The finding that monoprotic carborane acids of the type H(CHB11X11) (X=Cl, Br) are the strongest pure acids isolated to date[1, 2] suggests that the analogous diprotic boron acids H2(B12X12) may have comparable or even higher acidity. The hydrated acids [H(H2O)n+]2[B12X122−] were prepared many years ago from aqueous solutions of their alkali metal salts using an ion-exchange resin in acid form[3] and were shown to be slightly stronger acids than H2SO4 in aqueous solution. However, the anhydrous acids are unknown. Can they be synthesized? Are they superacids? Of further interest is that the B12H122− ion starting material is considerably cheaper than the isoelectronic CB11H12− carborane ion, so there is potential for cost savings relative to carborane acids, which are too expensive for widespread use.
An indication that the all-boron acids H2(B12X12) should show comparable acid strengths to their analogous carborane acids H(CHB11X11) comes from the position of their anions on the ν(NH) basicity scale. In this ranking, the N–H stretching frequencies of contact-ion-pair trioctylammonium salts Oct3N+–H⋯anion− are compared in CCl4 solution.[2, 4] The higher the ν(NH) frequency, the lower the basicity of the anion. As shown in Table 1, the B12Cl122− salt has almost the same ν(NH) frequency as the CHB11Cl11− salt. This result is surprising inasmuch as the dinegative charge on the B12Cl122− ion might have been expected to render it more basic than the uninegative CHB11Cl11− ion. It suggests that chloride substituents on both anions form an effective screen for negative charge that is delocalized and buried within the icosahedral cage. Similar conclusions can be drawn from the data on the B12Br122− ion, although low solubility of its trioctylammonium salt in CCl4 allow comparisons to be made only for crystalline salts. It is also clear from the data in Table 1 that the boron anions are much less basic than the (HSO4)22− ion, so their conjugate acids are expected to be much stronger than 100% H2SO4, whose acidity (H0=−12 on the Hammett scale) defines the onset of superacidity.
Table 1.
ν(NH) frequencies of tri-n-octylammonium salts (in cm−1).
| Anion | ν(NH) in CCl4 | ν(NH) solid |
|---|---|---|
| CHB11Cl11−[a] | 3163 | 3180 |
| B12Cl122− | 3165 | 3167 |
| CHB11Br11−[a] | 3140 | 3150 |
| B12Br122− | insoluble | 3140 |
| (HSO4)22− | 3021, 2660 | 3080 |
Ref. [4].
The synthetic pathway to the anhydrous diprotic acids exploits multistep metathesis reactions similar to those used in the preparation of H(CHB11Cl11).[1] Starting with the silver salts of B12Br122− and B12Cl122−, their respective trityl (C-(C6H5)3+) salts [Eq. (1)] and triethylsilylium compounds [Eq. (2)] have been prepared and characterized by X-ray crystallography.[5]
| (1) |
| (2) |
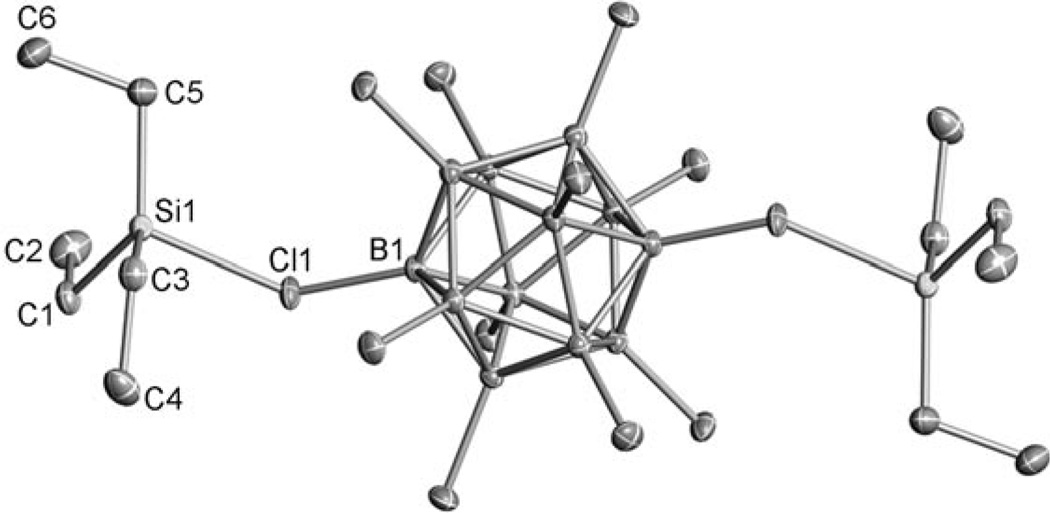
The structures of the trityl salts are unremarkable and similar to that of the B12F122− ion,[6] but those of the triethylsilylium derivatives are informative with regard to how the dianions act as Lewis bases. As illustrated in Figure 1 for the B12Cl122− ion, the triethylsilyl groups adopt 1,12 or trans positions, presumably to minimize electrostatic repulsions between the electropositive silicon centers and to pack most efficiently in the crystal lattice. The sum of the C-Si-C angles, whose approach towards 360° is used as a measure of developing silylium ion character in an R3Siδ+ moiety,[7, 8] is 348.3°. This value is close to 349.5° in Et3Si(CHB11Cl11),[9] thus indicating similar low Lewis basicities of the B12Cl122− and CHB11Cl11− ions.
