Abstract
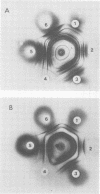
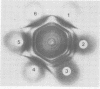
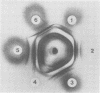
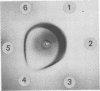
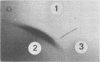
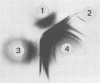
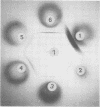
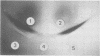
A strain-specific virulence-associated antigen has been found in Neisseria gonorrhoeae strain F-62. Using immunodiffusion in agar gel, it has been shown that the antigen is distinguishable from endotoxin and the virulence-associated toxic protein. It does not appear to be derived from pili. The antigen was not detected in T1 and/or T2 colony type cultures of 10 other isolates. It exhibited a possible partial immunological relationship with an antigen found in one additional strain. It was susceptible to digestion with Pronase and trypsin.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arko R. J., Kraus S. J., Brown W. J., Buchanan T. M., Kuhn U. S. Neisseria gonorrhoeae: effects of systemic immunization on resistance of chimpanzees to urethral infection. J Infect Dis. 1974 Aug;130(2):160–164. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.2.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton C. C., Jr The structure, function, synthesis and genetic control of bacterial pili and a molecular model for DNA and RNA transport in gram negative bacteria. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun;27(8):1003–1054. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1965.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng A., Kwapinski J. B., Ronald A. R. Isolation and immunological characterization of a unique toxic cytoplasmic polymer of type 1 Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Aug;20(8):1163–1167. doi: 10.1139/m74-180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANIELSSON D. THE DEMONSTRATION OF N. GONORRHOEAE WITH THE AID OF FLUORESCENT ANTIBODIES. 3. STUDIES BY IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE AND DOUBLE DIFFUSION-IN-GEL TECHNIQUE ON THE ANTIGENIC RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN STRAINS OF N. GONORRHOEAE. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;64:243–266. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.64.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALBERT S. P., SWICK L., SONN C. The use of precipitin analysis in agar for the study of human streptococcal infections. II. Ouchterlony and Oakley technics. J Exp Med. 1955 May 1;101(5):557–576. doi: 10.1084/jem.101.5.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson R. I. Typing the gonococcus. Br Med J. 1970 Jul 11;3(5714):107–107. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5714.107-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Cohen I. R., Norins L. C., Schroeter A. L., Reising G. Neisseria gonorrhoeae. II. Colonial variation and pathogenicity during 35 months in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):596–605. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.596-605.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAY J. R., RAWLINS G. A. A micro method for agar-gel precipitin reactions. J Clin Pathol. 1962 Mar;15:186–189. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.2.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERGENHAGEN S. E., HAMPP E. G., SCHERP H. W. Preparation and biological activities of endotoxins from oral bacteria. J Infect Dis. 1961 May-Jun;108:304–310. doi: 10.1093/infdis/108.3.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punsalang A. P., Jr, Sawyer W. D. Role of pili in the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):255–263. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.255-263.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Kraus S. J., Gotschlich E. C. Studies on gonococcus infection. I. Pili and zones of adhesion: their relation to gonococcal growth patterns. J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):886–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WADSWORTH C. A slide microtechnique for the analysis of immune precipitates in gel. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1957;10(6):355–360. doi: 10.1159/000228394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]