Abstract
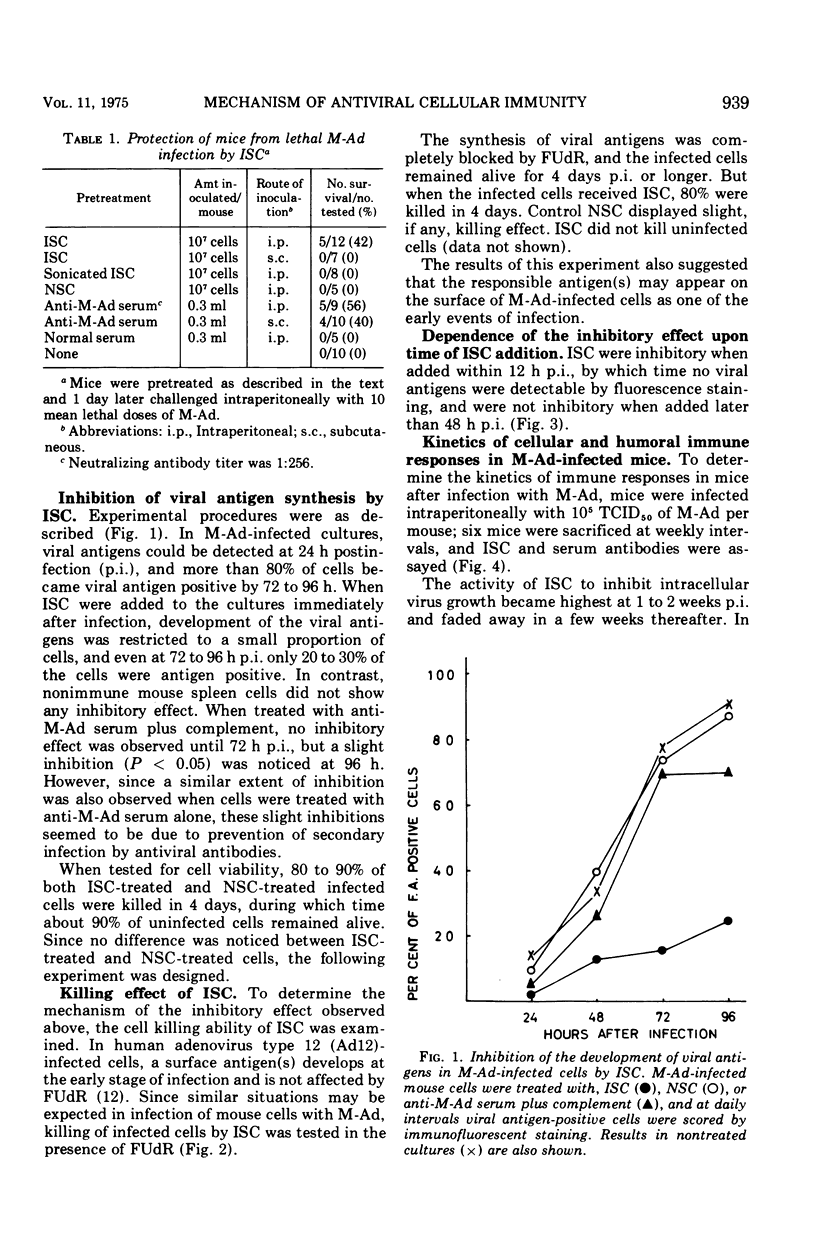
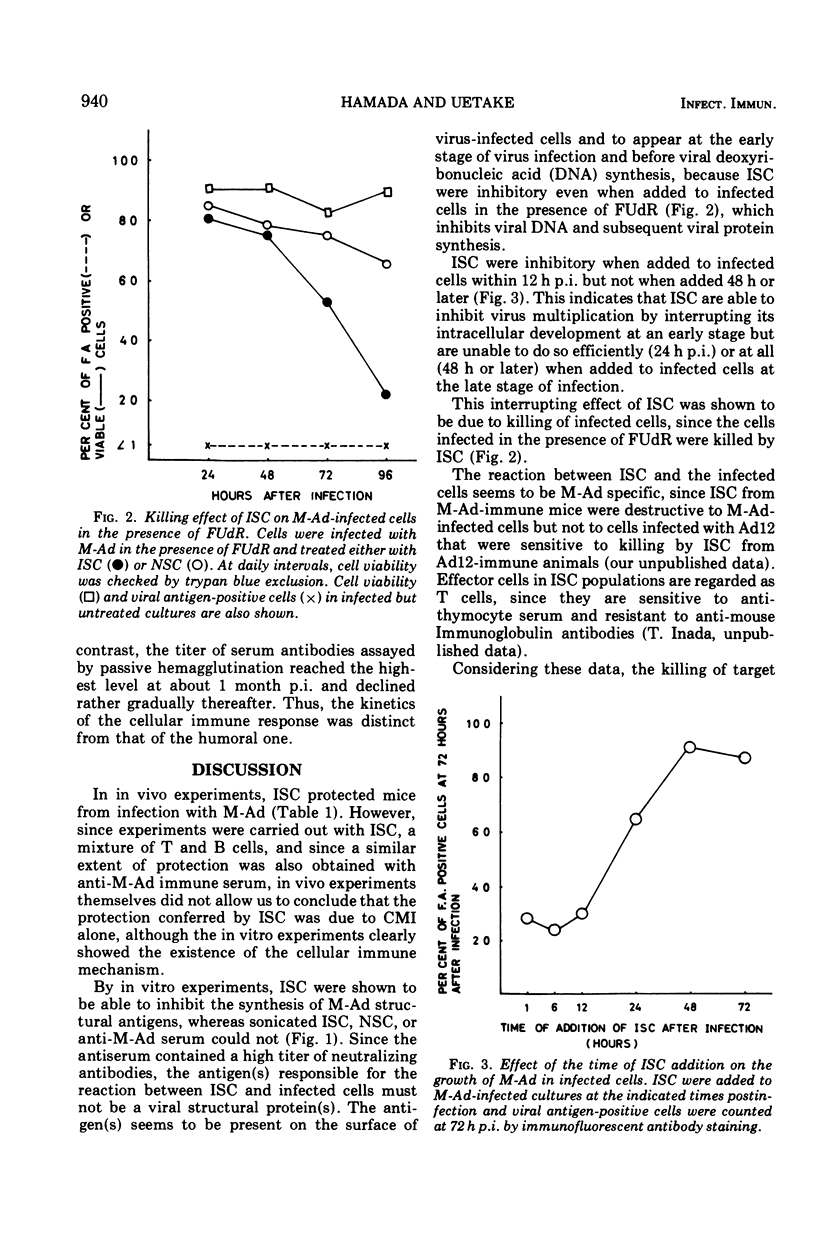
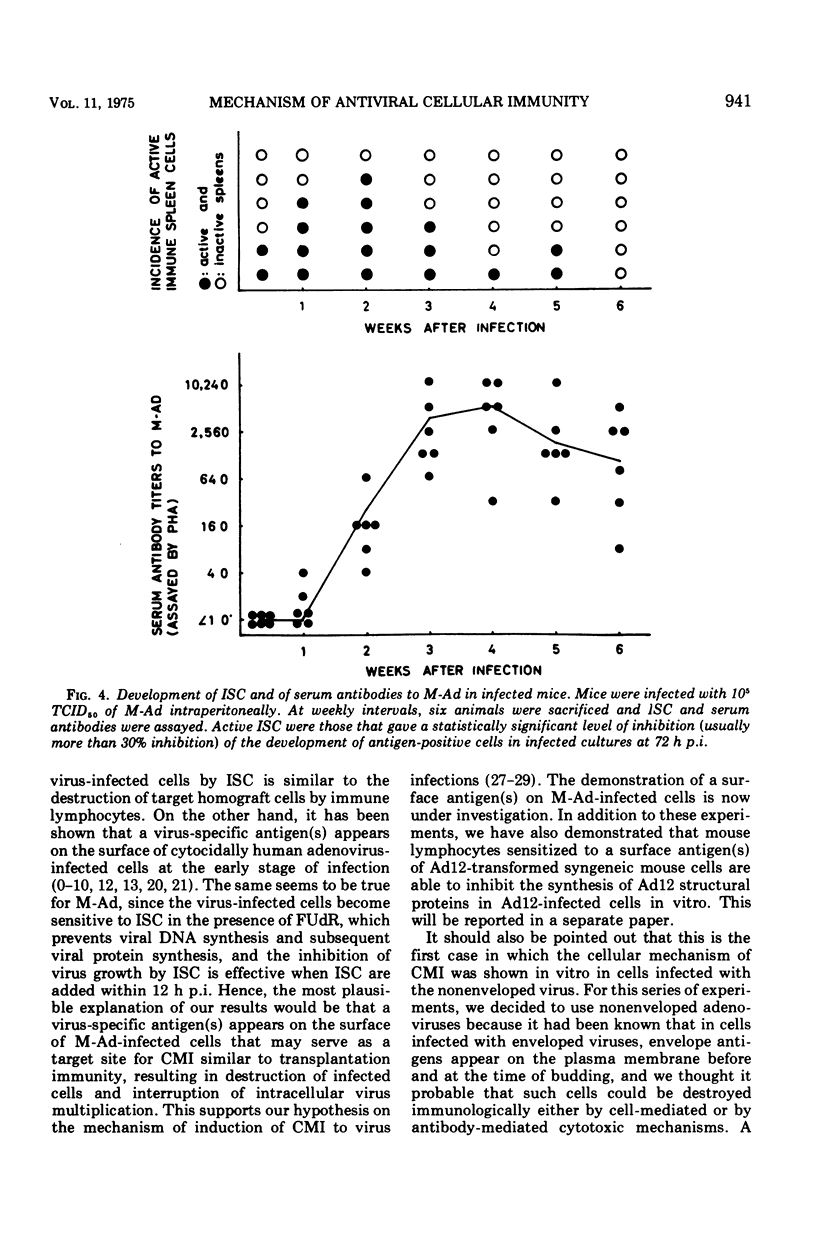
Mice were protected from lethal infection with mouse adenovirus (M-Ad) by adoptive transfer of immune spleen cells (ISC) that were prepared from mice immunized with M-Ad and not protected by sonicated ISC. However, a similar extent of protection was also observed by passive immunization with anti-M-Ad serum. In contrast, by in vitro experiments ISC were shown to be able to interrupt intracellular multiplication of M-Ad, whereas sonicated ISC, unimmunized mouse spleen cells, or anti-M-Ad serum were unable to do so. ISC were inhibitory in vitro when added within 12 h postinfection but not when added later. The inhibitory activity of ISC was regarded as due to cell killing by ISC, since the trypan blue exclusion test showed that above 80% of infected cells were killed by ISC even when 5'-fluorodeoxyuridine was added to the cells to block viral deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis, under which conditions control infected cells, to which ISC were not added or normal spleen cells were added, were kept alive at least for a few days. Kinetics studies in M-Ad-infected mice showed that the inhibitory activity of ISC became highest at 1 to 2 weeks postinfection and faded away thereafter in a few weeks, whereas serum antibody titer assayed by passive hemagglutination reached its peak level at about 4 weeks postinfection and declined gradually therafter.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C. Cell-mediated immune responses to virus infections and virus-induced tumours. Br Med Bull. 1967 Jan;23(1):60–65. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. B., Stevens D. A., Merigan T. C. Selective increase in lymphocyte interferon response to vaccinia antigen after revaccination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2632–2636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasgow L. A. Cellular immunity in host resistance to viral infections. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Jul;126(1):125–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasgow L. A. Leukocytes and interferon in the host response to viral infections. II. Enhanced interferon response of leukocytes from immune animals. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2185–2191. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2185-2191.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. A., Cooperband S. R., Kibrick S. Immune specific induction of interferon production in cultures of human blood lymphocytes. Science. 1969 Jun 20;164(3886):1415–1417. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3886.1415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTLEY J. W., ROWE W. P. A new mouse virus apparently related to the adenovirus group. Virology. 1960 Jul;11:645–647. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada C., Nakajima S., Uetake H. Detection of a specific surface antigen(s) in adenovirus type 12-transformed cells by fluorescent antibody technique. Jpn J Microbiol. 1973 Jul;17(4):297–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1973.tb00776.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer J. R., Cooper M. D., Gabrielsen A. E., Good R. A. Lymphopenic forms of congenital immunologic deficiency diseases. Medicine (Baltimore) 1968 May;47(3):201–226. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196805000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. Tumor antigens. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1966;20:223–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.20.100166.001255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz S. S., Williams J. A., Howard B. E., Sigel M. M. Adenovirus antibody measured by the passive hemagglutination test. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):205–212. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.205-212.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodmell D. L., Notkins A. L. Cellular immunity to herpes simplex virus mediated by interferon. J Exp Med. 1974 Sep 1;140(3):764–778. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.3.764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima S., Hamada C., Uetake H. Tumor-specific transplantation antigen activity of freshly adenovirus-infected cells. Intercurrent immunization against viral tumorigenesis with virus-infected cells. Jpn J Microbiol. 1974 May;18(3):243–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1974.tb00952.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notkins A. L. Immune mechanisms by which the spread of viral infections is stopped. Cell Immunol. 1974 Mar 30;11(1-3):478–483. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D. Destruction of virus-infected cells by immunological mechanisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1971;25:283–290. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.25.100171.001435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen L. E., Jordan G. W., Stevens D. A., Merigan T. C. Lymphocyte interferon production and transformation after Herpes simplex infections in humans. J Immunol. 1974 Feb;112(2):728–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEVETHIA S. S., KATZ M., RAPP F. NEW SURFACE ANTIGEN IN CELLS TRANSFORMED BY SIMIAN PAPOVAVIRUS SV40. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Jul;119:896–901. doi: 10.3181/00379727-119-30330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UETAKE H., LURIA S. E., BURROUS J. W. Conversion of somatic antigens in Salmonella by phage infection leading to lysis or lysogeny. Virology. 1958 Feb;5(1):68–91. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uetake H., Hamada C., Nakajima S. [Mechanism of induction of immunity to virus infections: interruption of intercellular virus multiplication]. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 1972 Nov;17(11):835–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheelock E. F., Toy S. T. Participation of lymphocytes in viral infections. Adv Immunol. 1973;16:123–184. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



