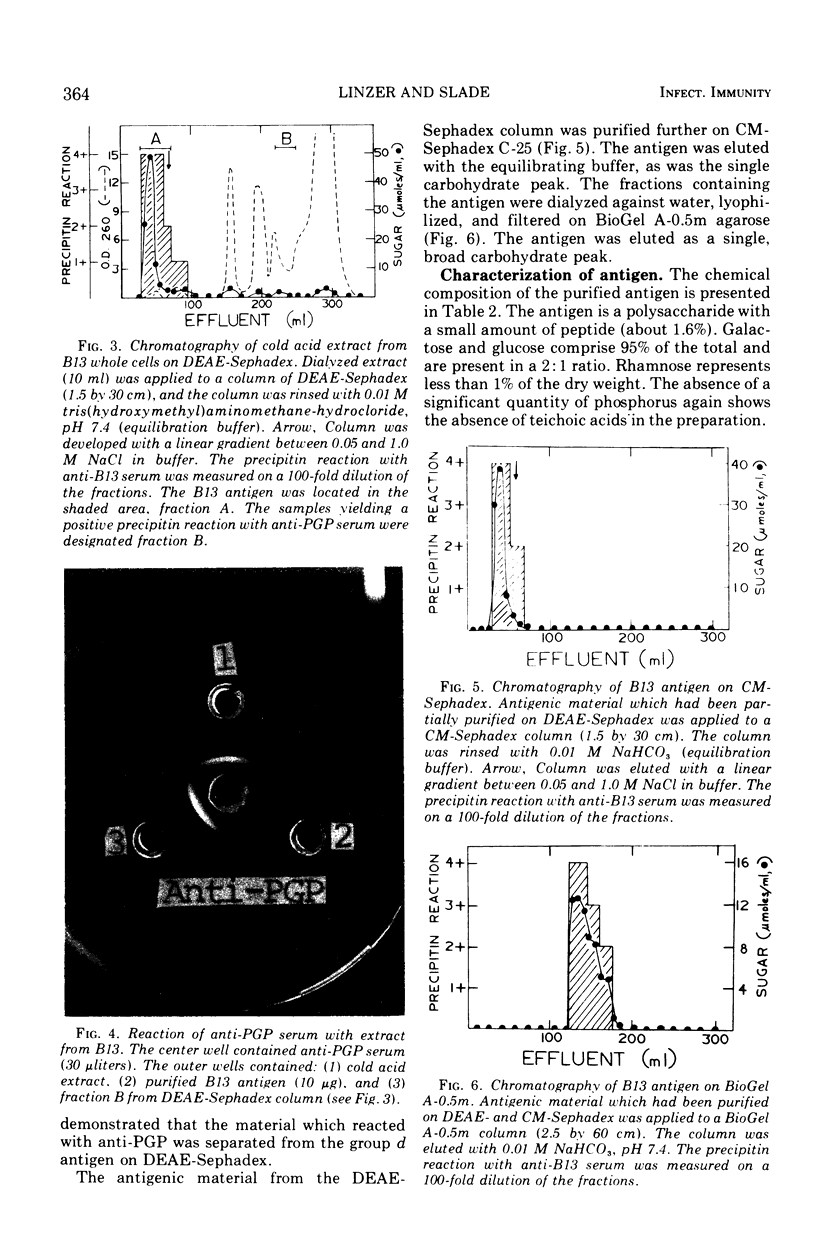
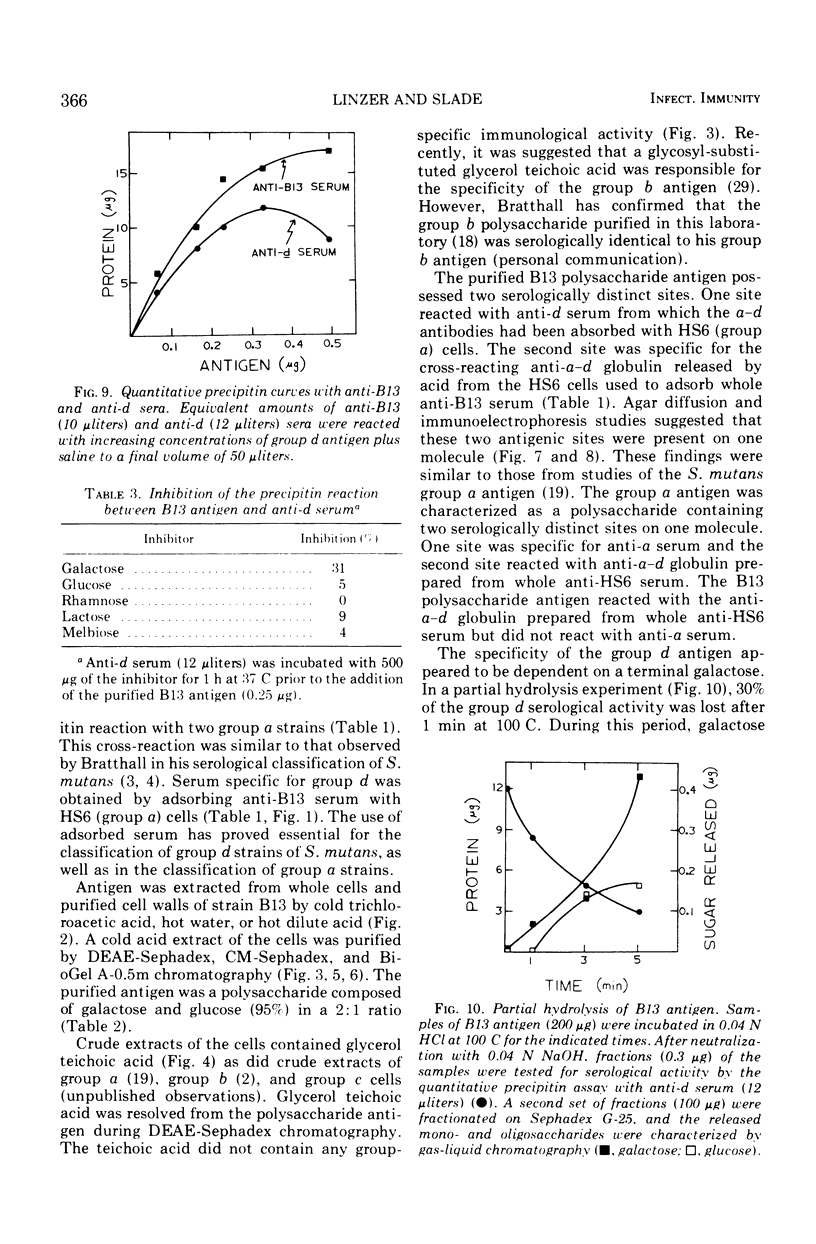
The Streptococcus mutans group d antigen of strain B13 has been purified and characterized with respect to chemical composition and immunochemical properties. The antigen was extracted from lyophilized cells or cell walls by using 5% trichloroacetic acid at 5 C for 16 h. The antigen could also be extracted with water or 0.01 N HCl at 100 C for 20 min. The antigen was purified by ion-exchange and gel chromatography and was found to contain 96% carbohydrate, 1.6% protein, and 0.3% phosphorus. Characterization by gas chromatography indicated that the polysaccharide was composed of galactose and glucose in a 2:1 ratio. The antigen contained two serologically active sites: one site specific for group d and a second site common to both group d and group a strains. Agar diffusion and immunoelectrophoresis indicated that the two sites existed on a single molecule. The immunological specificity of the group d polysaccharide site depended on a terminal d-galactose. The purified B13 antigen did not react with antisera specific for the glycerol teichoic acid from streptococci. Anti-d serum rapidly agglutinated whole cells, indicating that the antibody receptor sites of the polysaccharide antigen were at the surface of the streptococcal cell.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratthall D. Demonstration of five serological groups of streptococcal strains resembling Streptococcus mutans. Odontol Revy. 1970;21(2):143–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratthall D. Immunofluorescent identification of Streptococcus mutans. Odontol Revy. 1972;23(2):181–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coykendall A. L. Genetic heterogeneity in Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):192–196. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.192-196.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. T., Genco R. J. Inhibition of glucosyltransferase activity by antisera to known serotypes of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):237–241. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.237-241.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZGERALD R. J., JORDAN H. V., STANLEY H. R. Experimental caries and gingival pathologic changes in the gnotobiotic rat. J Dent Res. 1960 Sep-Oct;39:923–935. doi: 10.1177/00220345600390052701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZGERALD R. J., KEYES P. H. Demonstration of the etiologic role of streptococci in experimental caries in the hamster. J Am Dent Assoc. 