Abstract
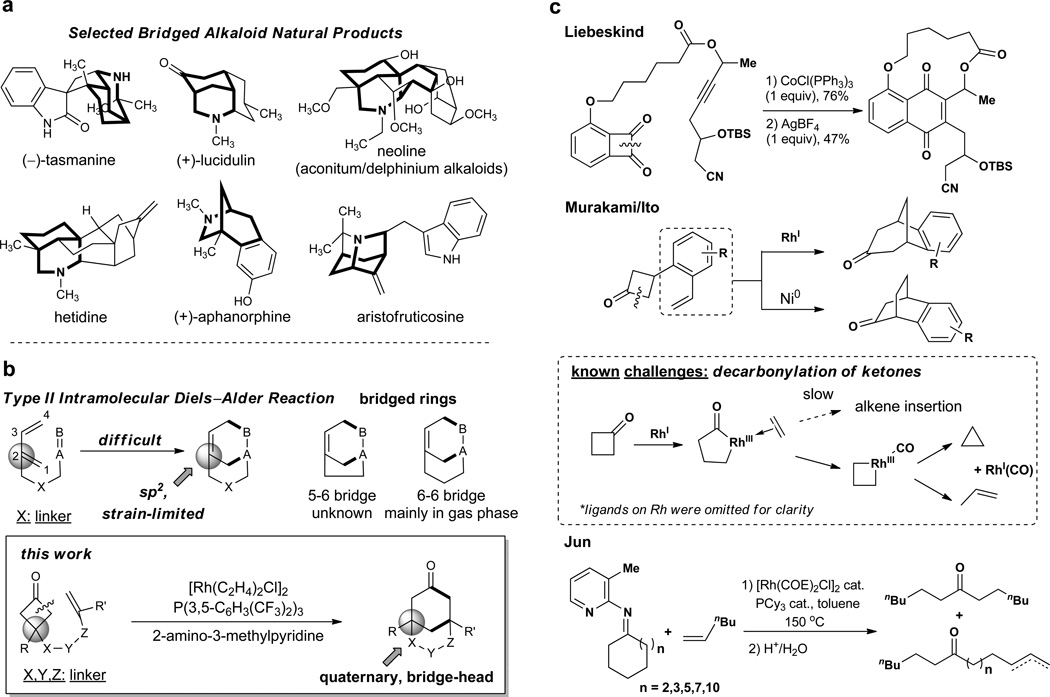
Bridged-ring systems are widely found in natural products and successful syntheses of them frequently feature intramolecular Diels-Alder (IMDA) reactions. These reactions are subclassified as either type I or type II IMDAs depending on how the diene motif is tethered to the rest of the substrate - type I are tethered at the 1-position of the diene and type II at the 2-position. While the type I IMDA has been used to great success, the molecular scaffolds accessible by type II IMDAs are limited by the strain inherent in the formation of a sp2-carbon at a bridgehead position. Here, we describe a complementary approach that provides access to these structures through the C−C activation of cyclobutanones and their coupling with olefins. Various alkenes have been coupled with cyclobutanones to provide a range of bridged skeletons. The ketone group of the products serves as a convenient handle for downstream functionalization.
The intramolecular Diels-Alder (IMDA) reaction, a [4π+2π] cycloaddition, is one of the most widely utilized reactions for preparing ring systems.1–10 According to how the diene motif is tethered to the dienophile, IMDA reactions are classified into two types: type I and type II.7 While vast success has been achieved for applying type I-IMDA (tethered at the 1-position of the diene) in fused-ring syntheses, in contrast, much limited scaffolds can be prepared by type II-IMDA (tethered at the 2-position of the diene) due to Bredt’s rule11 (unfavorable sp2 carbon at the bridge-head position). For example, while 6–6 and 5–6 bridged rings are commonly found in various bioactive molecules (Fig. 1a), formation of 6–6 bridged rings ([3.3.1]-bicycle) via type II-IMDA was mainly restricted in gas phase12–14 and to our knowledge, no 5–6 bridged rings ([3.2.1]-bicycle) has been observed to date using such an approach (Fig. 1b). Stimulated by the challenge of type II-IMDA, in this communication, we describe an alternative [4+2] coupling method that is capable of providing type II-IMDA-like products via a cooperative C–C bond activation of cyclobutanones. Using this methodology, a complementary scope of bridged skeletons, including a variety of 6–6 and 5–6 bridged rings, can be accessed; furthermore, the ketone group of the products can serve as a convenient handle to access other functional groups or ring systems.
