Abstract
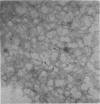
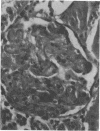
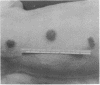
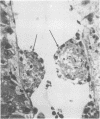
Endotoxic lipopolysachharide (LPS) was obtained from phenol-water extraction of cell walls prepared from mass-cultivated Fusobacterium necrophorum. The LPS was relatively free of nucleic acids and low in protein, and constituted about 4% of the cell walls. Upon acid hydrolysis, some of the components detected were hexosamines (7.0%), neutral and reducing sugars (50.5%), heptose (6.4%), 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate (0.8%), lipid A (21.0%), and phosphorus (1.7%). Under electron microscopy the LPS appeared mainly as ribbon-like trilaminar structures, and upon chemical treatment it displayed a behavior resembling that reported in certain enterobacterial LPS. The LPS was lethal to mice, 11-day-old chicken embryos, and rabbits. Endotoxicity in mice was enhanced at least 1,380-fold by the addition of 12.5 mug of actinomycin D. Induced tolerance to lethal effect of the endotoxin and rapidly acquired resistance to infection by F. necrophrum viable cells were also demonstrated in mice. The endotoxin produced both localized and generalized Shwartzman reactions as well as biphasic pyrogenic responses in rabbits. These results firmly establish the presence of a classical endotoxin in F. necrophorum, thus providing strong support to our recent suggestion that cell wall-associated components may contribute significantly to the pathogenicity of F. necrophorum.
Full text
PDF

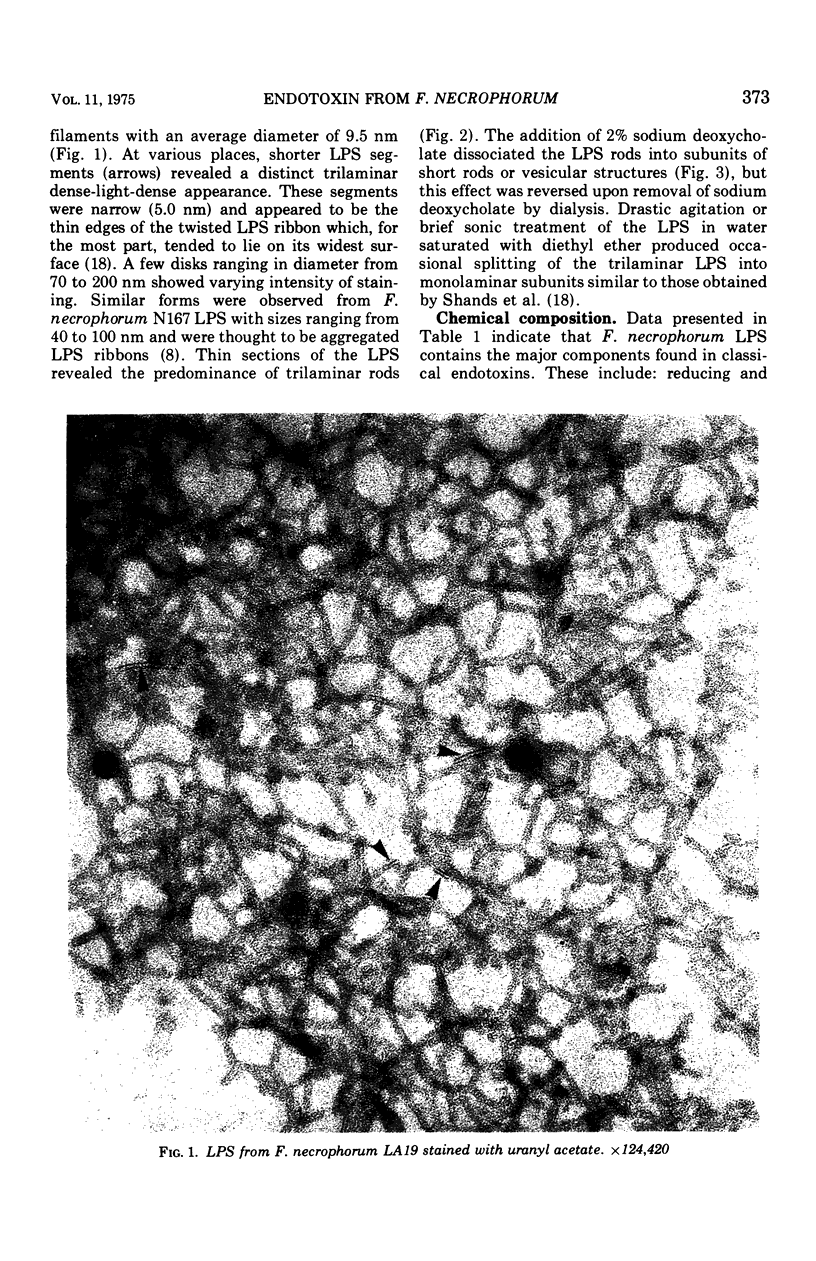
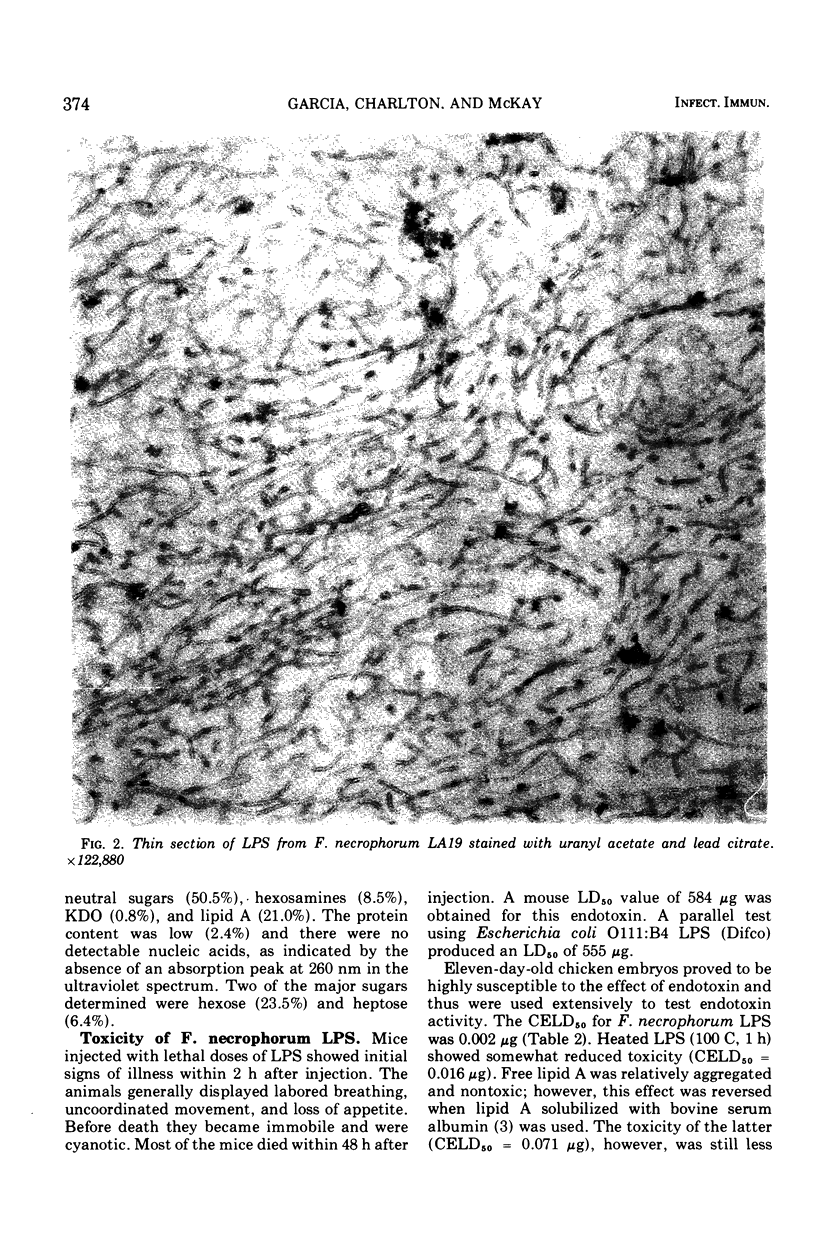
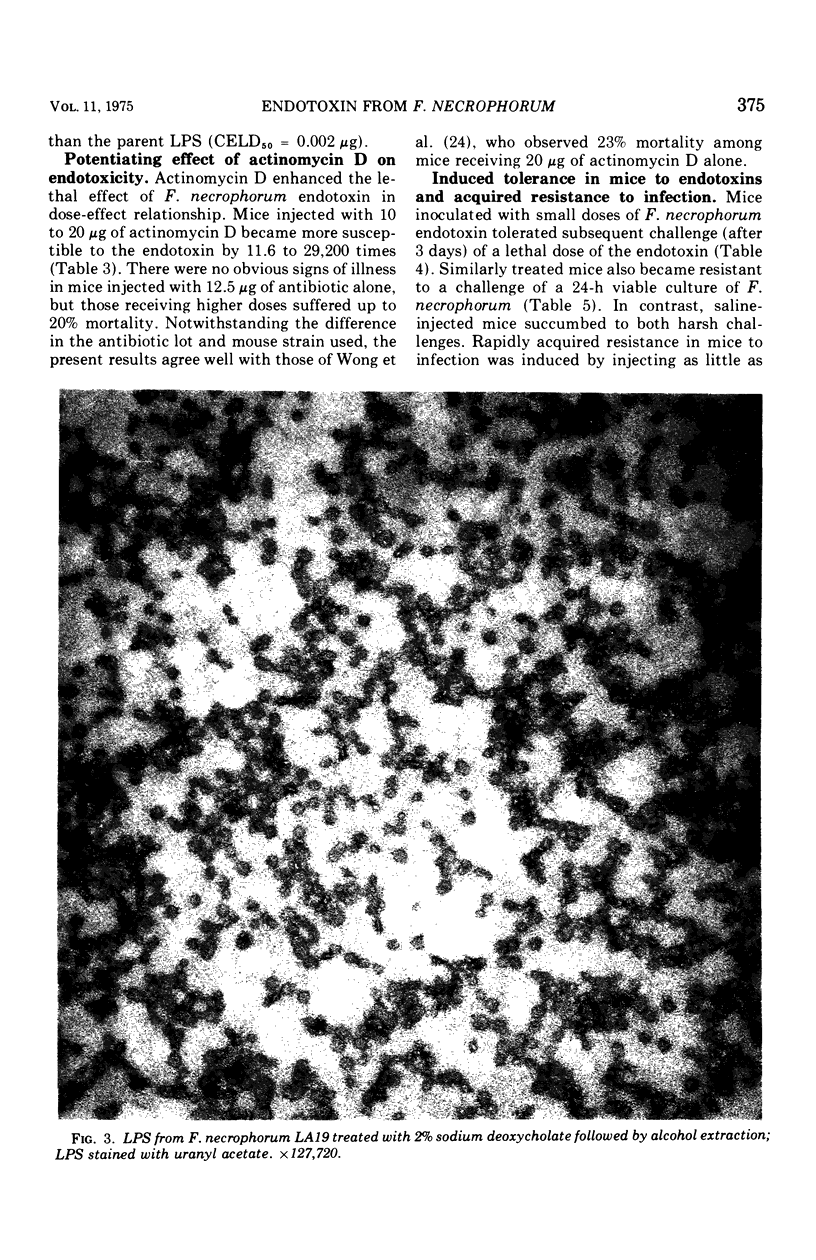
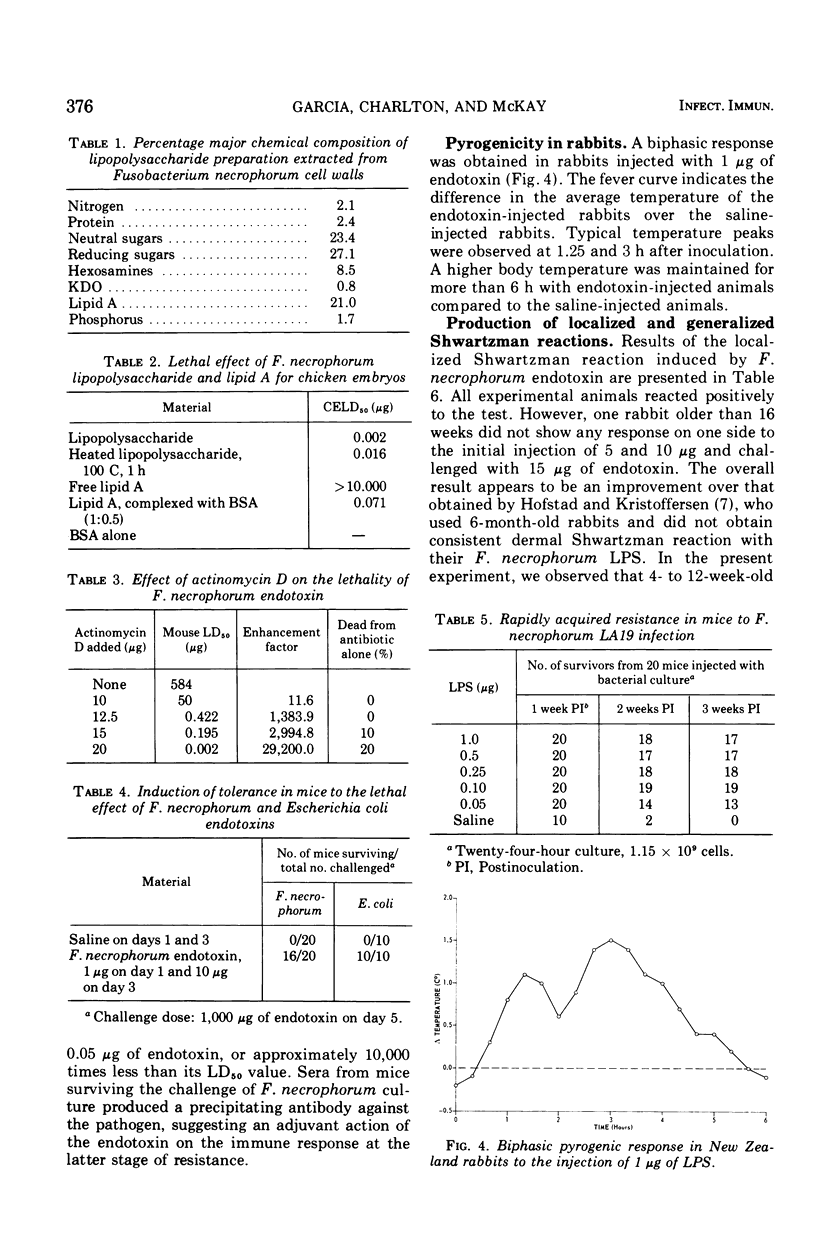


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albizo J. M., Surgalla M. J. Isolation and Biological Characterization of Pasteurella pestis Endotoxin. Infect Immun. 1970 Sep;2(3):229–236. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.3.229-236.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke K., Gray G. W., Reaveley D. A. The cell walls of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. General composition. Biochem J. 1967 Nov;105(2):749–754. doi: 10.1042/bj1050749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Rietschel E. T., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Interaction of lipopolysaccharides and lipid A with complement. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Mar 1;19(1):143–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M. M., McKay K. A. A satisfactory medium and technique for the mass cultivation of Sphaerophorus necrophorus. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Feb;19(2):296–298. doi: 10.1139/m73-046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M. M., Neil D. H., McKay K. A. Application of immunofluorescence to studies on the ecology of Sphaerophorus necrophorus. Appl Microbiol. 1971 May;21(5):809–814. doi: 10.1128/am.21.5.809-814.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstad T., Kristoffersen T. Preparation and chemical characteristics of endotoxic lipopolysaccharide from three strains of Sphaerophorus necrophorus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(3):385–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00077.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstad T., Kristoffersen T., Selvig K. A. Electron microscopy of endotoxic lipopolysaccharide from Bacteroides, Fusobacterium and sphaerophorus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(3):413–419. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00054.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner K. C., Finkelstein R. A. Bioassay of endotoxin: correlation between pyrogenicity for rabbits and lethality for chick embryos. J Infect Dis. 1966 Dec;116(5):529–536. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.5.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudbach J. A., Anacker R. L., Haskins W. T., Johnson A. G., Milner K. C., Ribi E. Physical aspects of reversible inactivation of endotoxin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):629–643. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52394.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands J. W., Jr, Graham J. A., Nath K. The morphologic structure of isolated bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 14;25(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90275-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenwirth A. C., Yin E. T., Sarmiento E. M., Wessler S. Bacterioidaceae endotoxin detection by Limulus assay. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1452–1454. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINZLER R. J. Determination of serum glycoproteins. Methods Biochem Anal. 1955;2:279–311. doi: 10.1002/9780470110188.ch10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. H., Miller C. E., Feeley J. C., Chan Y. K. Determination of endotoxicity in bacterial vaccines. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Mar;25(3):403–407. doi: 10.1128/am.25.3.403-407.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]