Abstract
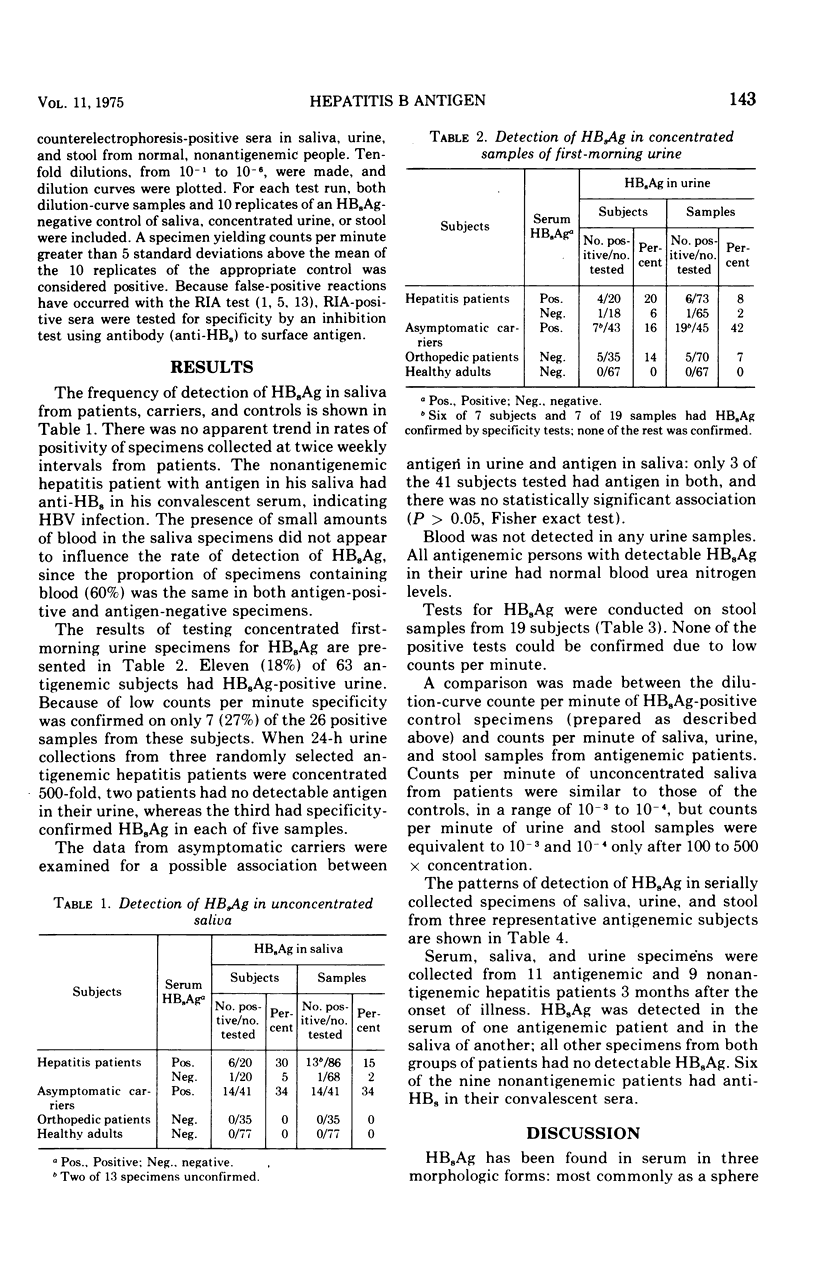
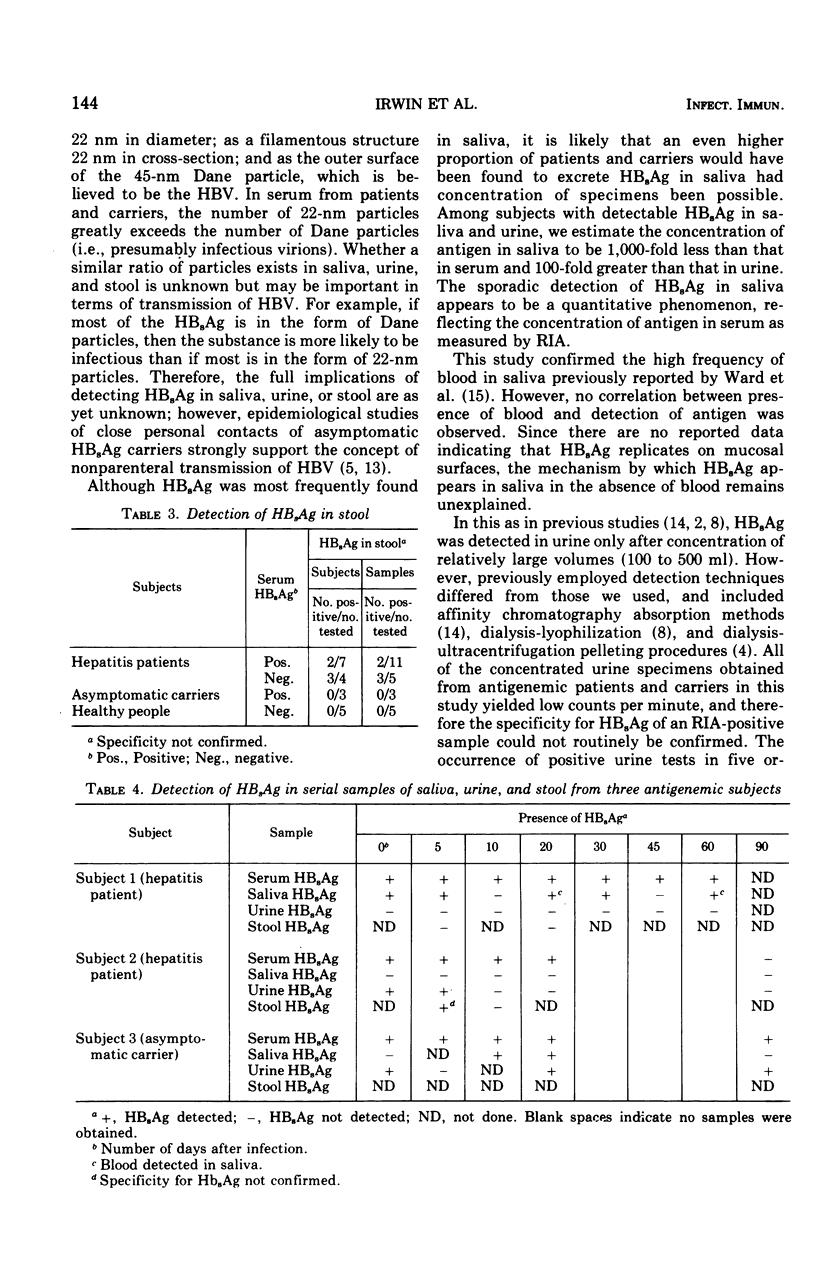
A survey of hepatitis B patients, asymptomatic hepatitis B antigen (HBsAg) carriers, and control subjects was conducted to determine the relationship between antigenemia and antigen excretion in saliva, urine, and stool. Radioimmunoassay was used to detect HBsAg. Specificity-confirmed HBsAg was detected in the saliva of 6 (30%) of 20 antigenemic patients, 1 (5%) of 20 nonantigenemic patients, 14 (34%) of 41 carriers, and 0 of 112 controls. HBsAg was detected in urine only after 100-fold concentration of first-morning specimens. Specificity-confirmed HBsAg was present in the urine of 7 (16%) of 43 carriers; unconfirmed HBsAg was found in the urine of 5 (13%) of 38 patients and 5 (5%) of 112 controls. Unconfirmed HBsAg was detected in concentrated stool specimens from 5 (46%) of 11 patients and 3 of 8 carriers and controls. Longitudinally collected specimens from antigenemic subjects showed no consistent patterns of antigen excretion.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alter H. J., Holland P. V., Purcell R. H., Gerin J. L. The Ausria test: critical evaluation of sensitivity and specificity. Blood. 1973 Dec;42(6):947–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apostolov K., Bauer D. J., Selway J. W., Fox R. A., Dudley F. J., Sherlock S. Australia antigen in urine. Lancet. 1971 Jun 19;1(7712):1274–1275. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91784-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grob P. J., Jemelka H. Faecal S.H. (Australia) antigen in acute hepatitis. Lancet. 1971 Jan 30;1(7692):206–208. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90949-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heathcote J., Cameron C. H., Dane D. S. Hepatitis-B antigen in saliva and semen. Lancet. 1974 Jan 19;1(7847):71–73. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92289-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irwin G. R., Allen A. M., Bancroft W. H., Karwacki J. J., Pinkerton R. H., Russell P. K. Hepatitis B antigen and antibody. Occurrence in families of asymptomatic HB AG carriers. JAMA. 1974 Mar 4;227(9):1042–1043. doi: 10.1001/jama.227.9.1042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krugman S., Giles J. P., Hammond J. Infectious hepatitis. Evidence for two distinctive clinical, epidemiological, and immunological types of infection. JAMA. 1967 May 1;200(5):365–373. doi: 10.1001/jama.200.5.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling C. M., Overby L. R. Prevalence of hepatitis B virus antigen as revealed by direct radioimmune assay with 125 I-antibody. J Immunol. 1972 Oct;109(4):834–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzur S. Menstrual blood as a vehicle of Australia-antigen transmission. Lancet. 1973 Apr 7;1(7806):749–751. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogra P. L. Immunologic aspects of hepatitis-associated antigen and antibody in human body fluids. J Immunol. 1973 May;110(5):1197–1205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piazza M., Di Stasio G., Maio G., Marzano L. A. Hepatitis B antigen inhibitor in human faeces and intestinal mucosa. Br Med J. 1973 May 12;2(5862):334–337. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5862.334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M., Brotman B., Jass D., Ikram H. Specificity of the direct solid-phase radioimmunoassay for detection of hepatitis-B antigen. Lancet. 1973 Jun 16;1(7816):1346–1350. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91674-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sgouris J. T. Limitations of the radioimmunoassay for hepatitis B antigen (HB Ag). N Engl J Med. 1973 Jan 18;288(3):160–161. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197301182880317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmuness W., Prince A. M., Hirsch R. L., Brotman B. Familial clustering of hepatitis B infection. N Engl J Med. 1973 Nov 29;289(22):1162–1166. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197311292892203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R., Borchert P., Wright A., Kline E. Hepatitis B antigen in saliva and mouth washings. Lancet. 1972 Oct 7;2(7780):726–727. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