Figure 1. The challenge of bridged-ring synthesis.
a, Selected alkaloid natural products with bridged-ring substructures. b, Comparison of the type II IMDA reaction - which is synthetically limited by the incipient strain in an unsaturated bridgehead carbon - and the approach described in this work. c, Previous work on metal-catalysed C−C activation of cyclobutanones towards coupling and potential challenges due to the decarbonylation of the ketones.
Results and discussion
C–C bond activation/functionalization recently merged a useful method for synthesizing complex scaffolds from relatively simpler starting materials.15–29 In particular, bridged-ring synthesis can be benefited by this strategy. The intramolecular insertion of alkynes into benzocyclobutendione C–C bonds was first reported by Liebeskind using a stoichiometric Co-complex (Fig. 1c).30 Seminal work by Murakami/Ito described intramolecular insertions of styrene-type olefins into cyclobutanones catalyzed by either cationic Rh1 or Ni0, albeit limited to benzo-fused skeletons (Fig. 1c).31–32 One key challenge for developing cyclobutanone-olefin couplings via metal-mediated oxidative addition into C–C bonds is the competing decarbonylation reaction (Fig. 1c), which leads to either ring contraction or fragmentation (for cyclobutanone activations via β-carbon elimination, see refs 32–39).31 Therefore, in order to develop a general cyclobutanone-olefin coupling that is broadly applicable for synthesizing bridged type II-IMDA-like products, the decarbonylation challenge has to be overcome and the scope of the olefin substrates (e.g. both aryl and alkyl substituted alkenes) as well as the variety of the bridged-scaffolds must be extended.
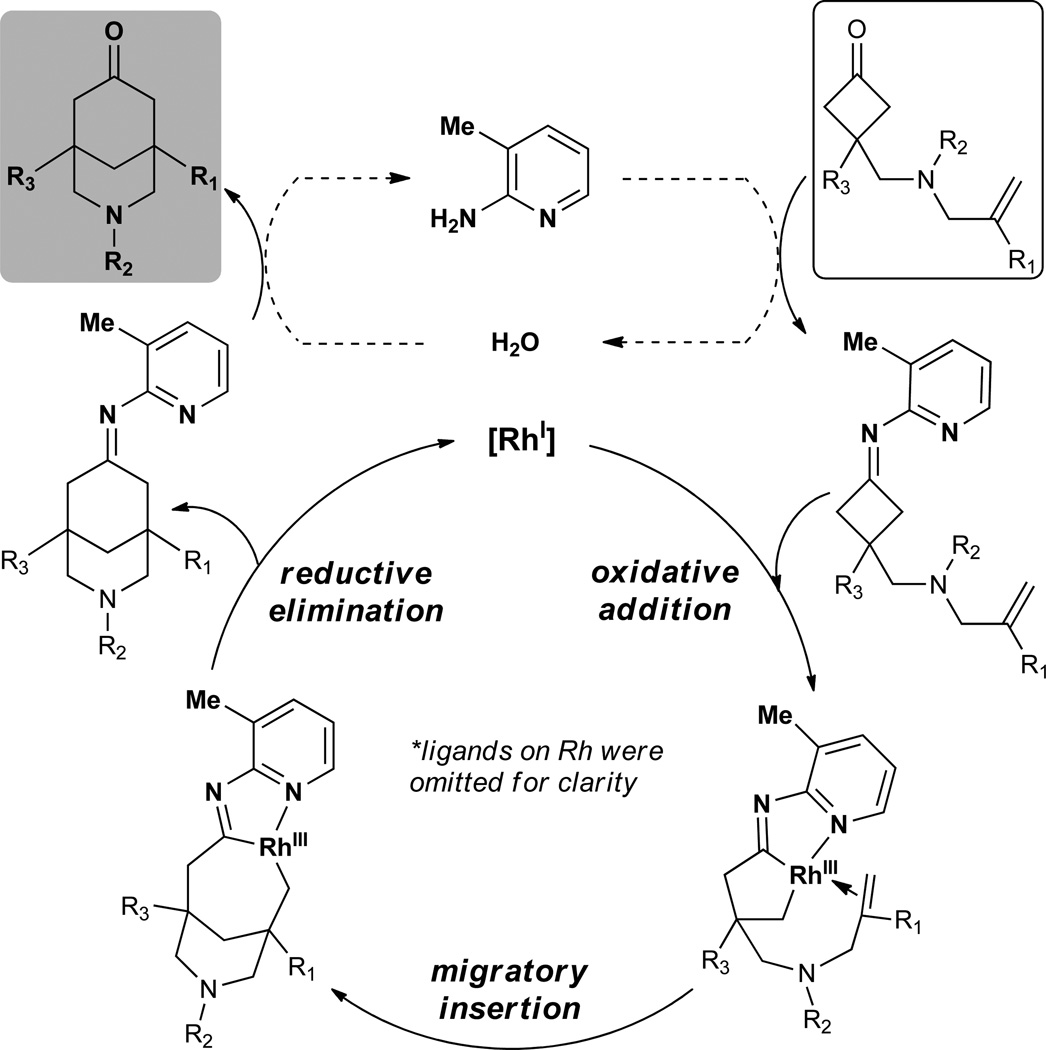
Our strategy is inspired by a “cofactor”-assisted C–C activation mode initially developed by Jun,40–42 which utilizes 2-amino-3-methylpyridine as a co-catalyst to generate an imine intermediate that serves as a directing group for cleaving the imine α C–C bond. This strategy has been effectively utilized to cleave medium to large cyclic ketimines in the presence of alkenes to afford ring-opened products (Fig. 1c). However, to the best of our knowledge, utilization of this mode in small-ring activation has not been reported previously. We hypothesized that employment of 2-amino-3-methylpyridine as a co-catalyst would benefit the desired intramolecular cyclobutanone-olefin coupling, depicted in Fig. 2. The amine would first form an imine with the cyclobutanone, which would then direct C–C