Abstract
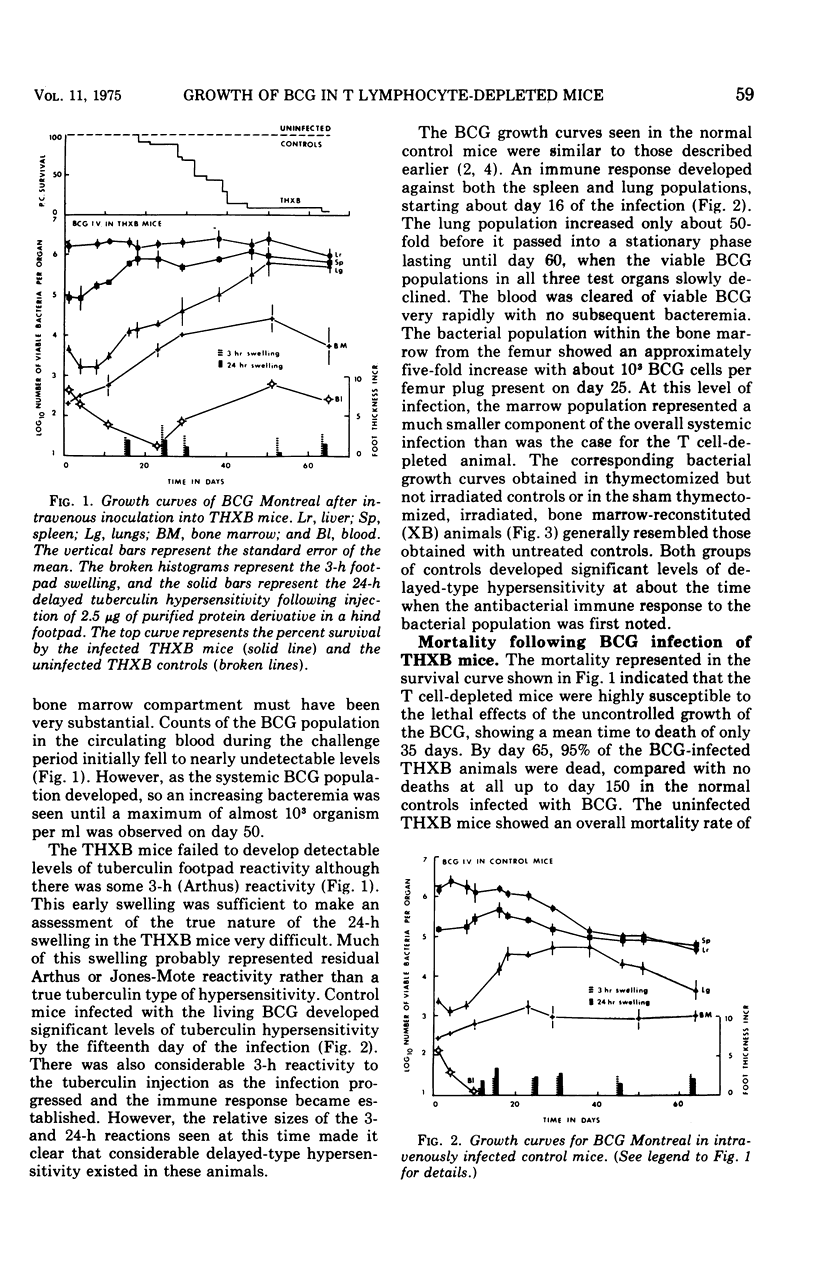
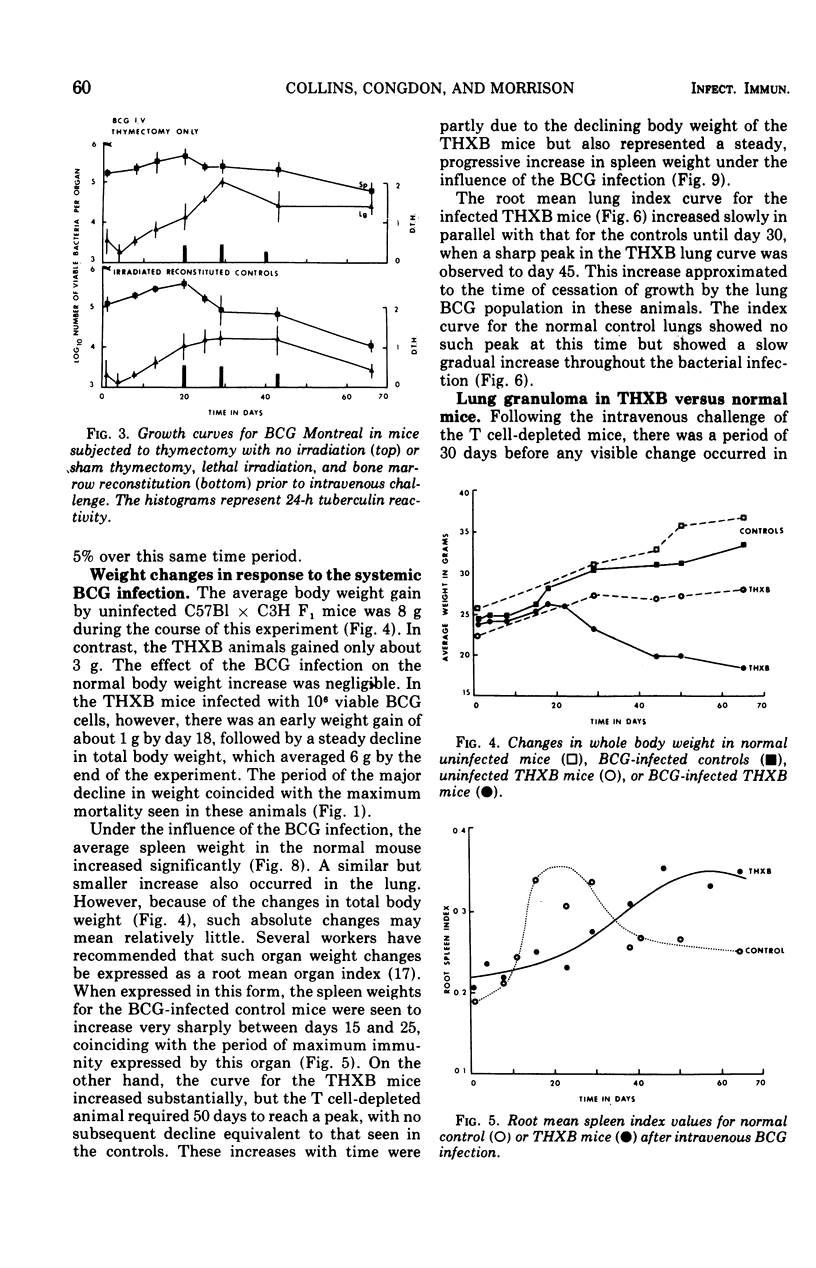
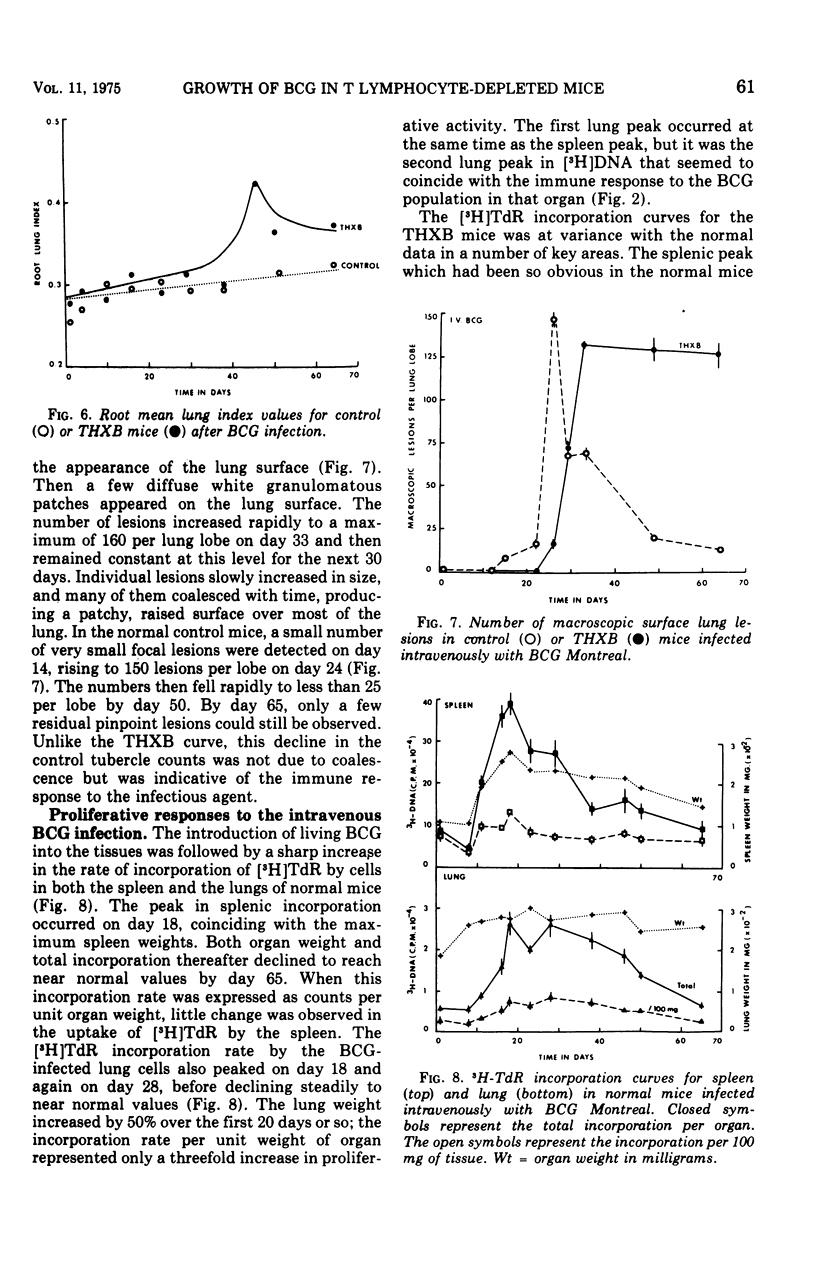
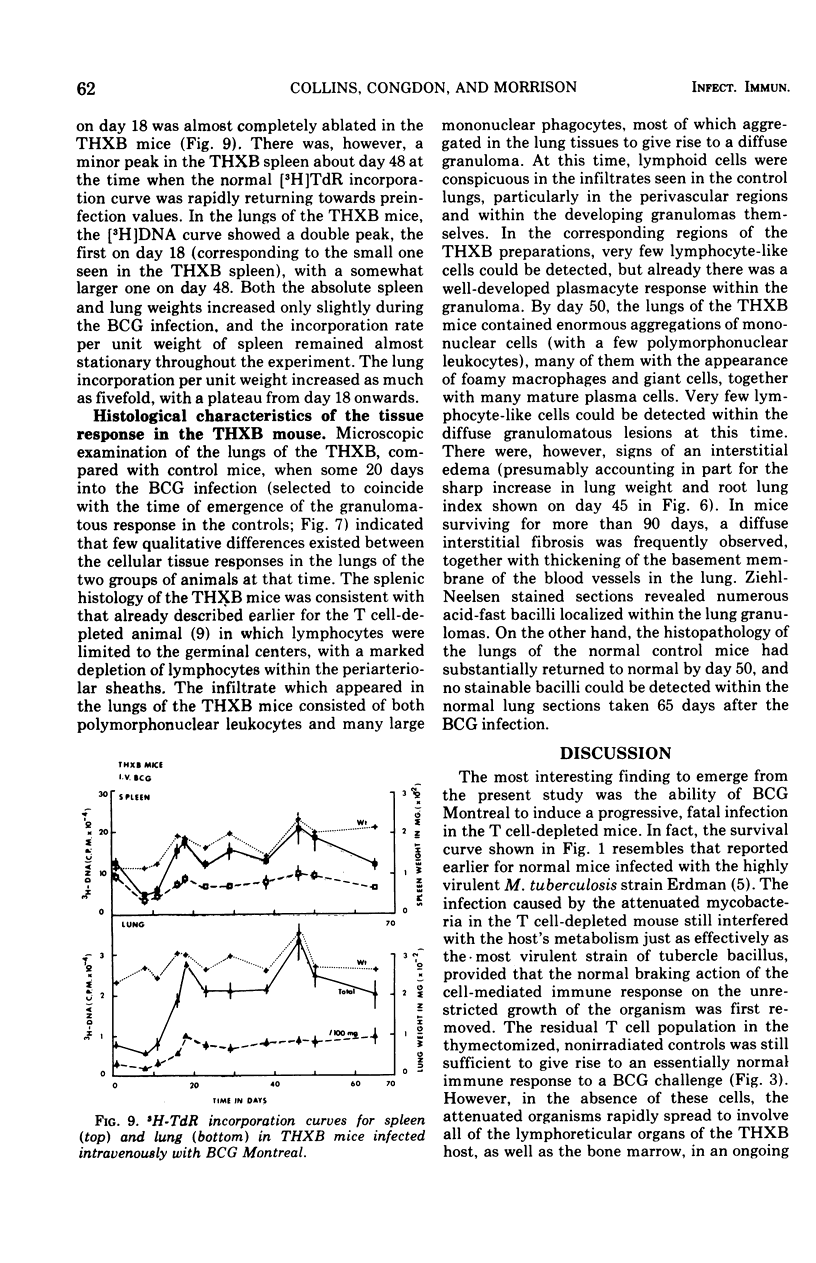
BCG Montreal (10-6 viable bacilli) injected intravenously into adult thymectomized, irradiated, and bone marrow-reconstituted (THXB) C57Bl times C3H F1 hybrid mice induced a progressive systemic infection which killed 95% of the animals within 60 days. Control mice infected with this dose of BCG did not die. The infected THXB mice failed to develop detectable levels of tuberculin hypersensitivity although they did show considerable Arthus (3 h) reactivity. The BCG-infected THXB mice lost weight progressively, and the root spleen and root lung indices increased substantially as the infection proceeded. None of the THXB mice developed an antibacterial immune response to the systemic BCG infection, and this was reflected by the continued persistence of macroscopic lung granuloma in these animals. The BCG-infected control mice developed as many surface tubercles as did the THXB animals, but the granulomas rapidly regressed in size and numbers in the normal mice. The lung changes correlated with the amount of tritiated thymidine incorporated by the lung cells in the later stages of the BCG infection. T cell depletion depressed the early splenic peak normally seen in BCG-infected controls, but, on the other hand, there was a progressive increase in lung counts in the THXB mice as the infection progressed and this late peak was not seen in the control animals. The significance of these findings is discussed in relation to the development of antituberculous immunity by BCG-infected mice.