Abstract
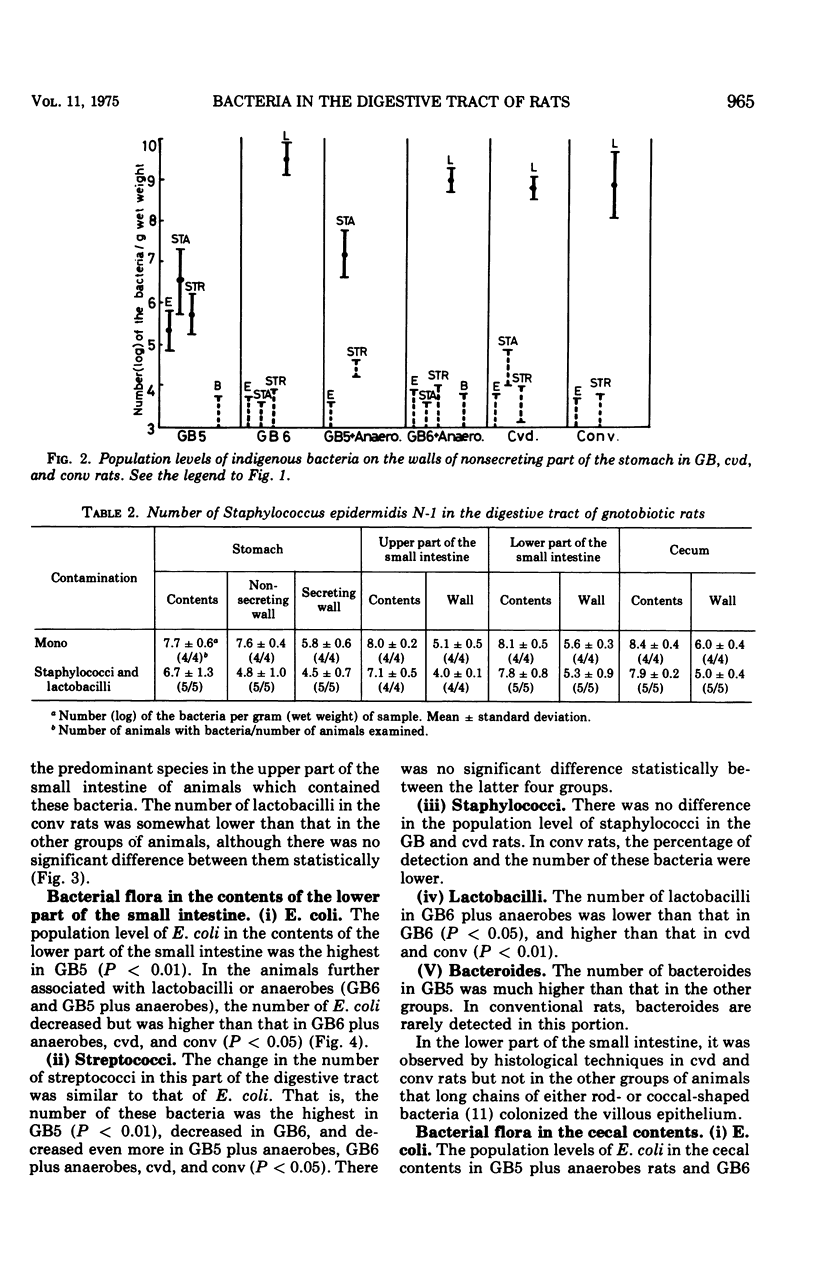
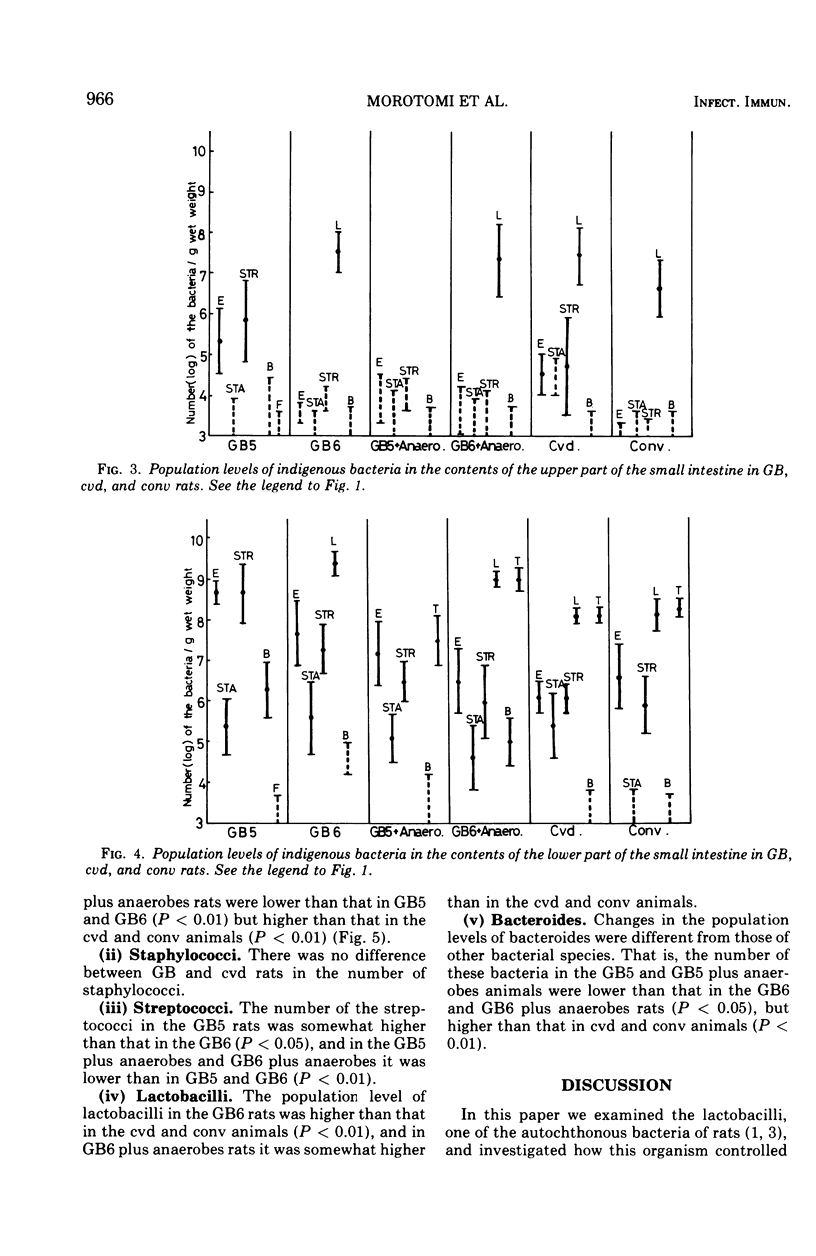
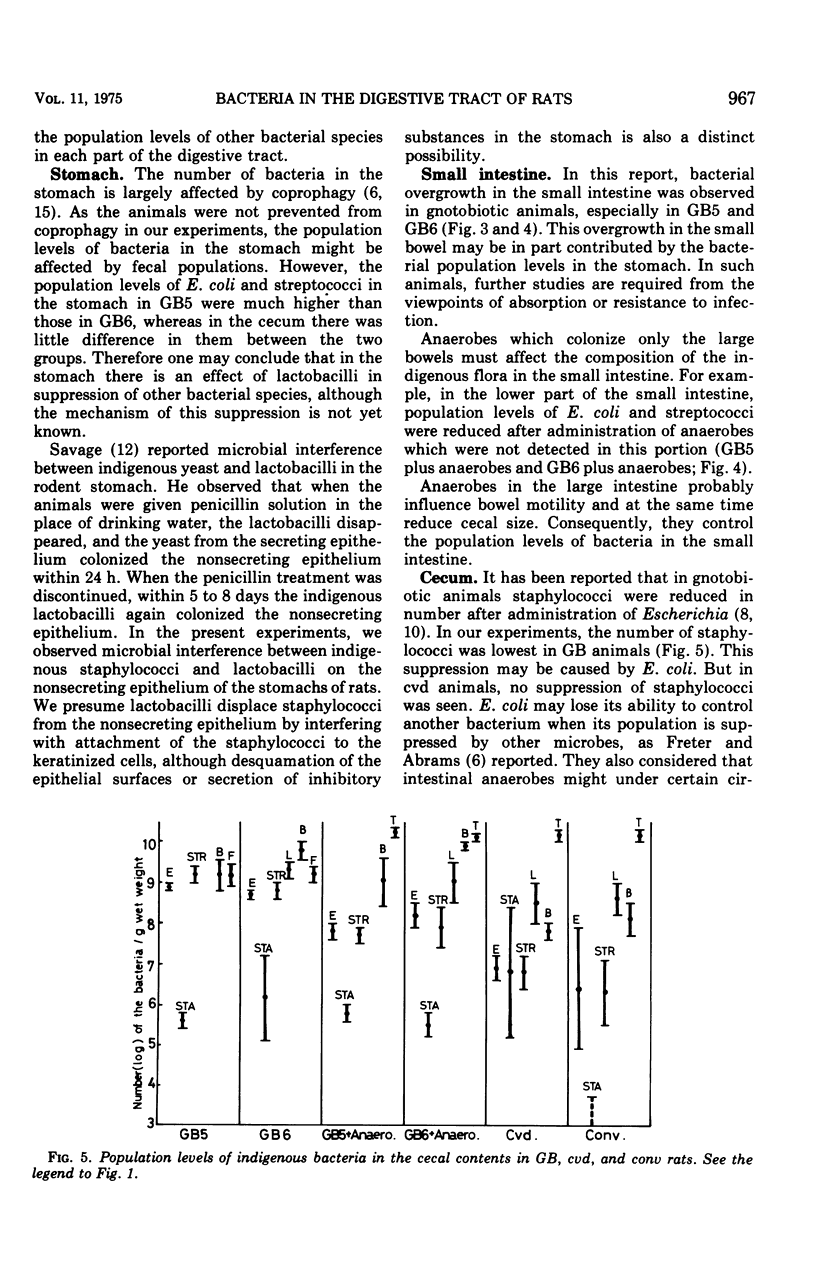
The localization and population levels of the indigenous bacterial flora of conventional rats were investigated by cultural and histological techniques. Lactobacilli predominate in the stomach and upper part of the small intestine and associate with keratinized cells of the nonglandular portion of stomach. Mixtures of varying complexity of pure cultures of indigenous bacteria were inoculated into germfree rats. The distribution of these bacteria was examined to investigate the effect of lactobacilli in controlling the composition of other bacterial species in each portion of the digestive tract. In the stomach and the upper part of the small intestine, lactobacilli controlled the population levels of other bacterial species. In the lower part of the small intestine, not only lactobacilli but also the anaerobes which colonized the large bowel influenced the population levels of other bacterial types. Staphylococci isolated from a conventional rat colonized specifically the keratinized cells of the nonsecreting epithelium of the stomach when the rats were free from lactobacilli. This colonization was not observed after inoculation of lactobacilli into the rats.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROWNLEE A., MOSS W. The influence of diet on lactobacilli in the stomach of the rat. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1961 Oct;82:513–516. doi: 10.1002/path.1700820227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOS R., SCHAEDLER R. W., COSTELLO R., HOET P. INDIGENOUS, NORMAL, AND AUTOCHTHONOUS FLORA OF THE GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:67–76. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. P., Mulcahy D., Takeuchi A., Savage D. C. Location and description of spiral-shaped microorganisms in the normal rat cecum. Infect Immun. 1972 Aug;6(2):184–192. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.2.184-192.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRETER R. In vivo and in vitro antagonism of intestinal bacteria against Shigellaflexneri. II. The inhibitory mechanism. J Infect Dis. 1962 Jan-Feb;110:38–46. doi: 10.1093/infdis/110.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freter R., Abrams G. D. Function of various intestinal bacteria in converting germfree mice to the normal state. Infect Immun. 1972 Aug;6(2):119–126. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.2.119-126.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freter R. Mechanism of Action of Intestinal Antibody in Experimental Cholera II. Antibody-Mediated Antibacterial Reaction at the Mucosal Surface. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):556–562. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.556-562.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYNELL G. G. Antibacterial mechanisms of the mouse gut. II. The role of Eh and volatile fatty acids in the normal gut. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Apr;44:209–219. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maejima K., Tajima Y. Association of gnotobiotic mice with various organisms isolated from conventional mice. Jpn J Exp Med. 1973 Aug;43(4):289–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita Y., Mitsuoka T., Kaneuchi C., Yamamoto T., Yamamoto S. Establishment of microorganisms isolated from chickens in the digestive tract of germ-free chickens. Jpn J Microbiol. 1972 Jan;16(1):27–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1972.tb00624.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C. Localization of certain indigenous microorganisms on the ileal villi of rats. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1505–1506. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1505-1506.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C., McAllister J. S., Davis C. P. Anaerobic bacteria on the mucosal epithelium of the murine large bowel. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):492–502. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.492-502.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C. Microbial interference between indigenous yeast and lactobacilli in the rodent stomach. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1278–1283. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1278-1283.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syed S. A., Abrams G. D., Freter R. Efficiency of various intestinal bacteria in assuming normal functions of enteric flora after association with germ-free mice. Infect Immun. 1970 Oct;2(4):376–386. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.4.376-386.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannock G. W., Savage D. C. Influences of dietary and environmental stress on microbial populations in the murine gastrointestinal tract. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):591–598. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.591-598.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