cleavage through forming a chelation complex with the metal (e.g. Rh). Subsequent olefin migratory insertion followed by reductive elimination is expected to provide the bridged scaffold and regenerate the metal catalyst. Finally, the resulting imine can be hydrolyzed to give the bridged-ketone product and 2-amino-3-methylpyridine, which can be recycled. Hence, this strategy, distinct from the previous cyclobutanone activations,31–32, 28 can ease the C–C cleavage but more importantly prevent the aforementioned decarbonylation problem, because the carbonyl group would be in situ protected by the imine formation. Moreover, in principle, both the transition metal and the aminopyridine can be catalytic.
Figure 2. Proposed catalytic cycle.
The key features include using metal-ligand cooperative activation of cyclobutanones and in situ carbonyl group protection to avoid decarbonylation.
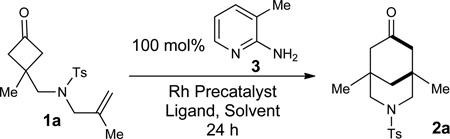
To test our hypothesis, cyclobutanone 1a was used as the model substrate, which was readily prepared in three steps from inexpensive commercially available materials. In the presence of 3-methyl-2-aminopyridine (3), a variety of Rh precatalysts, ligands and solvents were examined (for details, see supplementary information). The conditions (cationic Rh with dppp) that gave the best results in the previous example (Fig. 1c, Murakami/Ito)31 did not provide any of the desired bicycle (entry 1, Table 1). However, [Rh(COD)Cl]2 was found to be a promising precatalyst and the desired bridged bicycle (3-azabicyclo[3,3,1]nonanone) 2a43–47 was obtained albeit in low yields (entry 2). The solvent effect was next evaluated and 1,4-dioxane proved to be the best solvent (entries 3–5). While the yield of bicycle 2a can be improved by adding more COD ligand (entry 6), employment of a monodentate electron-deficient phosphine ligand was found more effective likely due to that the migratory insertion and reductive elimination steps can be accelerated with more π-acidic ligands (entries 7–9). Use of bidentate ligands, such as dppp and dppb, showed no catalytic activity. [Rh(COD)Cl]2 (10 mol %) with P(3,5-C6H3(CF3)2)3 (22 mol %) was found to give full conversion with an 82% isolated yield of product 2a (entry 9). Use of a catalytic amount of cofactor 3 (20 mol %) is also feasible albeit giving a slightly lower yield (76%) with extended reaction time (entry 10). Ultimately, use of 5 mol% [Rh(C2H4)2Cl]2 (10 mol% total on Rh) and 24 mol% P(3,5-C6H3(CF3)2)3 provided aza[3,3,1]nonanone 2a in 87% isolated yield (entry 11).
Table 1.
