Abstract
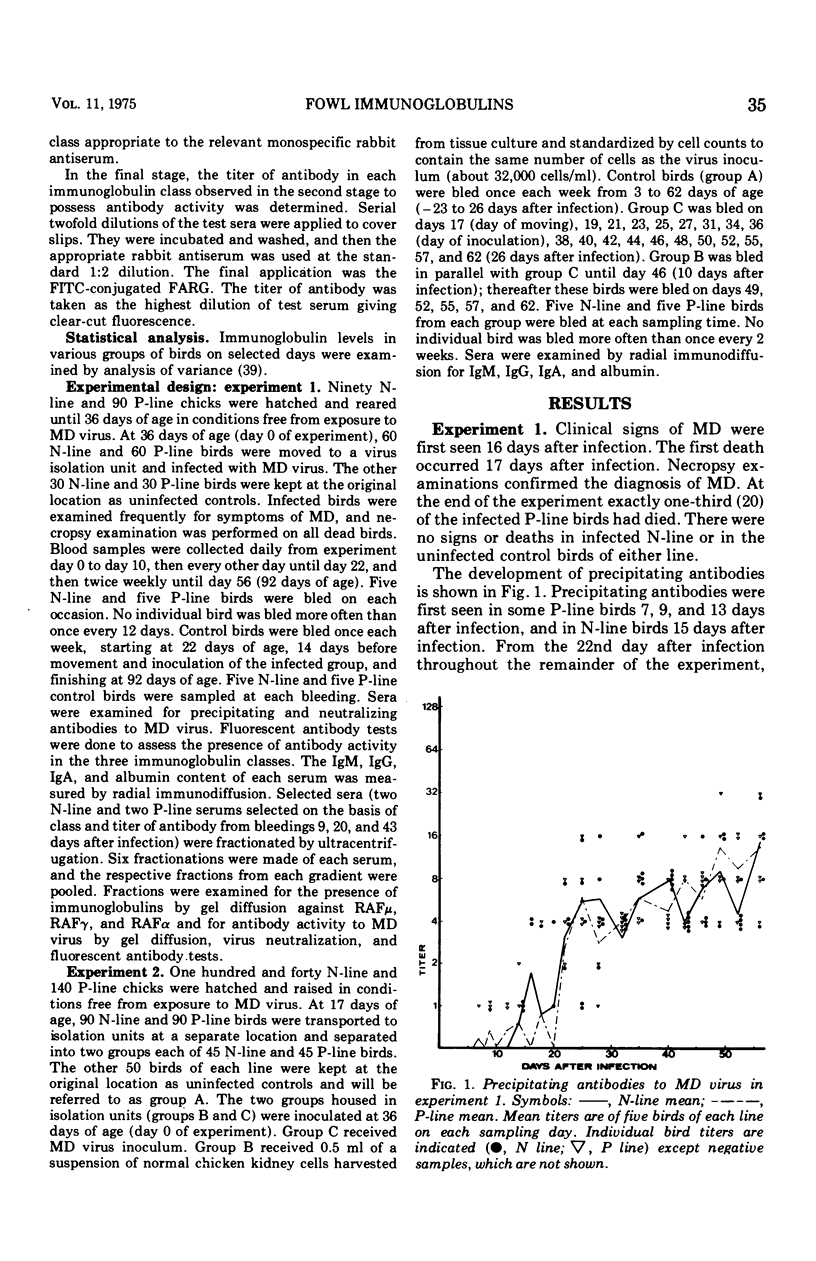
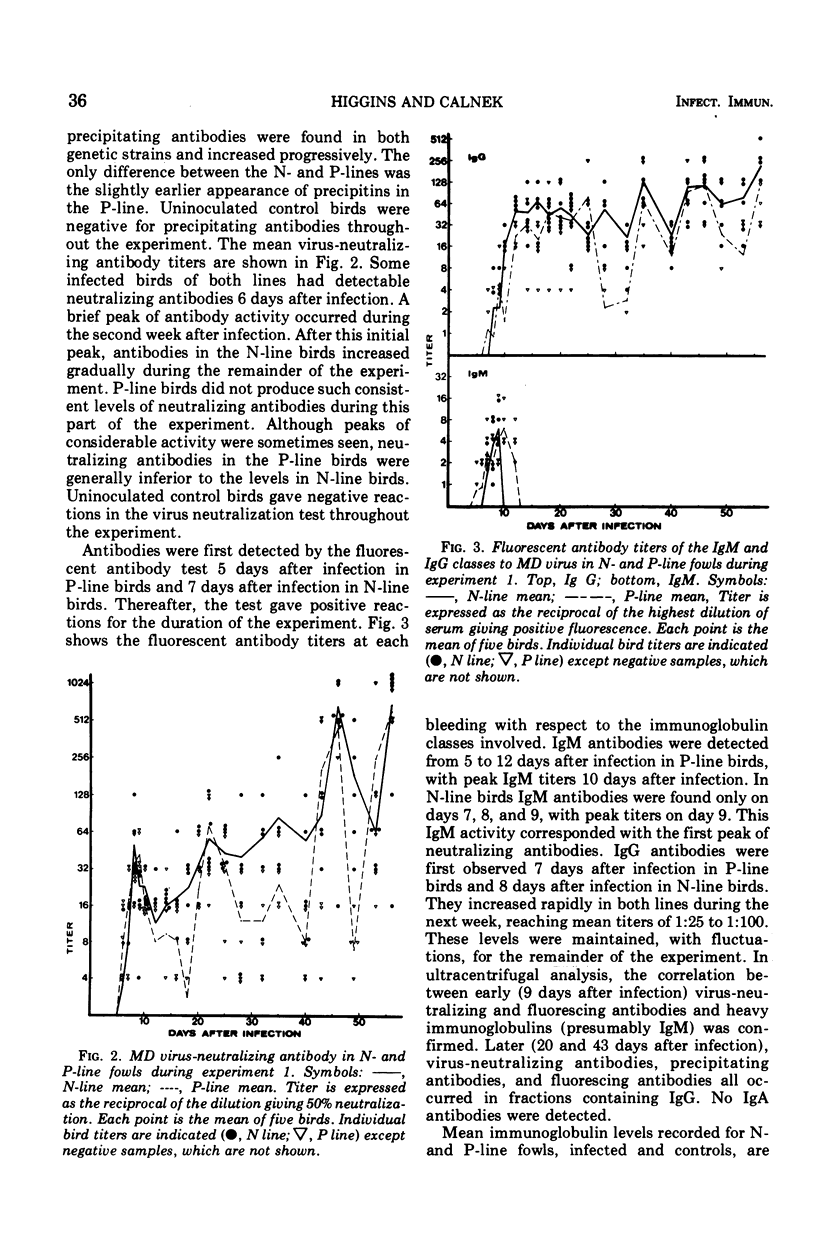
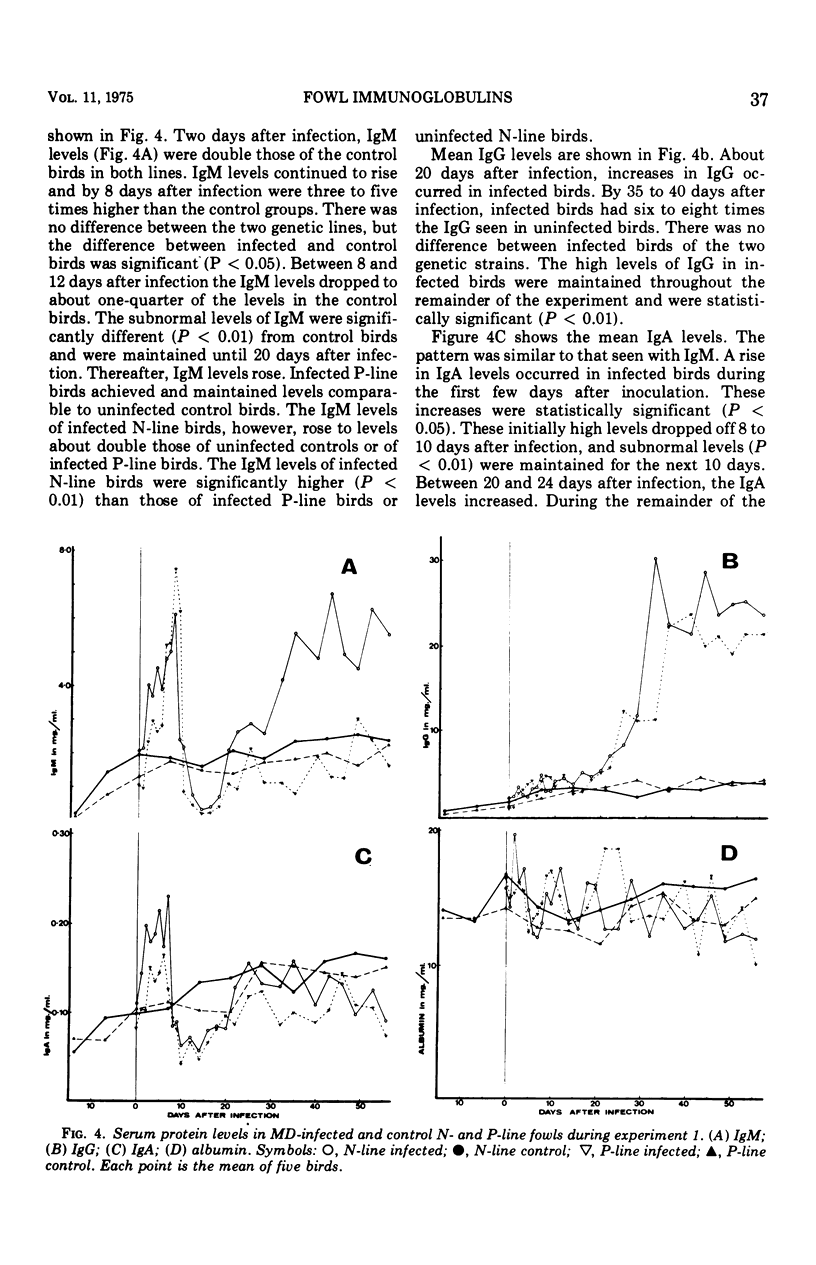
Five-week-old birds of resistant (N) and susceptible (P) genetic lines were inoculated with the JM strain of Marek's disease (MD) virus. MD occurred only in P-line birds; one-third had died by the end of the experiment (63 days after inoculation). Sera were examined for antibodies (precipitating, virus neutralizing,and fluorescing), and immunoglobulins were measured. Antibodies were associated with immunoglobulin classes by density gradient centrifugation and utilization of specific antisera to gowl immunoglobulins in indirect immunofluorescence. Precipitating antibodies were found in both lines; they first appeared 7 days after inoculation in P-line birds and 14 days after inoculation in N-line birds, but thereafter there was no difference between the two genetic lines. A peak of neutralizing antibody occurred in both lines between 6 and 12 days. Thereafter neutralizing antibodies increased gradually throughout the experiment. Neutralizing antibody levels were at this stage often higher in N-line than in P-line birds. The fluorescent antibody test showed transient immunoglobulin (Ig) M antibody from 7 to 9 days in N-line birds and 5 to 12 days in P-line birds; this corresponded with the initial peak of neutralizing antibody. Antibodies were seen from 7 to 8 days after inoculation and increased gradually durin gthe experiment, generally paralleling the secondary increase in neutralizing antibodies. Ultracentrifugation confirmed the presence of IgM and IgG antibodies as described. Antibodies of the IgA class were not found. The alterations in serum immunoglobulin levels occurred in three phrases: (i) 1 to 9 days postinfection, there was an increase in IgM and IgA compared with uninfected control birds; (ii) 10 to 20 days postinfection, Ig M and IgA levels were lower than in control birds; and (iii) 21 days postinfection, until the end of experiment, IgA returned to normal levels, IgG increased to about eight times higher than in control birds, and IgM in P-line birds returned to normal levels and in N-line birds reached and maintained levels about double those of control birds. Another experiment was designed to examine the separate effects of moving and inoculation of uninfected kidney cells and virus-infected kidney cells. The changes in immunoglobulins observed in the first experiment occurred only after infection with MD virus and were not related to movement or handling stress. It was concluded that no significant primary difference exists in the humoral immune system between fowls resistant and susceptible to MD; all differences could be related to the immunosuppressive effects of MD, which are greater in susceptible birds apparently due to the greater lymphoid tissue damage in these strains.