Figure 1.
X-ray crystal structure of (Et3Si)2(B12Cl12).
A further illustration of the comparable Lewis basicities of the B12Cl122− and CHB11Cl11− ions comes from the formation of the hydride-bridged cation [Et3Si-H-SiEt3]2− [B12Cl12] when excess silane is used in Equation (2). This cation forms reversibly when silane competes with the anion for coordination to the Et3Si+ moiety and is readily identified by its ν(Si-H-Si) band at approximately 1870 cm−1 in the IR spectrum of the isolated solid.[9] Similarly, halocarbon solvents such as o-dichlorobenzene (ODCB) are sufficiently basic to compete with the anion for coordination to the Et3Si+ moiety.[9] Since excess silane and solvent molecules can interfere with the subsequent formation of the unsolvated H2(B12X12) acids, thus lowering their purity, considerable care must be taken to remove them from the silylium derivatives by drying under vacuum. Such contaminants include toluene that can be carried through from the trityl salt preparation.
Silylium ion character in the (Et3Si)2B12X12 derivatives is sufficiently strong that chloride abstraction from anhydrous HCl proceeds readily according to Equation (3) at sub ambient temperatures to give the desired acids H2(B12X12) as nearly colorless solids in essentially quantitative yields.
| (3) |
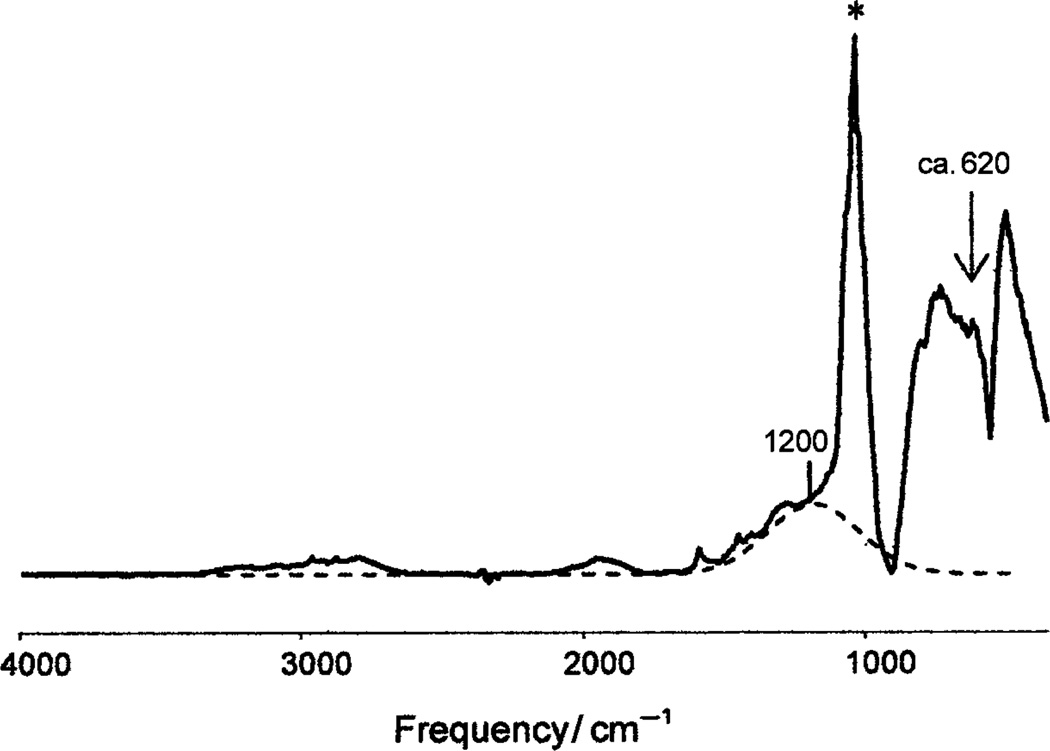
Both H2(B12Br12) and H2(B12Cl12) are distinctively characterized in their solid-state IR spectra by broad, low-energy absorptions associated with short, strong, symmetrical X-H-X hydrogen bonding.[10, 11] As shown in Figure 2, these bands appear at 1200 and approximately 620 cm−1 for H2(B12Cl12) compared to 1100 and 615 cm−1 in H(CHB11Cl11). In the analogous bromide, they appear at 1080 and approximately 570 cm−1. The lower-energy band is particularly strong, but its exact frequency is made uncertain by Evans holes.[11] Given the overarching tendency of strongly acidic protons to attain symmetrical (or nearly symmetrical) di-solvation,[10] and by analogy to H(CHB11Cl11) whose X-ray structure shows Cl-H+-Cl bridges in a 2D polymeric chain structure,[11] a 3D network structure with X-H+-X bridges is the only reasonable structure for H2(B12X12) acids. This 3D structure would also explain why these acids cannot be sublimed under vacuum up to 200°C for purification and possible single-crystal growth, even though carborane acids can be vaporized around 150°C.[11]
Figure 2.
IR spectrum of H2(B12Cl12) showing the two broad absorptions at 1200 (Gaussian fit shown by dashed line) and ca. 620 cm−1 (with Evans holes) characteristic of symmetrical Cl-H+-Cl bridge bonding. The major anion absorption is marked with an asterisk.