Selected optimization studies
 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Catalyst | Ligand/Additive | Solvent | Temp. (°C) |
Yield (%)* |
| 1 | 5 mol% [Rh(nbd)dppp]PF6 |
10 mol% BHT |
Xylenes | 130 | 0 |
| 2 | 10 mol% [Rh(COD)Cl]2 |
Toluene | 130 | <5 | |
| 3 | 10 mol% [Rh(COD)Cl]2 |
CIPh | 150 | 23(34) | |
| 4 | 10 mol% [Rh(COD)Cl]2 |
Xylenes | 150 | 27(30) | |
| 5 | 10 mol% [Rh(COD)Cl]2 |
1,4-Dioxane | 150 | 43(51) | |
| 6 | 10 mol% [Rh(COD)Cl]2 |
20 mol% COD |
1,4-Dioxane | 150 | 47(57) |
| 7 | 10 mol% [Rh(COD)Cl]2 |
20 mol% P(C6F5)3 |
1,4-Dioxane | 150 | 58(65) |
| 8 | 10 mol% [Rh(COD)Cl]2 |
10 mol% P(3,5-C6H3(CF3)2)3 |
1,4-Dioxane | 150 | 67(74) |
| 9 | 10 mol% [Rh(COD)Cl]2 |
22 mol% P(3,5-C6H3(CF3)2)3 |
1,4-Dioxane | 150 | 82 |
| 10 | 10 mol% [Rh(COD)Cl]2† |
22 mol% P(3,5-C6H3(CF3)2)3 |
1,4-Dioxane | 150 | 76(88) |
| 11 |
5 mol% [Rh(C2H4)2Cl]2 |
24 mol% P(3,5-C6H3(CF3)2)3§ |
1,4-Dioxane | 150 | 87 |
| 12 | 5 mol% [Rh(C2H4)2Cl]2‡ |
24 mol% P(3,5-C6H3(CF3)2)3§ |
1,4-Dioxane | 150 | 0‖ |
Isolated yield; numbers in parentheses are brsm yield.
20 mol% 3 was used with 71 h reaction time.
no 3 was added.
The reaction time was 48 h.
Decarbonylation products were observed as an inseperable mixture.
The use of cofactor 3 was critical. In the absence of 3, no [4+2] product was observed; decarbonylation products and the Rh-carbonyl complex (a dead catalyst, see supplementary information) can be detected by LCMS, HRMS and 1H-NMR (entry 12). This control experiment strongly supports our hypothesis that decarbonylation can be inhibited by using 2-amino-3-methylpyridine (vide supra). The structure of bridged-bicycle 2a was unambiguously confirmed by 1H, 13C NMR, IR, HRMS and X-ray crystallography. Given that the nitrogen-containing scaffold was obtained when the nitrogen-tether was employed, we expect this method can potentially be useful for alkaloid synthesis (Fig. 1a).
With the optimized conditions in hand, we next investigated the substrate scope (Table 2). In general, cyclobutanones tethered with 1,1-disubstituted olefins were converted into the corresponding 3-azabicyclo[3,3,1]nonanones smoothly. Not surprisingly, increasing the steric bulk on the olefin substituent from methyl to isopropyl to cyclopentyl slowed the reaction (entries 1–5), but the desired bridged bicycles were all nevertheless obtained in good to modest yields. Monosubstituted olefins can also insert into the C–C bond of cyclobutanones efficiently (entries 6 and 7). Changing the protecting group on the nitrogen from Ts to carbamate (CO2Me) did not significantly affect the reactivity (entry 7 vs 6). Aryl-substituted olefins were found to be more challenging substrates likely due to their stability issue under the reaction conditions; nevertheless, it is encouraging to note that they can still participate in this transformation, albeit with relatively lower efficiency. The more electron-rich aryl olefins provided much higher yields than the corresponding electron-poor substrates (entries 8–10). Changing the quaternary carbon substitution (from Me to Et) on cyclobutanones did not significantly affect the reactivity (entry 11).
Table 2.