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Collins F. M., Mackaness G. B., Montalbine V., Smith M. M. A comparison of the Steenken minimal inhibitory concentration and the Canetti proportion methods for determining levels of drug resistance in cultures of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1968 Aug;98(2):189–200. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1968.98.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Mackaness G. B. The relationship of delayed hypersensitivity to acquired antituberculous immunity. I. Tuberculin sensitivity and resistance to reinfection in BCG-vaccinated mice. Cell Immunol. 1970 Sep;1(3):253–265. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Miller T. E. Growth of a drug-resistant strain of Mycobacterium bovis (BCG) in normal and immunized mice. J Infect Dis. 1969 Nov;120(5):517–533. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.5.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Smith M. M. A comparative study of the virulence of mycobacterium tuberculosis measured in mice and guinea pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1969 Nov;100(5):631–639. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1969.100.5.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Wayne L. G., v Montalbine The effect of cultural conditions on the distribution of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the spleens and lungs of specific pathogen-free mice. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974 Aug;110(2):147–156. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1974.110.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY D. F., GRAHAM-SMITH H., NOBLE J. L. Variations in natural resistance to tuberculosis. J Hyg (Lond) 1960 Jun;58:215–227. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400038304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim T. H., Kubica G. P. Long-term preservation and storage of mycobacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Sep;24(3):311–317. doi: 10.1128/am.24.3.311-317.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. Importance of thymus-derived lymphocytes in cell-mediated immunity to infection. Cell Immunol. 1973 Apr;7(1):166–176. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J., Mackaness G. B. Immunological control of macrophage proliferation in vivo. Infect Immun. 1973 Jul;8(1):68–73. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.1.68-73.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees R. J. New prospects for the study of leprosy in the laboratory. Bull World Health Organ. 1969;40(5):785–800. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees R. J. Recent bacteriologic, immunologic and pathologic studies on experimental human leprosy in the mouse foot pad. Int J Lepr. 1965 Jul-Sep;33(3 Suppl):646–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees R. J., Waters M. F., Weddell A. G., Palmer E. Experimental lepromatous leprosy. Nature. 1967 Aug 5;215(5101):599–602. doi: 10.1038/215599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard C. C., Congdon C. C. Increased growth of Mycobacterium leprae in thymectomized-irradiated mice after foot pad inoculation. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1968 Apr-Jun;36(2):224–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya K., Mori R., Nomoto K., Nakayama H. Experimental mycobacterial infections in neonatally thymectomized mice. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1967 Sep;96(3):469–477. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1967.96.3.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truitt G. L., Mackaness G. B. Cell-mediated resistance to aerogenic infection of the lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Dec;104(6):829–843. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.104.6.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUMANS G. P., YOUMANS A. S. AN ACUTE PULMONARY GRANULOMATOUS RESPONSE IN MICE PRODUCED BY MYCOBACTERIAL CELLS AND ITS RELATION TO INCREASED RESISTANCE AND INCREASED SUSCEPTIBILITY TO EXPERIMENTAL TUBERCULOUS INFECTION. J Infect Dis. 1964 Apr;114:135–151. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.2.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