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addinger H. K., Calnek B. W. Pathogenesis of Marek's disease: early distribution of virus and viral antigens in infected chickens. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 May;50(5):1287–1298. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.5.1287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank S. E., Leslie G. A., Clem L. W. Antibody affinity and valence in viral neutralization. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):665–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAREY J., WARNER N. L. GAMMA-GLOBULIN SYNTHESIS IN HORMONALLY BURSECTOMIZED CHICKENS. Nature. 1964 Jul 11;203:198–199. doi: 10.1038/203198a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnek B. W. Effects of passive antibody on early pathogenesis of Marek's disease. Infect Immun. 1972 Aug;6(2):193–198. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.2.193-198.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnek B. W., Hitchner S. B. Localization of viral antigen in chickens infected with Marek's disease herpesvirus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969 Oct;43(4):935–949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnek B. W. Influence of age at exposure on the pathogenesis of Marek's disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Sep;51(3):929–939. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.3.929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnek B. W., Madin S. H. Characteristics of in vitro infection of chicken kidney cell cultures with a herpesvirus from Marek's disease. Am J Vet Res. 1969 Aug;30(8):1389–1402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill A. E., Chubb R. C., Baxendale W. The attenuation, with loss of oncogenicity, of the herpes-type virus of Marek's disease (strain HPRS-16) on passage in cell culture. J Gen Virol. 1969 Jun;4(4):557–564. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-4-4-557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISEN H. N., SISKIND G. W. VARIATIONS IN AFFINITIES OF ANTIBODIES DURING THE IMMUNE RESPONSE. Biochemistry. 