Abstract
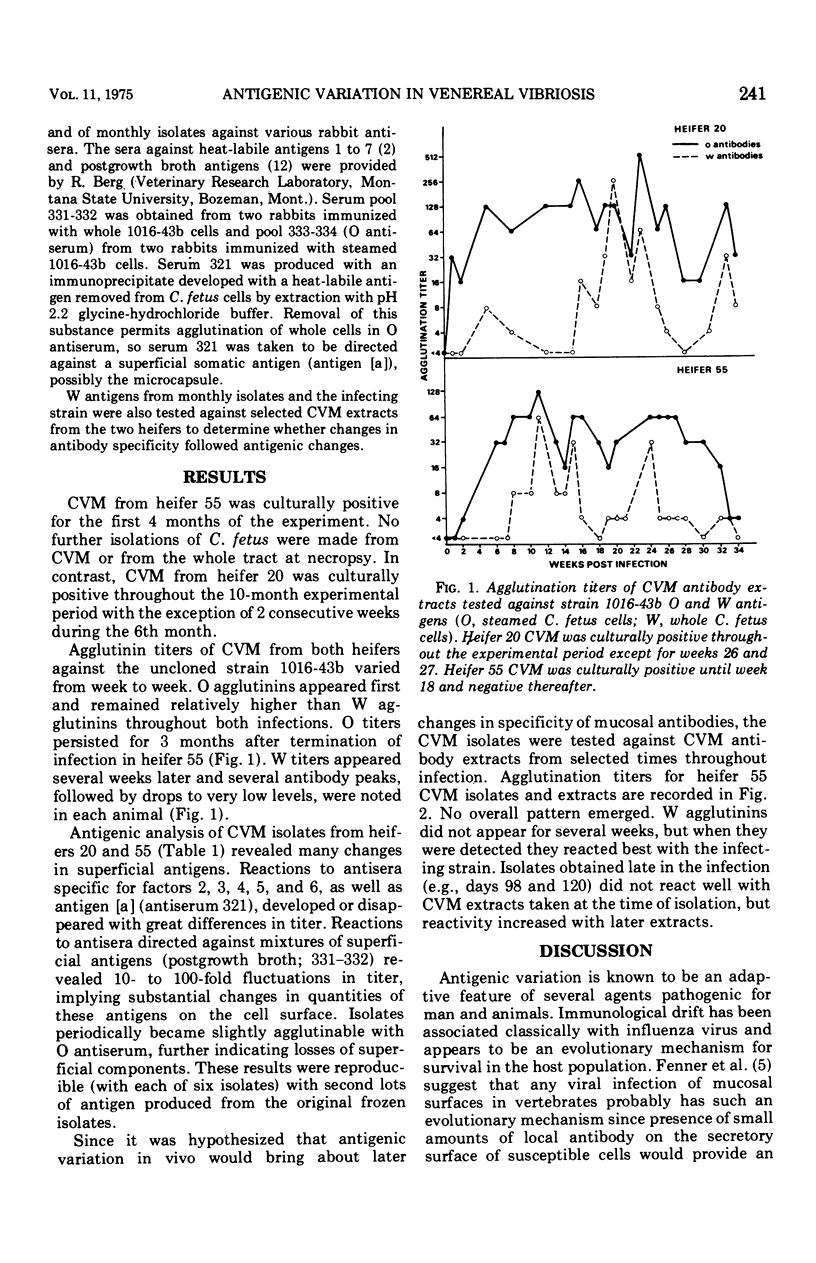
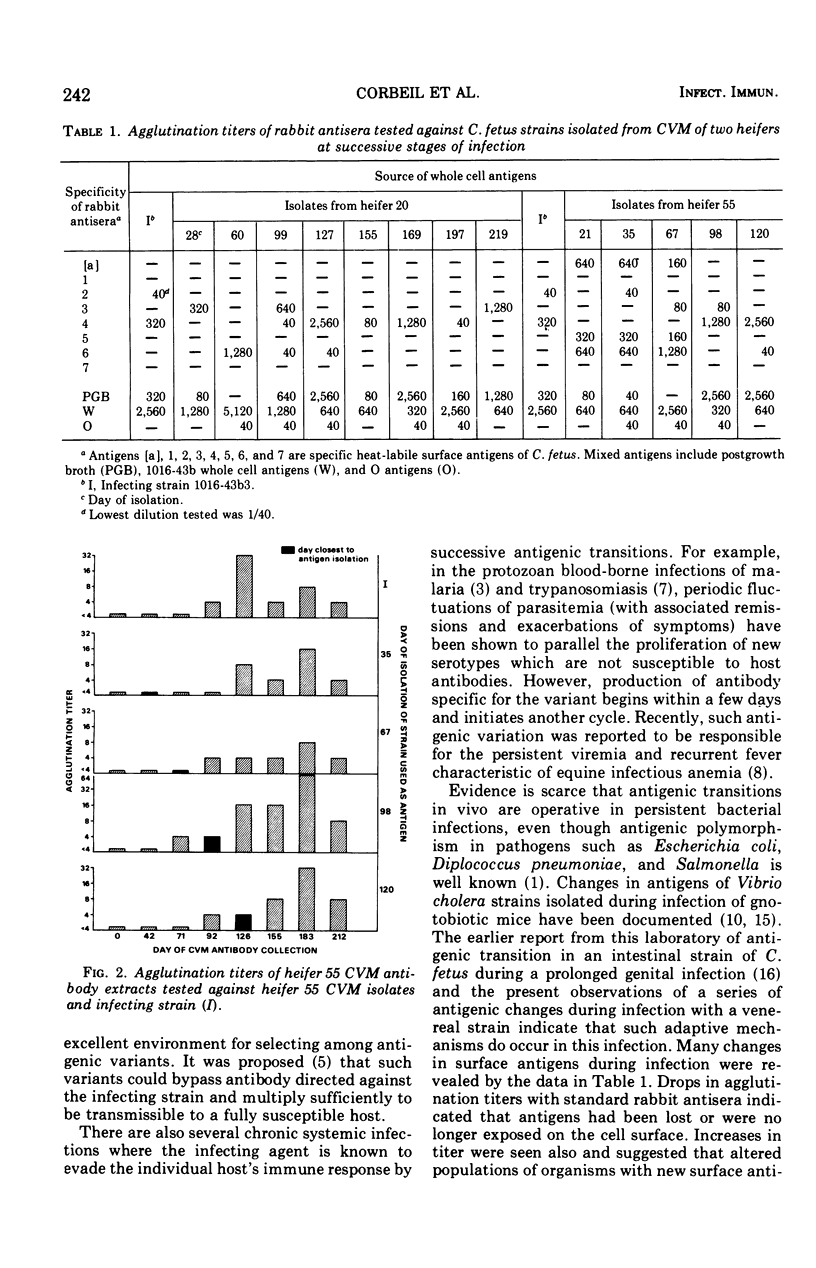
Host parasite relationships in the female genital tract were studied in bovine venereal vibriosis by investigating agglutinin production and alterations in superficial antigens of the bacterium during the course of infection in two heifers. Cervicovaginal mucus (CVM) steamed cell agglutinins were shown to appear earlier and remain at consistently higher levels than whole-cell agglutinins. Whole-cell agglutinin titers fluctuated much more than steamed cell titers, suggesting possible changes in whole-cell antigens. Marked antigenic variation was demonstrated in successive monthly CVM isolates from the two heifers by agglutination tests with rabbit antisera of various specificities. Some changes in CVM antibody specificity during the infection were noted also. Antigenic variation in the bacterium was proposed as a mechanism for maintenance of the asymptomatic cervicovaginal carrier state in the presence of antibody.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg R. L., Jutila J. W., Firehammer B. D. A revised classification of Vibrio fetus. Am J Vet Res. 1971 Jan;32(1):11–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown I. N., Brown K. N., Hills L. A. Immunity to malaria: the antibody response to antigenic variation by Plasmodium knowlesi. Immunology. 1968 Jan;14(1):127–138. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS G. W., McWHORTER A. C., EDWARDS P. R. Natural occurrence of induced or artificial flagellar antigens in Salmonella newport. J Bacteriol. 1962 Feb;83:348–350. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.2.348-350.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray A. R. Some principles of the immunology of trypanosomiasis. Bull World Health Organ. 1967;37(2):177–193. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G., Webster R. G. Selection of antigenic mutants of influenza viruses. Isolation and peptide mapping of their hemagglutination proteins. Virology. 1968 Feb;34(2):193–202. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90230-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. E., Wong K. H., Feeley J. C., Forlines M. E. Immunological conversion of Vibrio chorlerae in gnotobiotic mice. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):739–742. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.739-742.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitscherlich E., Heider R. Formenwechsel der O-Antigene bei Vibrio fetus. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1968 Jun;15(4):486–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. L. Purification and Partial Characterization of a Vibrio fetus Immunogen. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):562–566. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.562-566.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan G. H., Osborne N. Gonococcal infections in the female. Obstet Gynecol. 1973 Jul;42(1):156–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogg J. E., Chang W. Phage conversion of serotypes in Vibrio fetus. Am J Vet Res. 1972 May;33(5):1023–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Miller C. E. Progressive changes of Vibrio serotypes in germ-free mice infected with Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):688–695. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.688-695.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurig G. D., Hall C. E., Burda K., Corbeil L. B., Duncan J. R., Winter A. J. Persistent genital tract infection with Vibrio fetus intestinalis associated with serotypic alteration of the infecting strain. Am J Vet Res. 1973 Nov;34(11):1399–1403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurig G. G., Hall C. E., Corbell L. B., Duncan J. R., Winter A. J. Bovine veneral vibriosis: cure of genital infection in females by systemic immunization. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):245–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.245-251.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINTER A. J., BURDA K., DUNN H. O. AN EVALUATION OF CULTURAL TECHNICS FOR THE DETECTION OF VIBRIO FETUS IN BOVINE SEMEN. Cornell Vet. 1965 Jul;55:431–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter A. J. An antigenic analysis of Vibrio fetus. 3. Chemical, biologic, and antigenic properties of the endotoxin. Am J Vet Res. 1966 May;27(118):653–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


