Abstract
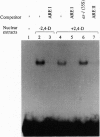
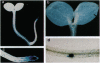
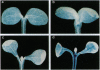
Detailed analysis of transgenic tobaccos containing a series of chimeric parB promoter/beta-glucuronidase (GUS) gene constructs allowed us to define two auxin-responsive elements (AREs) of 48 bp and 95 bp (positions -210 to -163 and -374 to -280) in the parB promoter. The two AREs responded independently to physiological concentrations of auxin. Gel retardation assays revealed binding of nuclear protein(s) to the sequence conserved between ARE I and ARE II. The auxin responsiveness of the parB promoter did not mediate the pathway through the as-1 element and transcription factor ASF-1. AREs I and II were responsive to auxin at physiological concentrations, whereas as-1 responded only to higher concentrations of auxin which may be interpreted as stress, though as-1 had been reported to be a minimal ARE [Liu, X. & Lam, E. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269, 668-675]. Histochemical staining of transgenic tobacco that contained a parB promoter/GUS construct demonstrated the expression of GUS activity in the shoot apex as well as in the root tips, suggesting the involvement of parB expression in meristematic activity or differentiation. The drastic change in auxin responsiveness in the transgenic plants between the 6th and 10th day after imbibition of seeds implies the development or the activation of auxin signal transduction systems during plant development.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ainley W. M., Walker J. C., Nagao R. T., Key J. L. Sequence and characterization of two auxin-regulated genes from soybean. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10658–10666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballas N., Wong L. M., Theologis A. Identification of the auxin-responsive element, AuxRE, in the primary indoleacetic acid-inducible gene, PS-IAA4/5, of pea (Pisum sativum). J Mol Biol. 1993 Oct 20;233(4):580–596. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benfey P. N., Ren L., Chua N. H. The CaMV 35S enhancer contains at least two domains which can confer different developmental and tissue-specific expression patterns. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2195–2202. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08342.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida S., Takahashi Y., Nagata T. Isolation of cDNA of an auxin-regulated gene encoding a G protein beta subunit-like protein from tobacco BY-2 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11152–11156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro S., Nakamura K. The nuclear factor SP8BF binds to the 5'-upstream regions of three different genes coding for major proteins of sweet potato tuberous roots. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Jan;18(1):97–108. doi: 10.1007/BF00018460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E., Benfey P. N., Gilmartin P. M., Fang R. X., Chua N. H. Site-specific mutations alter in vitro factor binding and change promoter expression pattern in transgenic plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7890–7894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X., Lam E. Two binding sites for the plant transcription factor ASF-1 can respond to auxin treatments in transgenic tobacco. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):668–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure B. A., Hagen G., Brown C. S., Gee M. A., Guilfoyle T. J. Transcription, organization, and sequence of an auxin-regulated gene cluster in soybean. Plant Cell. 1989 Feb;1(2):229–239. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi Y., Hasezawa S., Kusaba M., Nagata T. Expression of the auxin-regulated parA gene in transgenic tobacco and nuclear localization of its gene products. Planta. 1995;196(1):111–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00193224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi Y., Kuroda H., Tanaka T., Machida Y., Takebe I., Nagata T. Isolation of an auxin-regulated gene cDNA expressed during the transition from G0 to S phase in tobacco mesophyll protoplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9279–9283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi Y., Nagata T. parB: an auxin-regulated gene encoding glutathione S-transferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):56–59. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi Y., Niwa Y., Machida Y., Nagata T. Location of the cis-acting auxin-responsive region in the promoter of the par gene from tobacco mesophyll protoplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8013–8016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theologis A., Huynh T. V., Davis R. W. Rapid induction of specific mRNAs by auxin in pea epicotyl tissue. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 5;183(1):53–68. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90280-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zettl R., Schell J., Palme K. Photoaffinity labeling of Arabidopsis thaliana plasma membrane vesicles by 5-azido-[7-3H]indole-3-acetic acid: identification of a glutathione S-transferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):689–693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Zaal E. J., Droog F. N., Boot C. J., Hensgens L. A., Hoge J. H., Schilperoort R. A., Libbenga K. R. Promoters of auxin-induced genes from tobacco can lead to auxin-inducible and root tip-specific expression. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Jun;16(6):983–998. doi: 10.1007/BF00016071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]