1964 Jul;3:996–1008. doi: 10.1021/bi00895a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. L., Patterson L. T. Changes in serum proteins associated with the immunosuppressive effects of acute leucosis (Marek's disease). J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1972 Apr;11(4):325–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILDEN R. V., ROSENQUIST G. L. DURATION OF ANTIBODY RESPONSE TO SOLUBLE ANTIGEN. Nature. 1963 Jul 6;199:87–87. doi: 10.1038/199087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmingsson E. J., Linna T. J. Ontogenetic studies on lymphoid cell traffic in the chicken. I. Cell migration from the bursa of Fabricius. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1972;42(5):693–710. doi: 10.1159/000230650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmingsson E. J. Ontogenetic studies on lymphoid cell traffic in the chicken. II. Cell traffic from the bursa of Fabricius to the thymus and the spleen in the embryo. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1972;42(6):764–774. doi: 10.1159/000230656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard E. B., Jannke C., Vickers J., Kenyon A. J. Elevated gamma globulin levels in Marek's disease (neural lymphomatosis) of domestic fowl. Cornell Vet. 1967 Apr;57(2):183–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincade P. W., Cooper M. D. Development and distribution of immunoglobulin-containing cells in the chicken. An immunofluorescent analysis using purified antibodies to mu, gamma and light chains. J Immunol. 1971 Feb;106(2):371–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincade P. W., Lawton A. R., Bockman D. E., Cooper M. D. Suppression of immunoglobulin G synthesis as a result of antibody-mediated suppression of immunoglobulin M synthesis in chickens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Dec;67(4):1918–1925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.4.1918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner K. G., Glick B., McDuffie F. C. Role of the bursa of Fabricius in IgG and IgM production in the chicken: evidence for the role of a non-bursal site in the development of humoral immunity. J Immunol. 1971 Aug;107(2):493–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann J. J., Waldman R. H., Togo Y., Heiner G. G., Dawkins A. T., Kasel J. A. Antibody response in respiratory secretions of volunteers given live and dead influenza virus. J Immunol. 1968 Apr;100(4):726–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin L. N., Leslie G. A. IgM-forming cells as the immediate precursor of IgA-producing cells during ontogeny of the immunoglobulin-producing system of the chicken. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):120–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perey D. Y., Biennenstock J. Effects of bursectomy and thymectomy on ontogeny of fowl IgA, IgG, and IgM. J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):633–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins J. C., Tucker D. N., Knope H. L., Wenzel R. P., Hornick R. B., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Evidence for protective effect of an inactivated rhinovirus vaccine administered by the nasal route. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Oct;90(4):319–326. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips P. A., Biggs P. M. Course of infection in tissues of susceptible chickens after exposure to strains of Marek's disease virus and turkey herpesvirus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Nov;49(5):1367–1373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce A. E., Chubb R. C., Long P. L. The significance of the bursa of Fabricius in relation to the synthesis of 7S and 19S immune globulins and specific antibody activity in the fowl. Immunology. 1966 Apr;10(4):321–337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purchase H. G., Biggs P. M. Characterization of five isolates of Marek's disease. Res Vet Sci. 1967 Oct;8(4):440–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringen L. M., Akhtar A. S. Electrophoretic analysis of serum proteins from paralyzed and unparalyzed chickens exposed to Marek's disease. Avian Dis. 1968 Feb;12(1):4–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samadieh B., Bankowski R. A., Carroll E. J. Electrophoretic analysis of serum proteins of chickens experimentally infected with Marek's disease agent. Am J Vet Res. 1969 May;30(5):837–846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulkind M. L., Kenny K., Herzberg M., Robbins J. B. The specific secondary biological activities of rabbit IgM and IgG anti-Salmonella typhimurium 'O' antibodies isolated during the development of the immune response. Immunology. 1972 Aug;23(2):159–170. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma J. M., Purchase H. G. Replication of Marek's disease virus in cell cultures derived from genetically resistant chickens. Infect Immun. 1974 Jun;9(6):1092–1097. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.6.1092-1097.