The acids have relatively low solubility in low-basicity solvents such as anhydrous liquid SO2, but the appearance of a downfield peak at δ=19.3 ppm in the 1H NMR spectrum of H2(B12Cl12) is consistent with ionization to the give the disolvated H(SO2)2+ ion.[11] The solid anhydrous acids are moisture-sensitive. As monitored by IR spectroscopy, the gradual appearance of broad ν(OH) bands in the range 3200–3600 cm−1 occurs as the broad bands associated with the acid X-H+-X group disappear, indicating the formation of H5O2+ and H7O3+ ions.[12]
The protonation of benzene has become a benchmark of superacidity above and beyond that of mineral acids.[2] The strongest traditional acids, triflic acid (H0=−14) and fluorosulfuric (H0=−15.1), do not protonate benzene, whereas carborane acids do.[13] This behavior indicates that the equivalent Hammett acidities of carborane acids must be −17 or greater. Like carborane acids, the Hammett acidities of the present acids cannot be measured directly because they are unavailable in liquid form.
Stirring a suspension of H2(B12X12) in the smallest possible volume of benzene (to minimize water contamination) converts the acids into slurries of their corresponding benzenium ion salts, formulated as [C6H7]2[B12X12]. The presence of the C6H7+ ion is established by IR spectroscopy, with diagnostic bands in the ν(CH) and ν(CC)/δ(CH)s regions. In particular, the ν(CH2) frequencies of the most acidic CH2 group at the protonated sp3 carbon atom appear as a broad absorption centered at 2733 cm−1 for X=Cl and 2664 cm−1 for X=Br. These frequencies are lower than those in the gas phase (2810, 2795 cm−1)[14] owing to H-bonding to halide atoms of the anions. The greater red shift for the bromide is consistent with the higher basicity of the B12Br122− ion relative to the B12Cl122− ion. As shown in Table 2, other identifying bands are all very close in frequency. IR bands attributable to X-H+-X bridged moieties are absent, thus indicating that H(B12X12)− ions, which would result from monoionization of the diprotic acids, must be absent. H2(B12X12) behaves as a diprotic acid: both hydrogen ions are sufficiently acidic to protonate benzene. The extraordinary stability of the B12X122− ions makes the isolation of the benzenium ion at room temperature straightforward. As expected for more basic arenes, the 2:1 arenium ion salts derived from protonating toluene and mesitylene can be isolated in a similar manner and characterized by IR spectroscopy (see the Supporting Information).