1960 Jul;61:9–19. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1960.0138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., van Houte J. On the formation of dental plaques. J Periodontol. 1973 Jun;44(6):347–360. doi: 10.1902/jop.1973.44.6.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggenheim B., Schroeder H. E. Biochemical and morphological aspects of extracellular polysaccharides produced by cariogenic streptococci. Helv Odontol Acta. 1967 Oct;11(2):131–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESS E. L., SLADE H. D. An electrophoretic examination of cell-free extracts from various serological types of group A hemolytic streptococci. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Mar;16(3):346–353. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan H. V., Keyes P. H. In vitro methods for the study of plaque formation and carious lesions. Arch Oral Biol. 1966 Aug;11(8):793–802. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(66)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno T., Slade H. D. Group a streptococcal polysaccharide antigens. Infect Immun. 1971 Mar;3(3):385–389. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.3.385-389.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Chemical composition and immunological specificity of the streptococcal group O cell wall polysaccharide antigen. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):707–714. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.707-714.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Extraction, purification, and chemical and immunological properties of the Streptococcus mutans group "a" polysaccharide cell wall antigen. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):190–198. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.190-198.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Mechanism of adherence of Streptococcus mutans to smooth surfaces. I. Roles of insoluble dextran-levan synthetase enzymes and cell wall polysaccharide antigen in plaque formation. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):555–562. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.555-562.