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma J. M., Stone H. A. Genetic resistance to Marek's disease. Delineation of the response of genetically resistant chickens to Marek's disease virus infection. Avian Dis. 1972 Jul-Sep;16(4):894–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. W., Calnek B. W. High-virulence Marek's disease virus infection in chickens previously infected with low-virulence virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 May;52(5):1595–1603. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.5.1595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer J. L. Marek's disease herpesvirus: in vivo and in vitro infection of kidney cells of different genetic strains of chickens. Avian Dis. 1969 Nov;13(4):753–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Meter R., Good R. A., Cooper M. D. Ontogeny of circulating immunoglobulin in normal, bursectomized and irradiated chickens. J Immunol. 1969 Feb;102(2):370–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman R. H., Bencic Z., Sinha R., Deb B. C., Sakazaki R., Tamura K., Mukerjee S., Ganguly R. Cholera immunology. II. Serum and intestinal secretion antibody response after naturally occurring cholera. J Infect Dis. 1972 Oct;126(4):401–407. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.4.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washburn K. W., Eidson C. S. Changes in concentration of plasma proteins associated with Marek's disease. Poult Sci. 1970 May;49(3):784–793. doi: 10.3382/ps.0490784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G. The immune response to influenza virus. 3. Changes in the avidity and specificity of early IgM and IgG antibodies. Immunology. 1968 Jan;14(1):39–52. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells A. F., Miller C. E., Nadel M. K. Rapid fluorescein and protein assay method for fluorescent-antibody conjugates. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):271–275. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.271-275.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakay-Rones Z., Levy R., Spira G. Secretory Newcastle disease virus antibodies from chicken respiratory tract. J Immunol. 1972 Aug;109(2):311–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakay-Rones Z., Spira G., Levy R. Local immunologic response to immunization with inactivated Newcastle disease virus. J Immunol. 1971 Oct;107(4):1180–1183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R., Jauker U., Droege W. Cellular composition of the chicken thymus; effects of neonatal bursectomy and hydrocortisone treatment. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Dec;3(12):812–818. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