Substrate Scope*
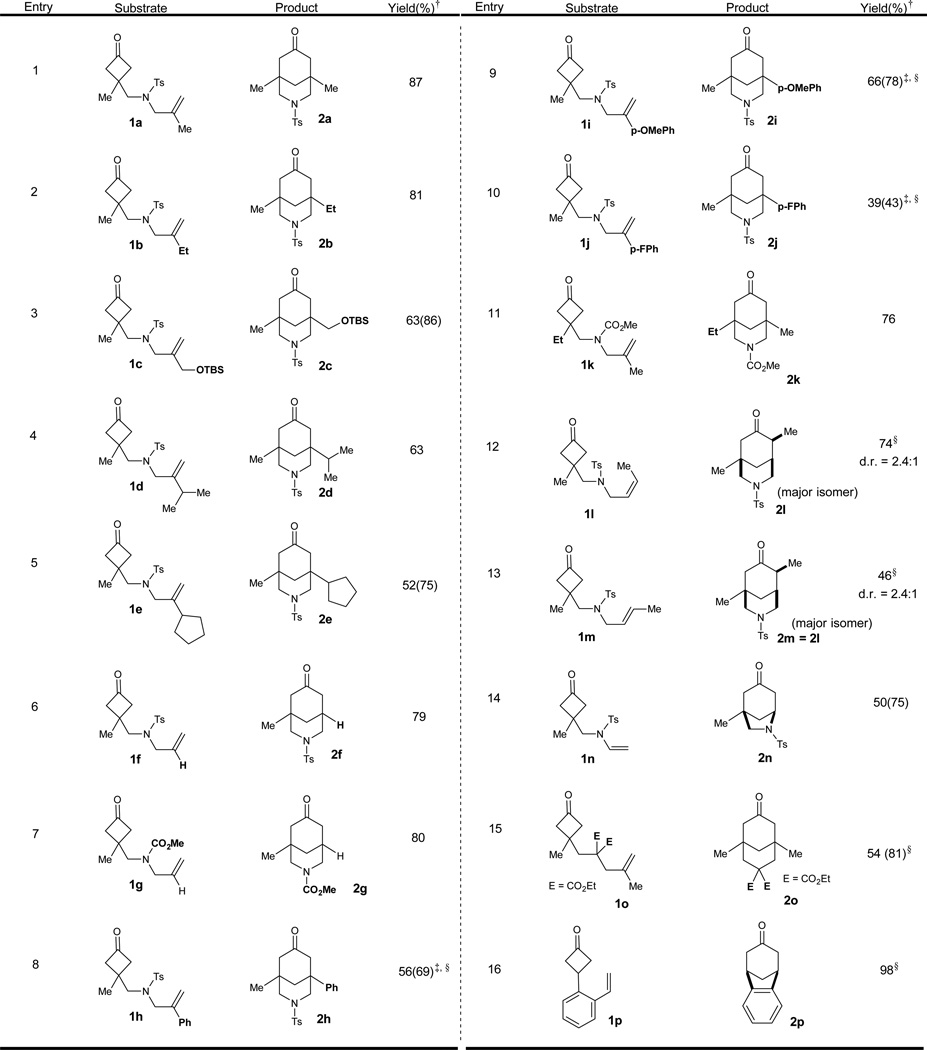 |
Reaction condition: [Rh(C2H4)2Cl]2 (5 mol%), P(3,5-C6H3(CF3)2)3 (24 mol%), 3 (100 mol%), 1,4-dioxane, 150 °C, 48 h.
Isolated yield; numbers in parentheses are brsm yield.
[Rh(C2H4)2Cl]2 (10 mol%) and P(3,5-C6H3(CF3)2)3 (48 mol%) were used.
24 h.
Both cis and trans-disubstituted olefins are suitable substrates, and higher reactivity was observed with the cis substrate (entries 12 and 13). Both substrates 1l and 1m provided the products with the same diastereomeric ratio (dr), probably due to an enamine equilibration. Besides forming 6–6 bridged [3.3.1] systems, the 5–6 bridged [3.2.1] scaffolds can also be obtained using this strategy. The vinyl sulfonamide 1n can participate to give the desired bridged ring (2n) (entry 14). In addition, substrates with all-carbon linkages were also found suitable (entries 15 and 16). It is interesting to note that with 1o as the substrate, a stable enamine derivative of 2o (with 2-amino-3-methylpyridine 3) can be isolated as the major product, which was confirmed by X-ray crystallography (see supplementary information). Subsequent hydrolysis with diluted acetic acid provided the ketone 2o in 54% (81% brsm) yield (entry 15). The substrate with an arene linkage (1p)31 provided the desired benzo-bicycle (2p) in nearly a quantitative yield under the standard conditions, suggesting a potentially broad substrate scope (entry 16).