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Mechanism of adherence of Streptococcus mutans to smooth surfaces. II. Nature of the binding site and the adsorption of dextran-levan synthetase enzymes on the cell-wall surface of the streptococcus. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):419–429. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.419-429.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Structure and immunological specificity of the Streptococcus mutans group b cell wall antigen. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):578–585. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.578-585.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson G. A., Bleiweis A. S., Small P. A., Jr Adherence inhibition of Streptococcus mutans: an assay reflecting a possible role of antibody in dental caries prophylaxis. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):419–427. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.419-427.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLADE H. D., SLAMP W. C. Studies on Streptococcus pyogenes. V. Biochemical and microscopic aspects of cell lysis and digestion by enzymes from Streptomyces albus. J Bacteriol. 1960 Jan;79:103–112. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.1.103-112.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherp H. W. Dental caries: prospects for prevention. Science. 1971 Sep 24;173(4003):1199–1205. doi: 10.1126/science.173.4003.1199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slade H. D. Extraction of Cell-Wall Polysaccharide Antigen from Streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1965 Sep;90(3):667–672. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.3.667-672.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaught R. M., Bleiweis A. S. Antigens of Streptococcus mutans. II. Characterization of an antigen resembling a glycerol teichoic acid in walls of strain BHT. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):60–67. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.60-67.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. M. A dextransucrase activity from Streptococcus FA-1. Arch Oral Biol. 1967 Dec;12(12):1659–1660. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(67)90202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachrisson B. U. Mast cells of the human gingiva. I. Investigations concerning the preservation and demonstration of mast cells in the gingival area. Odontol Revy. 1968;19(1):1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]