Table 2.
Frequencies of the C6H7+ ion as a function of counterion (in cm−1).
| Counterion | ν(CH2) (average) |
ν(CH)aromatic | ν(CC) + δ(CCH) |
|---|---|---|---|
| none[a] | 2810, 2795 (2803) | 3110, 3080 | |
| CB11H6Cl6−[b] | 2770, 2720 (2745) | 3100, 3072, 3040, 3028 | 1601 |
| B12Cl122− | 2753, 2713 (2733) | 3092, 3070, 3035 | 1600 |
| CB11H6Br6−[b] | 2757, 2714 (2736) | 3095, 3073, 3066, 3023 | 1600 |
| B12Br122− | 2664 | 3084, 3060, 3028, 3015 | 1597 |
In summary, the new anhydrous diprotic acids H2(B12X12) with X=Cl and Br have been prepared. They have comparable acidity to carborane acids H(CHB11X11). Because they protonate benzene, their acidities must be at least 105 greater than that of 100% H2SO4, that is, well into the superacidity region. These are the first examples of diprotic superacids, and the finding that both protons of H2(B12X12) are able to protonate benzene is significant inasmuch as the second ionization might be expected to be of lower strength than the first. Finally, the all-boron acids are less expensive to prepare than their analogous carborane acids, although this advantage is tempered by the generally lower solubilities of B12X122− salts compared to those of CHB11X11−.[15]
Supplementary Material
Footnotes
We thank Prof. Dr. E. S. Stoyanov for invaluable assistance with the IR measurements and their interpretation and Dr. Bruno Donnadieu for X-ray crystallographic support. This work was supported by the National Science Foundation (CHE-039878 to C.A.R. and an NSF Graduate Fellowship to A.A.).
Supporting information for this article is available on the WWW under http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/anie.200900214.
References
- 1.Juhasz M, Hoffmann S, Stoyanov ES, Kim K-C, Reed CA. Angew. Chem. 2004;116:5466–5469. doi: 10.1002/anie.200460005. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 5352 – 5355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Reed CA. Chem. Commun. 2005:1669–1677. doi: 10.1039/b415425h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Knoth WH, Miller HC, Sauer JC, Balthis JH, Chia YT, Muetterties EL. Inorg. Chem. 1964;3:159–167. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Stoyanov ES, Kim K-C, Reed CA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006;128:8500–8508. doi: 10.1021/ja060714v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.CCDC 721536, 721537, 721538 and 721539 ([trityl]2− [B12Br12]·2 toluene, [trityl]2[B12Cl12]·2ODCB, (Et3Si)2− (B12Br12)·ODCB, and (Et3Si)2(B12Cl12)) contain the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data can be obtained free of charge from The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre via www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/data_request/cif.
- 6.Ivanov SV, Miller SM, Anderson OP, Solntsev KA, Strauss SH. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003;125:4694–4695. doi: 10.1021/ja0296374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Reed CA. Acc. Chem. Res. 1998;31:325–332. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Küppers T, Bernhardt E, Eujen R, Willner H, Lehmann CW. Angew. Chem. 2007;119:6462–6465. doi: 10.1002/anie.200701136. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 6346 – 6349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hoffmann SP, Kato T, Tham FS, Reed CA. Chem. Commun. 2006:767–769. doi: 10.1039/b511344j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Stasko D, Hoffmann SP, Kim K-C, Fackler NLP, Larsen AS, Drovetskaya T, Tham FS, Reed CA, Rickard CEF, Boyd PDW. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002;124:13869–13876. doi: 10.1021/ja012671i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Stoyanov ES, Hoffmann SP, Juhasz M, Reed CA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006;128:3160–3161. doi: 10.1021/ja058581l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Stoyanov ES, Stoyanova IV, Tham FS, Reed CA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008;130:12128–12138. doi: 10.1021/ja803535s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Reed CA, Kim K-C, Stoyanov ES, Stasko D, Tham FS, Mueller LJ, Boyd PDW. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003;125:1796–1804. doi: 10.1021/ja027336o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Solcà N, Dopfer O. Angew. Chem. 2002;114:3781–3784. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 3628 – 3631. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Note added in proof: Parallel synthetic studies on the precursors to the acids have recently been published: Geis V, Guttsche K, Knapp C, Scherer H, Uzun R. Dalton Trans. 2009 doi: 10.1039/b821030f.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.