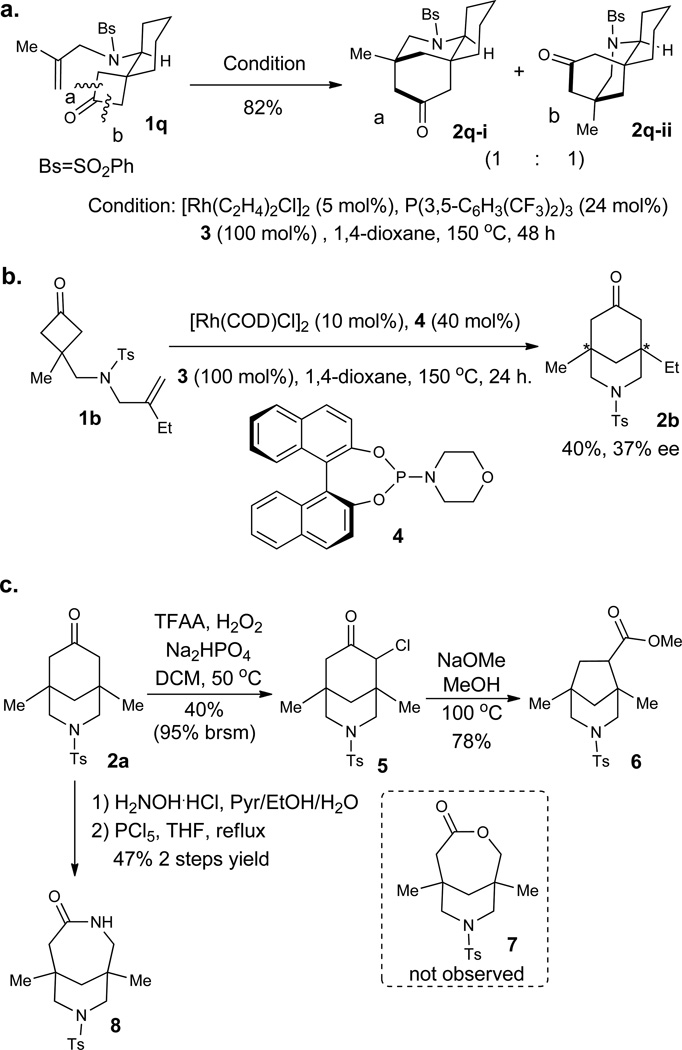
Substrate 1q with a spirocyclic center was also investigated for this transformation (Fig. 3a). Two diastereomers of the desired product were obtained due to the diastereotopic difference between the two α-C–C bonds. The products 2q-i and 2q-ii contain interesting tricyclic bridged and fused scaffolds, which have been found in a number of aconitum/delphinium alkaloids (Fig. 1a, vide supra). Structures of both products were unambiguously confirmed by X-ray crystallography of their 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone derivatives (see supplementary information). Furthermore, preliminary studies have revealed that chiral phosphoramidite ligands, such as 4, effect the desymmetrization of cyclobutanone 1b with promising levels of enantioselectivity (Fig. 3b, 37% ee).48–49 This result suggests that the “cofactor”-assisted C–C activation mode is amenable to asymmetric catalysis, and work on this topic is ongoing.
Figure 3. Potentials and applications in bridged-ring synthesis.
a, Construction of fused-bridged tricyclic structures. b, Potentials for developing an enantioselective transformation. c, Use of the carbonyl group in the product as a handle to access ring-contracted and expanded bridged rings.
Finally, we demonstrated the carbonyl group in the formed bridged bicycles can serve as a convenient handle to access other ring systems through either ring contraction or expansion (Fig. 3c). Treatment of 2a under Baeyer–Villiger oxidation conditions gave the α-chloroketone unexpectedly. Subsequent Favorskii rearrangement afforded the ring-contraction product (6) in 78% yield. Oxime formation followed by Beckmann rearrangement provided the ring-expansion product (7–6 bridged amide, 8) uneventfully.
Conclusion
In summary, we have developed a unique strategy to enable a “saturated analogue” of type II-IMDA reaction between cyclobutanones and simple alkenes via a Rh-catalyzed “cofactor”-assisted C–C activation approach. Substrates with different tethers and olefin substitutions (both aryl and alkyl alkenes) underwent this transformation. The resulting ketone bicycles can be readily further functionalized through carbonyl chemistry. While sharing a common feature to form 6-membered rings, this approach can provide scaffolds that are difficult to prepare using conventional IMDA reactions. Another advantage is that unactivated alkyl or aryl-substituted alkenes, instead of Michael acceptors (typically used in type-II IMDA)7, can be used as coupling partners. We expect the strategy developed here may provide inspirations for designing new tactics to synthesize complex natural products and other bioactive molecules.
Methods
In a nitrogen filled glove box, a 1-dram vial was charged with [Rh(C2H4)2Cl]2 (1.9 mg, 5 mol%), tris[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]phosphine (16 mg, 24 mol%) and 2-amino-3-picoline (10 μl, 0.1 mmol). A solution of starting material 1a (32 mg, 0.1 mmol) in dioxane (1 ml, 0.1 M) was added and the 1-dram vial was capped and the solution was maintained at 152 °C for 48 h. The reaction was removed from the glove box and purified by flash chromatography. The product 2a was obtained as a bright orange solid (28 mg, 87%). The procedure to prepare compound 2a is generally representative for all the products shown in Table 2. Any deviations from this protocol are specified in the footnote of the table.
