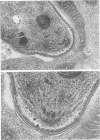
Abstract
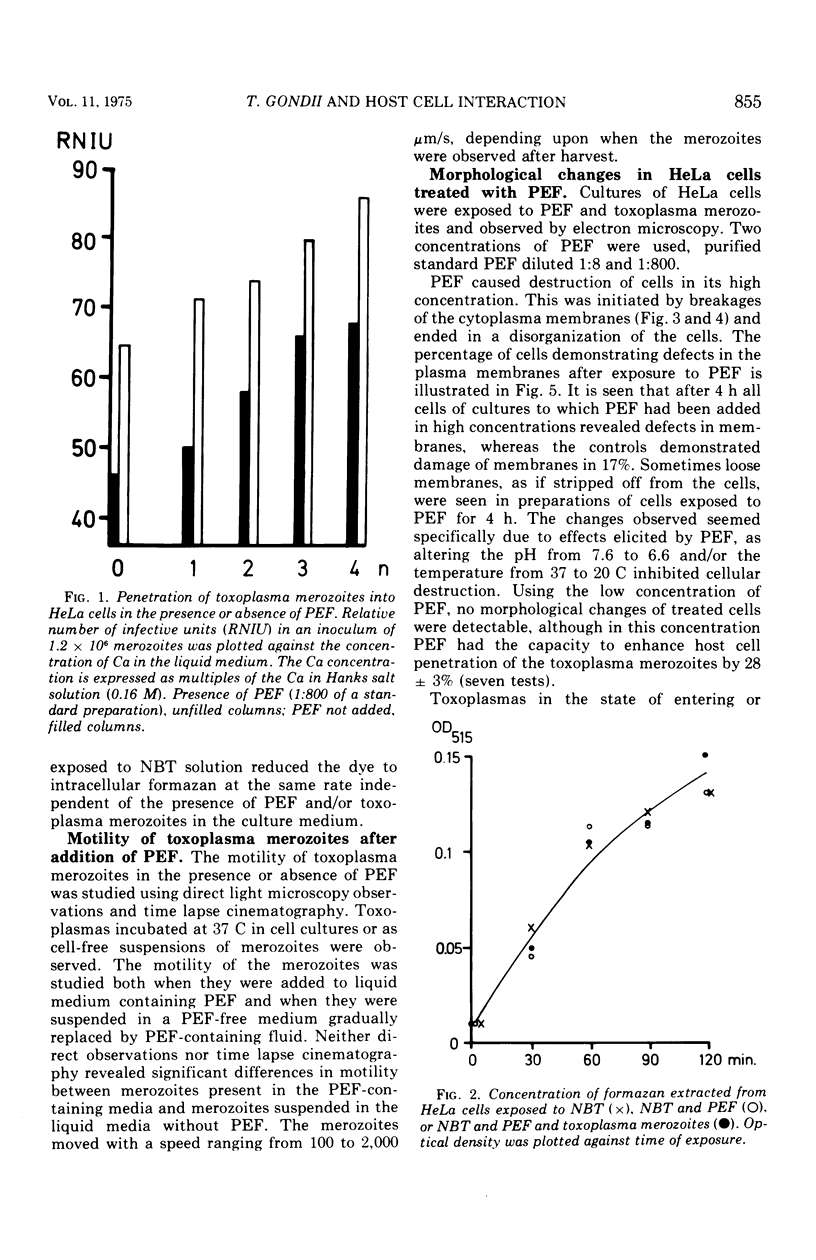
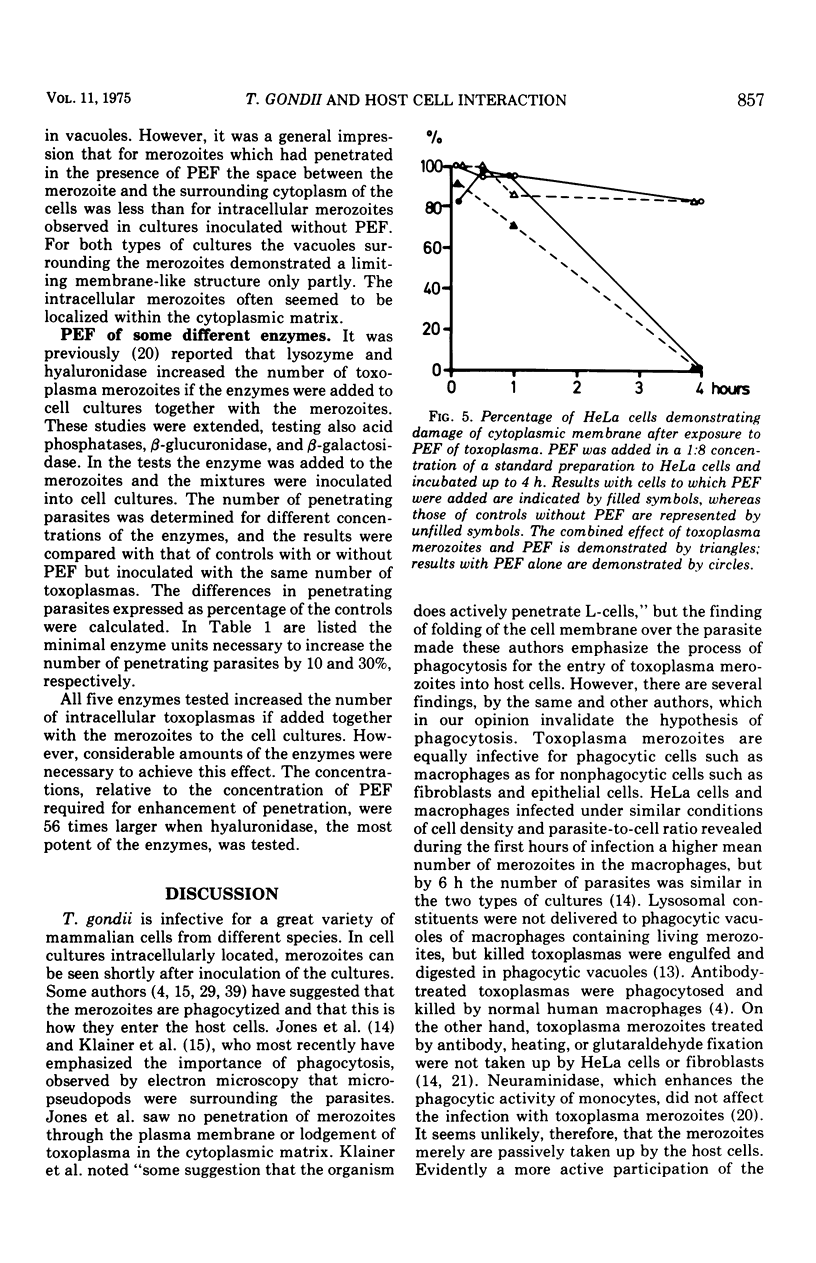
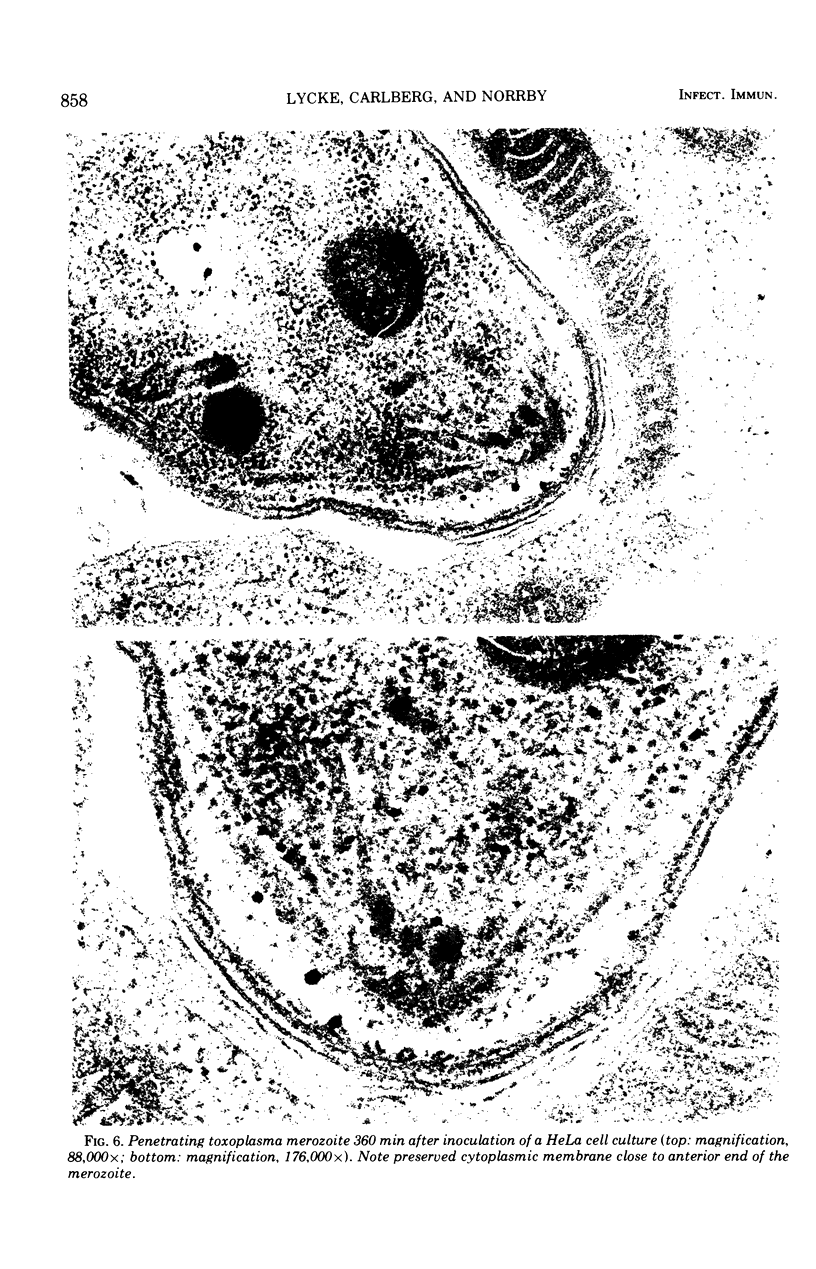
A protein with a molecular weight of 70,000 to 150,000 which was extracted from merozoites of Toxoplasma gondii enhanced the host cell penetration of the merozoites. The optimal pH and temperature for penetration of merozoites coincided with those favoring the action of the penetration-enhancing protein. In addition, a dependence on Ca and Mg existed for penetration of merozoites, either in the presence or absence of this protein. No evidence was found that indicated that the enhancing effect on penetration elicited by the protein was due to increased phagocytic capacity of host cells (HeLa) or improved motility of the merozoites. Electron microscopy demonstrated that the protein, in high concentration, caused disruption of cytoplasmic membranes. In a 100-fold-lower concentration, which still caused a marked enhancement of penetration, no such effect was observed. However, the vacuoles surrounding the penetrated parasites seemed smaller than for merozoites penetrating in cultures to which no penetration-enhancing factor was given, and the membranes limiting the vacuoles demonstrated discontinuities more often. The penetration-enchancing effect of some known enzymes was studies. However, none of these enzymes seemed to correspond to the penetration-enhancing protein of toxoplasma. The mode of entry of toxoplasma merozoites into host cells is discussed. It is concluded that phagocytosis must play a less important role and that merozoites actively penetrate the cytoplasmic membranes of the host cells. The penetration is proposed to be a result of combined mechanical and chemical actions. It is suggested that an enzymatic function of the penetration-enhancing factor released by the merozoites is of importance. The membrane limiting the vacuole of a penetrated merozoite seems to be newly formed in the cell after penetration is completed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akao S. Toxoplasma gondii: aspartate aminotransferase in cell membrane. Exp Parasitol. 1971 Feb;29(1):26–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(71)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akao S. Toxoplasma gondii: localization of peroxidase activity. Exp Parasitol. 1971 Apr;29(2):250–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(71)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. E., Jr, Remington J. S. Effect of normal and activated human macrophages on Toxoplasma gondii. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1154–1174. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehner R. L., Nathan D. G. Quantitative nitroblue tetrazolium test in chronic granulomatous disease. N Engl J Med. 1968 May 2;278(18):971–976. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196805022781801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bommer W., Höfling K. H., Heunert H. H. Lebendebeobachtungen über das Eindringen von Toxoplasmen in die Wirtszelle. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1968 Dec 6;93(49):2365–passim. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1110941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAPELLA J. A., KAUFMAN H. E. ENZYME HISTOCHEMISTRY OF TOXOPLASMA GONDII. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1964 Sep;13:664–666. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1964.13.664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FULTON J. D., SPOONER D. F. Metabolic studies on Toxoplasma gondii. Exp Parasitol. 1960 Jun;9:293–301. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(60)90037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayer R., Hammond D. M., Chobotar B., Elsner Y. Y. Cultivation of Besnoitia jellisoni in bovine cell cultures. J Parasitol. 1969 Jun;55(3):645–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARNHAM P. C., BAKER J. R., BIRD R. G. Fine structure of cystic form of Toxoplasma gondii. Br Med J. 1962 Jan 13;1(5271):83–84. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5271.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Hirato K., Yanagawa R. A cinematographic study of the penetration of cultured cells by Toxoplasma gondii. Jpn J Vet Res. 1966 Dec;14(3):81–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. C., Hirsch J. G. The interaction between Toxoplasma gondii and mammalian cells. II. The absence of lysosomal fusion with phagocytic vacuoles containing living parasites. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1173–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. C., Yeh S., Hirsch J. G. The interaction between Toxoplasma gondii and mammalian cells. I. Mechanism of entry and intracellular fate of the parasite. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1157–1172. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klainer A. S., Krahenbuhl J. L., Remington J. S. Scanning electron microscopy of Toxoplasma gondii. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Mar;75(1):111–118. doi: 10.1099/00221287-75-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUND E., LYCKE E., SOURANDER P. A cinematographic study of Toxoplasma gondii in cell cultures. Br J Exp Pathol. 1961 Aug;42:357–362. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYCKE E., LUND E. A TISSUE CULTURE METHOD FOR TITRATION OF INFECTIVITY AND DETERMINATION OF GROWTH RATE OF TOXOPLASMA GONDII. 2. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1964;60:221–233. doi: 10.1111/apm.1964.60.2.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYCKE E., LUND E. ENHANCEMENT BY LYSOZYME AND HYALURONIDASE OF THE PENETRATION BY TOXOPLASMA GONDII INTO CULTURED HOST CELLS. Br J Exp Pathol. 1965 Apr;46:189–199. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYCKE E., LUND E., FALSEN E. THE EFFECT OF IMMUNE SERUM AND ACTIVATOR ON THE INFECTIVITY OF TOXOPLASMA GONDII FOR CELL CULTURE. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;63:206–220. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.63.2.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund E., Hansson H. A., Lycke E., Sourander P. Enzymatic activities of Toxoplasma gondii. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;68(1):59–67. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.68.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke E., Norrby R., Remington J. Penetration-enhancing factor extracted from Toxoplasma gondii which increases its virulence for mice. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):785–788. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.785-788.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaren D. J., Paget G. E. A fine structural study on the merozoite of Eimeria tenella with special reference to the conoid apparatus. Parasitology. 1968 Aug;58(3):561–571. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000028869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby R. Host Cell Penetration of Toxoplasma gondii. Infect Immun. 1970 Sep;2(3):250–255. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.3.250-255.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby R. Immunological Study on the Host Cell Penetration Factor of Toxoplasma gondii. Infect Immun. 1971 Feb;3(2):278–286. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.2.278-286.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby R., Lycke E. Factors enhancing the host-cell penetration of Toxoplasma gondii. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):53–58. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.53-58.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULVERTAFT R. J., VALENTINE J. C., LANE W. F. The behaviour of Toxoplasma gondii on serum-agar culture. Parasitology. 1954 Nov;44(3-4):478–484. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000019156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park B. H., Fikrig S. M., Smithwick E. M. Infection and nitroblue-tetrazolium reduction by neutrophils. A diagnostic acid. Lancet. 