Abstract
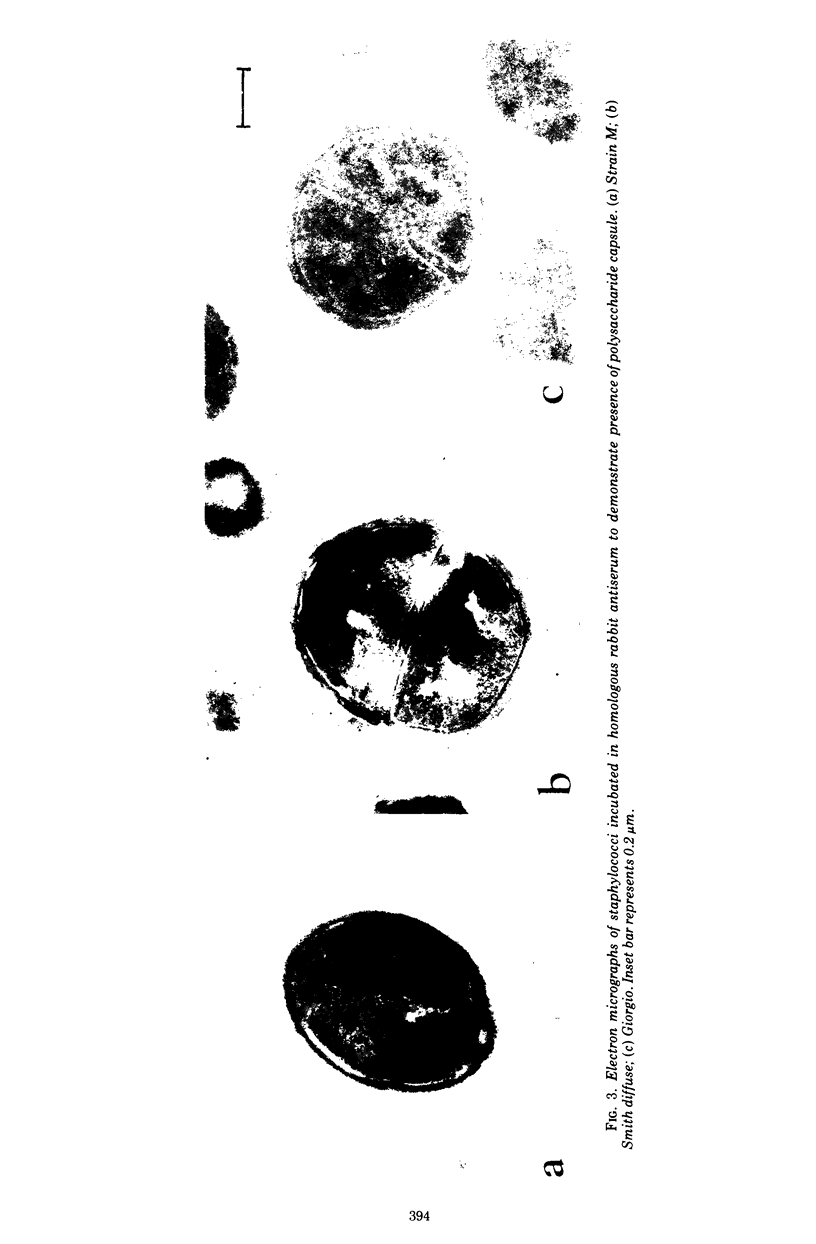
Strain M, classified as a Staphylococcus aureus, behaves like the other rare encapsulated staphylococcal strains. It was clumping-factor negative, grew in diffuse-type colonies in serum-soft agar, and produced rapidly fatal disease in mice. Strain M was highly resistant to phagocytosis by human or mouse leukocytes and required both specific antibody and heat-labile serum factor(s) for efficient ingestion by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Electron micrographs confirmed the presence of a large capsule. Agglutination studies, active or passive mouse protection experiments, and opsonic studies revealed that strain M represents a new, immunologically distinct strain of encapsulated staphylococcus. Strain M differs from other known encapsulated staphylococci in several other respects: its cellular and colonial morphology is atypical; its LD50 in the mouse peritoneal model is 100 times less than that of other mouse lethal strains; it is poorly opsonized by normal human serum; and, finally, it possesses an unusually large capsule as seen in electron micrographs.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BATTEN J. C., DINEEN P. A. P., MCCUNE R. M., Jr The effect of antimicrobial drugs on an experimental staphylococcal infection in mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1956 Aug 31;65(3):91–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1956.tb36627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNHEIMER A. W., SCHWARTZ L. L. Isolation and composition of staphylococcal alpha toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:455–468. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., BACON G. A. The basis of virulence in Pasteurella pestis: comparative behaviour of virulent and avirulent strains in vivo. Br J Exp Pathol. 1954 Apr;35(2):134–143. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartell P. F., Orr T. E., Geffen A., Iorio P. Experimental infection of mice with Staphylococcus aureus: evidence against alpha toxin and the terminal size of the bacterial population as determinants of lethality. J Infect Dis. 1968 Dec;118(5):481–490. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.5.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dossett J. H., Kronvall G., Williams R. C., Jr, Quie P. G. Antiphagocytic effects of staphylococcal protein A. J Immunol. 1969 Dec;103(6):1405–1410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekstedt R. D., Yoshida K. Immunity to staphylococcal infection in mice: effect of living versus killed vaccine, role of circulating antibody, and induction of protection-inducing antigen(s) in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):745–750. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.745-750.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINKELSTEIN R. A., SULKIN S. E. Characteristics of coagulase positive and coagulase negative staphylococci in serum-soft agar. J Bacteriol. 1958 Mar;75(3):339–344. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.3.339-344.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOSTER W. D. THE ROLE OF ALPHA-HAEMOLYSIN IN THE PATHOGENICITY OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:535–541. doi: 10.1002/path.1700860231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsum U., Forsgren A., Hjelm E. Role of protein A in the serum-soft agar technique. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):583–586. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.583-586.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOENIG M. G. Factors relating to the virulence of staphylococci. I. Comparative studies on two colonial variants. Yale J Biol Med. 1962 Jun;34:537–559. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOENIG M. G., MELLY M. A., ROGERS D. E. Factors relating to the virulence of Staphylococci. II. Observations on four mouse-pathogenic strains. J Exp Med. 1962 Nov 1;116:589–599. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.5.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M. G., Melly M. A. The importance of surface antigens in staphylococcal virulence. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jul 23;128(1):231–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb11641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LI I. W., KAPRAL F. A. Virulence and coagulases of Staphylococcus aureus. II. Survival of certain coagulase-negative mutants in the organs of intravenously infected rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1962 Nov-Dec;111:204–208. doi: 10.1093/infdis/111.3.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOURIA D. B., KAMINSKI T. IMMUNITY IN EXPERIMENTAL STAPHYLOCOCCAL INFECTIONS. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Oct;62:535–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEILL J. M., ABRAHAMS I., KAPROS C. E. A comparison of the immunogenicity of weakly encapsulated and of strongly encapsulated strains of Cryptococcus neoformans (Torula histolytica). J Bacteriol. 1950 Feb;59(2):263–275. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.2.263-275.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGERS D. E., MELLY M. A. Observations on the immunology of pathogenic staphylococci. Yale J Biol Med. 1962 Jun;34:560–581. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. C. A capsulate Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1969 Aug;2(3):253–260. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-3-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILEY B. B. A new virulence test for Staphylococcus aureus and its application to encapsulated strains. Can J Microbiol. 1961 Dec;7:933–943. doi: 10.1139/m61-118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. C., Park J. T. Chemical characterization of a new surface antigenic polysaccharide from a mutant of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):874–884. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.874-884.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Ekstedt R. D. Relation of mucoid growth of Staphylococcus aureus to clumping factor reaction, morphology in serum-soft agar, and virulence. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):902–908. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.902-908.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K. Isolation of an additional capsular-type strain of Staphylococcus aureus by the serum-soft agar technique. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):833–834. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.833-834.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Smith M. R., Naito Y. Biological and Immunological Properties of Encapsulated Strains of Staphylococcus aureus from Human Sources. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):528–532. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.528-532.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Takeuchi Y. Comparison of Compact and Diffuse Variants of Strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):523–527. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.523-527.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zygmunt W. A., Tavormina P. A. Lysostaphin: model for a specific enzymatic approach to infectious disease. Prog Drug Res. 1972;16:309–333. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7081-8_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]