Acknowledgements
We thank CPRIT (R1118) for a startup fund, NIH (1R01GM109054-01) and the Welch Foundation (F 1781) for research grants. G. D. is a Searle Scholar. We thank Profs. Sessler, Siegel and Anslyn for loaning chemicals. Dr. Lynch is acknowledged for X-ray crystallography. We also thank Johnson Matthey for a donation of Rh salts. Chiral Technologies is acknowledged for a donation of chiral HPLC columns. Mr. Thompson is thanked for proof reading of this manuscript.
Footnotes
Author Contributions
H.M.K. and G.D. conceived and designed the experiments. H.M.K. performed the experiments. H.M.K and G.D. analysed the data. H.M.K. and G.D. co-wrote the manuscript.
References
- 1.Oppolzer W. Intramolecular [4+2] and [3+2] cycloadditions in organic synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1977;16:10–23. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Brieger G, Bennett JN. The intramoecular Diels-Alder reaction. Chem. Rev. 1980;80:63–97. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fallis AG. The intramolecular Diels-Alder reaction: recent advances and synthetic applications. Can. J. Chem. 1984;62:183–234. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Craig D. Sterochemical aspects of the intrmolecular Diels-Alder reaction. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1987;16:187–238. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Roush WR. In: Comprehensive Organic Synthesis. Trost BM, Fleming I, Paquette LA, editors. Vol. 5. Oxford, UK: Pergamon Press; 1991. pp. 513–550. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Fallis AG. Harvesting Diels and Alder’s Garden: synthetic investigations of intramolecular [4+2] cycloadditions. Acc. Chem. Res. 1999;32:464–474. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bear BR, Sparks SM, Shea KJ. The type 2 intramolcular Diels-Alder reaciotn: synthesis and chemistry of bridgehead alkene. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001;40:820–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Marsault E, Toro A, Nowak P, Deslongchamps P. The transannular Diels-Alder strategy: applications to total synthesis. Tetrahedron. 2001;57:4243–4260. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Suzuki Y, Murata T, Takao K, Tadano K. The intramolecular Diels-Alder strategy: applications to total synthesis of natural products. J. Synth. Org. Chem. Jpn. 2002;60:679–690. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ciganek E. The Intramolecular Diels–Alder Reaction. Organic Reactions. 2004:1–374. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bredt J. Über sterische Hinderung in Brückenringen (Bredtsche Regel) und über die meso-trans-Stellung in kondensierten Ringsystemen des Hexamethylens. Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1924;437:1–13. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Shea KJ, Wise S. Intramolecular Diels-Alder reacition. A new entry into brigehead bicyclo[3.n.1]alkenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1978;100:6519–6521. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Shea KJ, Wise S. Intramolecular diels-alder cycloadditions. Synthesis of substituted derivatives of bicyclo[3.n.1]bridgehead alkenes. Tetrahedron Lett. 1979;20:1011–1014. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Shea KJ, et al. Applications of the intramolecular Diels-Alder reaction to the formation of strained molecules. Synthesis of bridgehead alkenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982;104:5708–5715. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jones WD. The fall of the C-C bond. Nature. 1993;364:676–677. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Murakami M, Ito Y. Cleavage of carbon-carbon single bonds by transition metals. Top. Organomet. Chem. 1999;3:97–129. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rybtchiski B, Milstein D. Metal insertion into c-c bonds in solution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999;38:870–883. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19990401)38:7<870::AID-ANIE870>3.0.CO;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Perthuisot C, et al. Cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond in biphenylene using transition metals. J. Catal. Mol. A. 2002;189:157–168. [Google Scholar]
- 19.van der Boom ME, Milstein D. Cyclometalated phosphine-based pincer complexes: Mechanistic insight in catalysis, coordination, and bond activation. Chem. Rev. 2003;103:1759–1792. doi: 10.1021/cr960118r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jun C-H. Transition metal-catalyzed carbon–carbon bond activation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2004;33:610–618. doi: 10.1039/b308864m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Miura M, Satoh T. Catalytic processes involving β-carbon elimination. Top. Organomet. Chem. 2005;14:1–20. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jun C-H, Park JW. Directed C-C bond activation by transition metal complexes. Top. Organomet. Chem. 2007;24:117–143. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Necas D, Kotora M. Rhodium-Catalyzed C-C Bond Cleavage Reactions. Curr. Org. Chem. 2007;11:1566–1592. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Crabtree RH. The organometallic chemistry of alkanes. Chem. Rev. 1985;85:245–269. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kondo T, Mitsudo TA. Ruthenium-catalyzed reconstructive synthesis of functional organic molecules via cleavage of carbon-carbon bonds. Chem. Lett. 2005;34:1462–1467. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ruhland K. Transition-metal-mediated cleavage and activation of C-C single bonds. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012;2012:2683–2706. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Korotvicka A, Necas D, Kotora M. Rhodium-catalyzed C-C bond cleavage reactions - an update. Curr. Org. Chem. 2012;16:1170–1214. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Seiser T, Saget T, Tran DN, Cramer N. Cyclobutanes in catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011;50:7740–7752. doi: 10.1002/anie.201101053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Dermenci A, Dong G. Decarbonylative C-C bond forming reactions mediated by transition metals. Sci. China Chem. 2013;56:685–701. [Google Scholar]