1968 Sep 7;2(7567):532–534. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. L., Hammond D. M., Anderson L. C., Speer C. A. Ultrastructural study of schizogony in Eimeria callospermophili. J Protozool. 1970 Nov;17(4):584–592. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1970.tb04732.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. L., Speer C. A., Hammond D. M. Penetration of Eimeria larimerensis sporozoites into cultured cells as observed with the light and electron microscopes. J Parasitol. 1971 Jun;57(3):615–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson J. R., Hammond D. M., Ernst J. V. Development of Eimeria alabamensis from cattle in mammalian cell cultures. J Protozool. 1971 Feb;18(1):120–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1971.tb03292.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield H. G., Garnham P. C., Shiroishi T. The fine structure of the sporozoite of Lankesteria culicis. J Protozool. 1971 Feb;18(1):98–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1971.tb03289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield H. G., Melton M. L. The fine structure and reproduction of Toxoplasma gondii. J Parasitol. 1968 Apr;54(2):209–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timofeev B. A. K voprosu o nalichii gialuronidazy i diffuzionnogo faktora u toksoplazm. Med Parazitol (Mosk) 1971 Jul-Aug;40(4):438–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VISCHER W. A., SUTER E. Intracellular multiplication of Toxoplasma gondi in adult mammalian macrophages cultivated in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Jul;86(3):413–419. doi: 10.3181/00379727-86-21117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeil C., Tusques J., Senelar R., André M. J., Rehel H. Etude au microscope électronique de l'ultrastructure des toxonèmes de Toxoplasma gondii, leur modification sous l'action lytique des anticorps antitoxoplasmiques. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1965 Aug 2;261(5):1384–1387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaman V., Colley F. C. Ultrastructural study of penetration of macrophages by Toxoplasma gondii. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1972;66(5):781–782. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(72)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Zypen E., Piekarski G. Ultrastrukturelle Unterschiede zwischen der sog. Proliferationsform (RH-Stamm, BK-Stamm) und dem sog. Cysten-Stadium (DX-Stamm) von Toxoplasma gondii. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1967;203(4):495–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]