Abstract
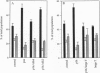
p16ink4 has been implicated as a tumor suppressor that is lost from a variety of human tumors and human cell lines. p16ink4 specifically binds and inhibits the cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6. In vitro, these kinases can phosphorylate the product of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor gene. Thus, p16ink4 could exert its function as tumor suppressor through inhibition of phosphorylation and functional inactivation of the retinoblastoma protein. Here we show that overexpression of p16ink4 in certain cell types will lead to an arrest in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. In addition, we show that p16ink4 can only suppress the growth of human cells that contain functional pRB. Moreover, we have compared the effect of p16ink4 expression on embryo fibroblasts from wild-type and RB homozygous mutant mice. Wild-type embryo fibroblasts are inhibited by p16ink4, whereas the RB nullizygous fibroblasts are not. These data not only show that the presence of pRB is crucial for growth suppression by p16ink4 but also indicate that the pRB is the critical target acted upon by cyclin D-dependent kinases in the G1 phase of the cell cycle.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S. J., Markowitz S., Fearon E. R., Willson J. K., Vogelstein B. Suppression of human colorectal carcinoma cell growth by wild-type p53. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):912–915. doi: 10.1126/science.2144057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates S., Parry D., Bonetta L., Vousden K., Dickson C., Peters G. Absence of cyclin D/cdk complexes in cells lacking functional retinoblastoma protein. Oncogene. 1994 Jun;9(6):1633–1640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danos O., Mulligan R. C. Safe and efficient generation of recombinant retroviruses with amphotropic and ecotropic host ranges. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6460–6464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Y., Turck C. W., Morgan D. O. Inhibition of CDK2 activity in vivo by an associated 20K regulatory subunit. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):707–710. doi: 10.1038/366707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Jenkins C. W., Li Y., Nichols M. A., Wu X., O'Keefe C. L., Matera A. G., Xiong Y. Growth suppression by p18, a p16INK4/MTS1- and p14INK4B/MTS2-related CDK6 inhibitor, correlates with wild-type pRb function. Genes Dev. 1994 Dec 15;8(24):2939–2952. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.24.2939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannon G. J., Beach D. p15INK4B is a potential effector of TGF-beta-induced cell cycle arrest. Nature. 1994 Sep 15;371(6494):257–261. doi: 10.1038/371257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Adami G. R., Wei N., Keyomarsi K., Elledge S. J. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90499-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P. W., Dowdy S. F., Eaton E. N., Arnold A., Weinberg R. A. Function of a human cyclin gene as an oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):709–713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P. W., Mittnacht S., Dulic V., Arnold A., Reed S. I., Weinberg R. A. Regulation of retinoblastoma protein functions by ectopic expression of human cyclins. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):993–1006. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90249-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inaba T., Matsushime H., Valentine M., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J., Look A. T. Genomic organization, chromosomal localization, and independent expression of human cyclin D genes. Genomics. 1992 Jul;13(3):565–574. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90126-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Fazeli A., Schmitt E. M., Bronson R. T., Goodell M. A., Weinberg R. A. Effects of an Rb mutation in the mouse. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):295–300. doi: 10.1038/359295a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamb A., Gruis N. A., Weaver-Feldhaus J., Liu Q., Harshman K., Tavtigian S. V., Stockert E., Day R. S., 3rd, Johnson B. E., Skolnick M. H. A cell cycle regulator potentially involved in genesis of many tumor types. Science. 1994 Apr 15;264(5157):436–440. doi: 10.1126/science.8153634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Matsushime H., Hiebert S. W., Ewen M. E., Sherr C. J. Direct binding of cyclin D to the retinoblastoma gene product (pRb) and pRb phosphorylation by the cyclin D-dependent kinase CDK4. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):331–342. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khatib Z. A., Matsushime H., Valentine M., Shapiro D. N., Sherr C. J., Look A. T. Coamplification of the CDK4 gene with MDM2 and GLI in human sarcomas. Cancer Res. 1993 Nov 15;53(22):5535–5541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukas J., Pagano M., Staskova Z., Draetta G., Bartek J. Cyclin D1 protein oscillates and is essential for cell cycle progression in human tumour cell lines. Oncogene. 1994 Mar;9(3):707–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer W. E., Amin M., Sauve G. J., Appella E., Ullrich S. J., Romano J. W. Wild type human p53 is antiproliferative in SV40-transformed hamster cells. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):973–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerson M., Harlow E. Identification of G1 kinase activity for cdk6, a novel cyclin D partner. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):2077–2086. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.2077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern J. P., Land H. Advanced mammalian gene transfer: high titre retroviral vectors with multiple drug selection markers and a complementary helper-free packaging cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3587–3596. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motokura T., Bloom T., Kim H. G., Jüppner H., Ruderman J. V., Kronenberg H. M., Arnold A. A novel cyclin encoded by a bcl1-linked candidate oncogene. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):512–515. doi: 10.1038/350512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobori T., Miura K., Wu D. J., Lois A., Takabayashi K., Carson D. A. Deletions of the cyclin-dependent kinase-4 inhibitor gene in multiple human cancers. Nature. 1994 Apr 21;368(6473):753–756. doi: 10.1038/368753a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo M., Theodoras A. M., Schumacher J., Roberts J. M., Pagano M. Human cyclin E, a nuclear protein essential for the G1-to-S phase transition. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 May;15(5):2612–2624. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.5.2612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto A., Demetrick D. J., Spillare E. A., Hagiwara K., Hussain S. P., Bennett W. P., Forrester K., Gerwin B., Serrano M., Beach D. H. Mutations and altered expression of p16INK4 in human cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):11045–11049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.11045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otterson G. A., Kratzke R. A., Coxon A., Kim Y. W., Kaye F. J. Absence of p16INK4 protein is restricted to the subset of lung cancer lines that retains wildtype RB. Oncogene. 1994 Nov;9(11):3375–3378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reifenberger G., Reifenberger J., Ichimura K., Meltzer P. S., Collins V. P. Amplification of multiple genes from chromosomal region 12q13-14 in human malignant gliomas: preliminary mapping of the amplicons shows preferential involvement of CDK4, SAS, and MDM2. Cancer Res. 1994 Aug 15;54(16):4299–4303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E. E., Ichimura K., Reifenberger G., Collins V. P. CDKN2 (p16/MTS1) gene deletion or CDK4 amplification occurs in the majority of glioblastomas. Cancer Res. 1994 Dec 15;54(24):6321–6324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano M., Gómez-Lahoz E., DePinho R. A., Beach D., Bar-Sagi D. Inhibition of ras-induced proliferation and cellular transformation by p16INK4. Science. 1995 Jan 13;267(5195):249–252. doi: 10.1126/science.7809631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano M., Hannon G. J., Beach D. A new regulatory motif in cell-cycle control causing specific inhibition of cyclin D/CDK4. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):704–707. doi: 10.1038/366704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheaff R. J., Roberts J. M. Tumor suppression. Lessons in p16 from phylum Falconium. Curr Biol. 1995 Jan 1;5(1):28–31. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J. Mammalian G1 cyclins. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1059–1065. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90636-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh P., Wong S. H., Hong W. Overexpression of E2F-1 in rat embryo fibroblasts leads to neoplastic transformation. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 15;13(14):3329–3338. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06635.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamenkovic I., Seed B. Analysis of two cDNA clones encoding the B lymphocyte antigen CD20 (B1, Bp35), a type III integral membrane protein. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1975–1980. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam S. W., Shay J. W., Pagano M. Differential expression and cell cycle regulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase 4 inhibitor p16Ink4. Cancer Res. 1994 Nov 15;54(22):5816–5820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam S. W., Theodoras A. M., Shay J. W., Draetta G. F., Pagano M. Differential expression and regulation of Cyclin D1 protein in normal and tumor human cells: association with Cdk4 is required for Cyclin D1 function in G1 progression. Oncogene. 1994 Sep;9(9):2663–2674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waga S., Hannon G. J., Beach D., Stillman B. The p21 inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases controls DNA replication by interaction with PCNA. Nature. 1994 Jun 16;369(6481):574–578. doi: 10.1038/369574a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. Tumor suppressor genes. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1138–1146. doi: 10.1126/science.1659741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Withers D. A., Harvey R. C., Faust J. B., Melnyk O., Carey K., Meeker T. C. Characterization of a candidate bcl-1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4846–4853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Hannon G. J., Zhang H., Casso D., Kobayashi R., Beach D. p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin kinases. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):701–704. doi: 10.1038/366701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Menninger J., Beach D., Ward D. C. Molecular cloning and chromosomal mapping of CCND genes encoding human D-type cyclins. Genomics. 1992 Jul;13(3):575–584. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90127-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Zhang H., Beach D. Subunit rearrangement of the cyclin-dependent kinases is associated with cellular transformation. Genes Dev. 1993 Aug;7(8):1572–1583. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.8.1572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L., van den Heuvel S., Helin K., Fattaey A., Ewen M., Livingston D., Dyson N., Harlow E. Inhibition of cell proliferation by p107, a relative of the retinoblastoma protein. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1111–1125. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Eb A. J., Graham F. L. Assay of transforming activity of tumor virus DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):826–839. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]