- 30.South MS, Liebeskind LS. Regiospecific total synthesis of (±)-nanaomycin A using phthaloylcobalt complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984;106:4181–4185. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Murakami M, Itahashi T, Ito Y. Catalyzed intramolecular olefin insertion into a carbon–carbon single bond. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002;124:13976–13977. doi: 10.1021/ja021062n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Murakami M, Ishida N, Miura T. Solvent and ligand partition reaction pathways in nickel-mediated carboxylation of methylenecyclopropanes. Chem. Commun. 2006:643–645. doi: 10.1039/b515684j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Murakami M, Ashida S, Matsuda T. Two-carbon ring expansion of cyclobutanone skeletons by nickel-catalyzed intermolecular alkyne insertion. Tetrahedron. 2006;62:7540–7546. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Murakami M, Ashida S, Matsuda T. Nickel-catalyzed intermolecular alkyne insertion into cyclobutanones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005;127:6932–6933. doi: 10.1021/ja050674f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Murakami M, Ashida S. Nickel-catalysed intramolecular alkene insertion into cyclobutanones. Chem. Commun. 2006:4599–4601. doi: 10.1039/b611522e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ashida S, Murakami M. Nickel-catalyzed [4+2+2]-type annulation reaction of cyclobutanones with diynes and enynes. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2008;81:885–893. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Liu L, Ishida N, Murakami M. Atom- and step-economical pathway to chiral benzobicyclo[2.2.2]octenones through carbon-carbon bond cleavage. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012;51:2485–2488. doi: 10.1002/anie.201108446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kumar P, Louie J. A single step approach to piperidines via Ni-catalyzed β-carbon elimination. Org. Lett. 2012;14:2026–2029. doi: 10.1021/ol300534j. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ishida N, Yuhki T, Murakami M. Synthesis of enantiopure dehydropiperidinones from α-amino acids and alkynes via azetidin-3-ones. Org. Lett. 2012;14:3898–3901. doi: 10.1021/ol3016447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lee H, Jun C-H. Catalytic carbon-carbon bond activation of unstrained ketone by soluble transition-metal complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999;121:880–881. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Park YJ, Park J-W, Jun C-H. Metal-organic cooperative catalysis in C-H and c-c bond activation and its concurrent recovery. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008;41:222–234. doi: 10.1021/ar700133y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Jun C-H, Lee H, Lim S-G. The c-c bond activation and skeletal rearrangement of cycloalkanone imine by Rh(I) catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001;123:751–752. doi: 10.1021/ja0033537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Luo S-P, Guo L-D, Gao L-H, Li S, Huang P-Q. Toward the total synthesis of haliclonin A: construction of a tricyclic substructure. Chem. Eur. J. 2013;19:87–91. doi: 10.1002/chem.201203203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mazurov AA, et al. Novel nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists containing carbonyl moiety as a hydrogen bond acceptor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013;23:3927–3934. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.04.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Cheng X, Waters SP. Pyridone annulation via tandem curtius rearrangement/6π-electrocyclization: total synthesis of (−)-lyconadin C. Org. Lett. 2013;15:4226–4229. doi: 10.1021/ol401954f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Breining SR, et al. Structure-activity studies of 7-heteroaryl-3-azabicyclo[3.3.1]non-6-enes: a novel class of highly potent nicotinic receptor ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2012;55:9929–9945. doi: 10.1021/jm3011299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Jirgensons A, Kauss V, Mishnev AF, Kalvinsh I. The synthesis of 3-amino-methylbicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes: Endo-selectivity in the Ritter reaction of 1,3,5,7 α-tetramethylbicyclo[3.3.1]nonan-3-ol. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1999;1:3527–3530. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Parker E, Cramer N. Asymmetric Rhodium(I)-Catalyzed C–C Activations with Zwitterionic Bis-phospholane Ligands. Organometallics. 2014;33:780–787. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Souillart L, Parker E, Cramer N. Highly enantioselective rhodium(I)-catalyzed activation of enantiotopic cyclobutanone c-c bonds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014;53:3001–3005. doi: 10.1002/anie.201311009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]