Abstract
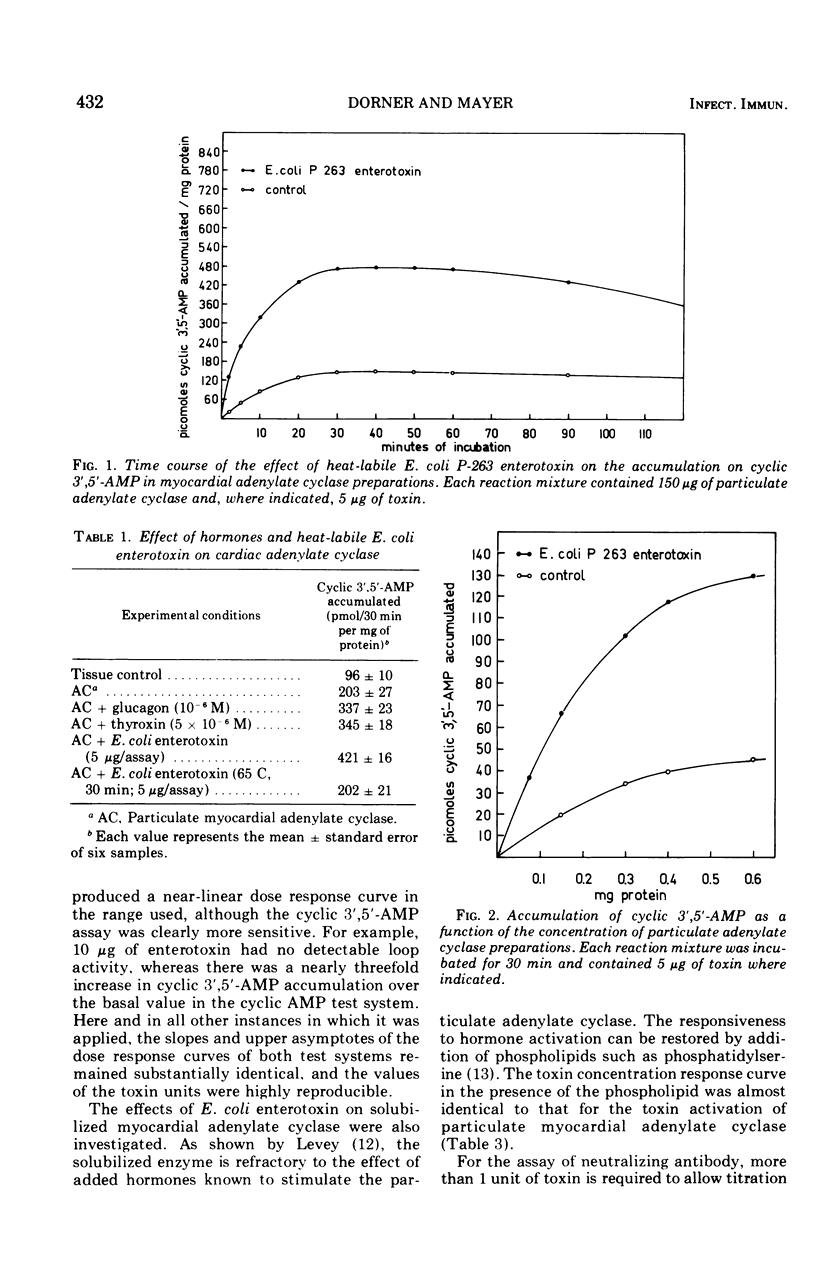
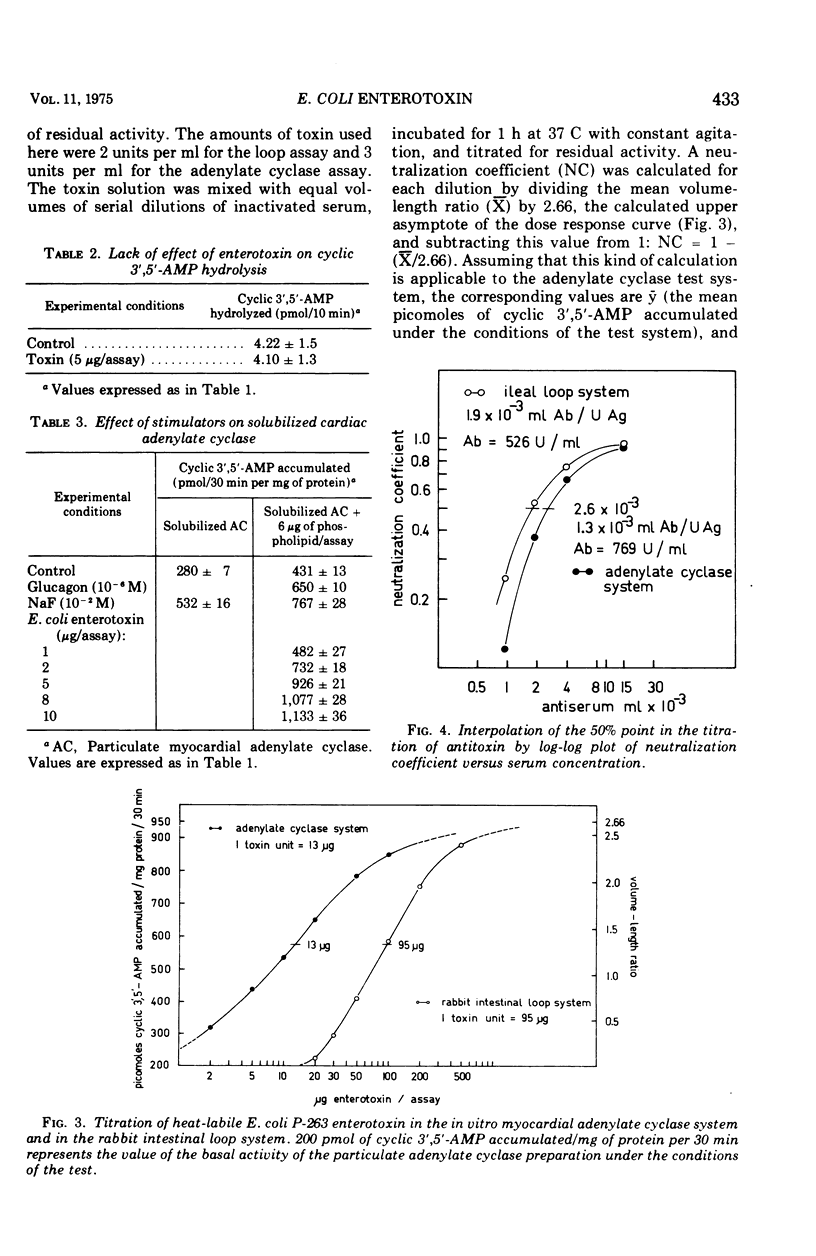
The enterotoxin from cell-free filtrates of the enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strain P-263 was found to stimulate adenylate cyclase activity in broken-cell preparations from myocardial tissue. Particulate and detergent-solubilized fractions from cat heart were incubated with enterotoxin and assayed for adenylate cyclase activity. Adenylate cyclase activity was stimulated by enterotoxin; the extent of stimulation was proportional to the concentration of enterotoxin. The data demonstrate that stimulation of enterotoxin-sensitive adenylate cyclase in this system provides a sensitive in vitro assay, either as an accurate measure of enterotoxin concentration or as an assay for antitoxic titers in sera. A parallel comparison showed that stimulation of fluid production in rabbit intestinal loops by enterotoxin was less sensitive.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beavo J. A., Hardman J. G., Sutherland E. W. Hydrolysis of cyclic guanosine and adenosine 3',5'-monophosphates by rat and bovine tissues. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5649–5655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows W., Musteikis G. M. Cholera infection and toxin in the rabbit ileal loop. J Infect Dis. 1966 Apr;116(2):183–190. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C. Detection of heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin with the use of adrenal cells in tissue culture. Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):334–336. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etkin S., Gorbach S. L. Studies on enterotoxin from Escherichia coli associated with acute diarrhea in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Jul;78(1):81–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Chen L. C., Curlin G. T., Evans D. G. Stimulation of adenyl cyclase by Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Nat New Biol. 1972 Apr 5;236(66):137–138. doi: 10.1038/newbio236137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L., Barnum D. A. A heat-labile enterotoxin from strains of Eschericha coli enteropathogenic for pigs. J Infect Dis. 1969 Oct;120(4):419–426. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai G. J., Burrows W. The titration of cholera toxin and antitoxin in the rabbit ileal loop. J Infect Dis. 1966 Dec;116(5):606–614. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.5.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler E. M. Enterotoxic activity of filtrates of escherichia coli in young pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1968 Dec;29(12):2263–2274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levey G. S. Restoration of glucagon responsiveness of solubilized myocardial adenyl cyclase by phosphatidylserine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 2;43(1):108–113. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levey G. S. Solubilization of myocardial adenyl cyclase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jan 6;38(1):86–92. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91087-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Baetz A. L. Comparative effects of enterotoxins from Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae on rabbit and swine small intestine. Lab Invest. 1971 Aug;25(2):133–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Engstrom G. W., Baetz A. L. Response of the rabbit ileal loop to cell-free products from Escherichia coli enteropathogenic for swine. J Infect Dis. 1970 Feb;121(2):182–187. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.2.182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J. The vasopressin-sensitive adenylate cyclase of the rat renal medulla. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4775–4781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Wallace C. K. Stimulation of jejunal secretion by a crude Escherichia coli enterotixin. Gastroenterology. 1972 Sep;63(6):439–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Gorbach S. L., Banwell J. G., Jacobs B., Chatterjee B. D., Mitra R. C. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from patients with severe cholera-like disease. J Infect Dis. 1971 Apr;123(4):378–385. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.4.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Gyles C. L. The effect of cell-free fluids prepared from cultures of human and animal enteropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli on ligated intestinal segments of rabbits and pigs. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Aug;3(3):403–409. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-3-403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Gyles C. L. The relationship between two apparently different enterotoxins produced by enteropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli of porcine origin. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Aug;3(3):387–401. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-3-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Halls S. Studies on Escherichia coli enterotoxin. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(2):531–543. doi: 10.1002/path.1700930212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. B., Gyles C. L., Barnum D. A. Production of diarrhea in pigs in response to Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Am J Vet Res. 1972 Dec;33(12):2511–2526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


