Abstract
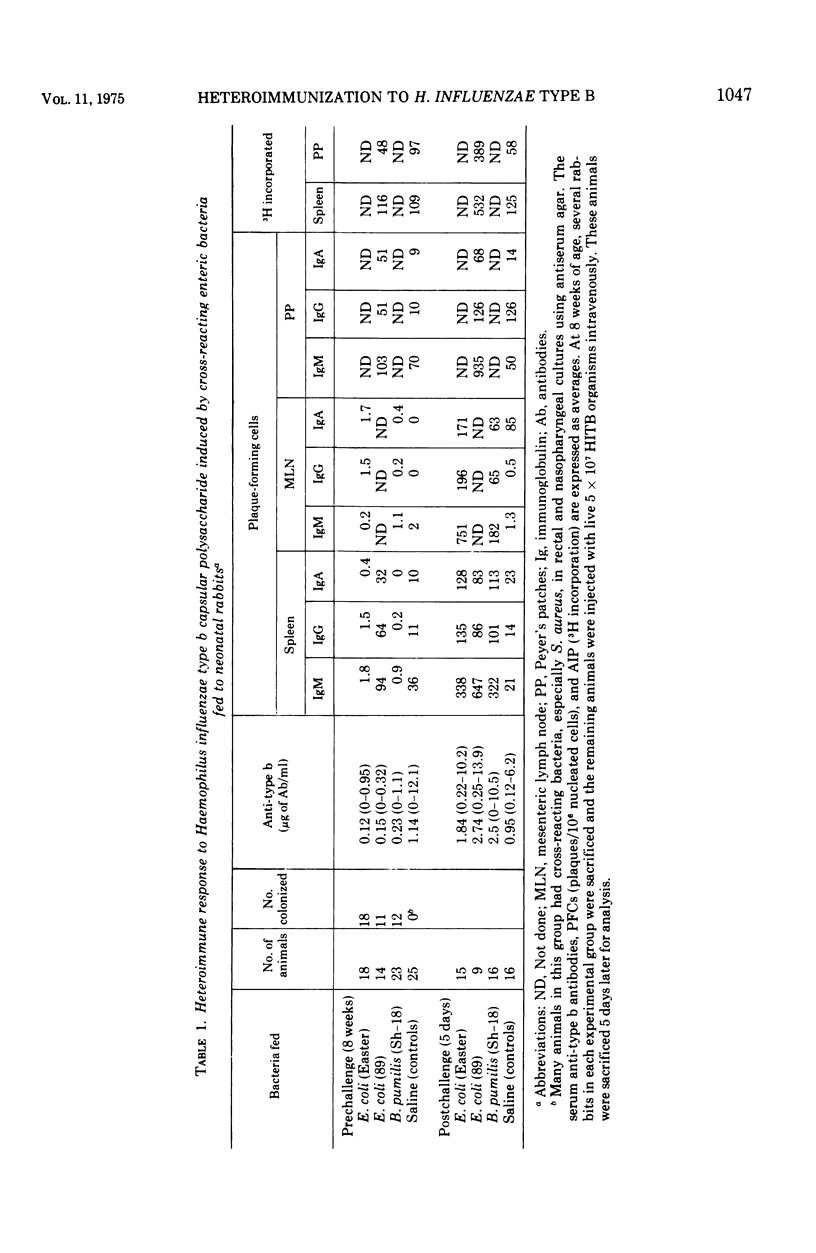
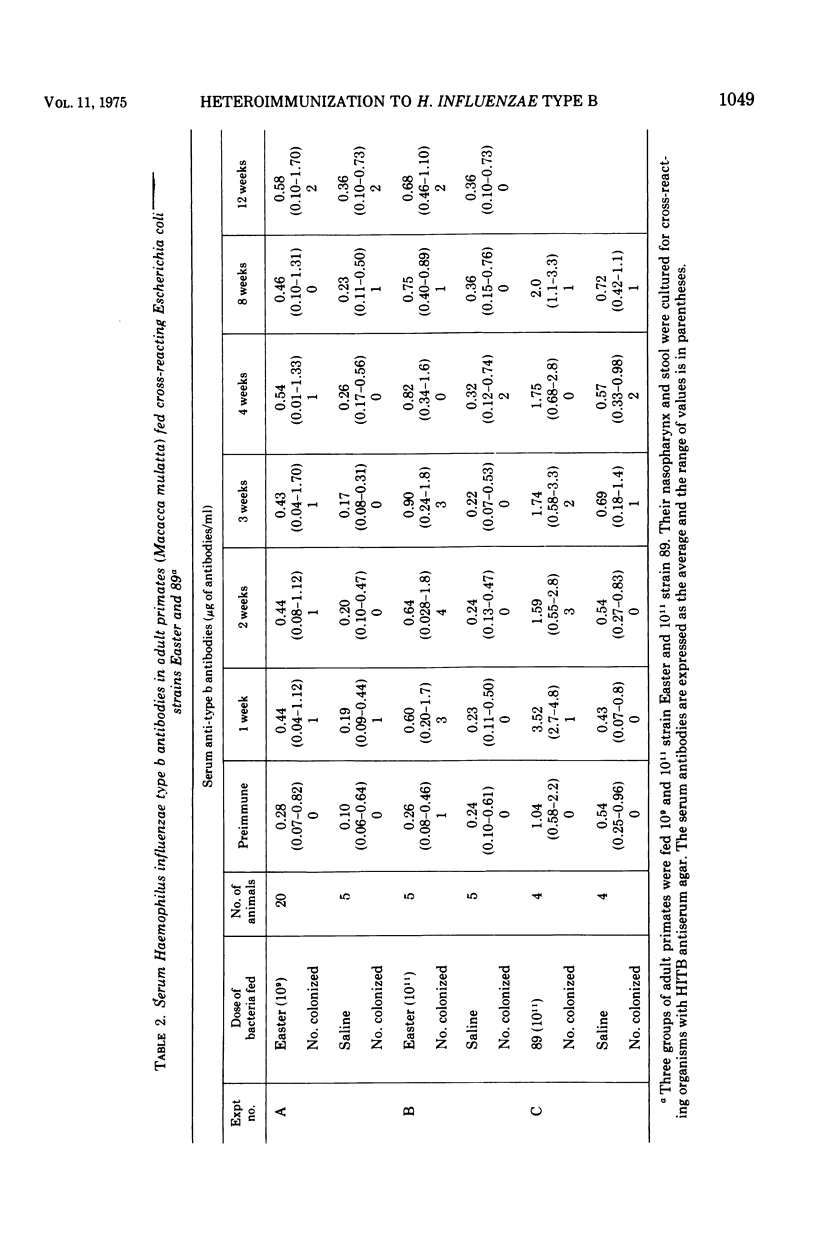
Cross-reacting Escherichia coli strains Easter and 89 and Bacillus pumilis fed to newborn rabbits and E. coli fed to adult rhesus monkeys did not exert untoward reactions. The E. coli regularly colonized the newborns' intestinal tract from 1 to 7 weeks. High doses of E. coli were necessary to colonize adult primates. Colonization occurred in fewer newborn rabbits and lasted only 1 to 3 weeks with B. pumilis. Colonized newborn rabbits and adult rhesus had an active Haemophilus influenzae type b (HITB) immune response. In the rabbit, colonization resulted in accelerated induction of immunoglobulin (Ig) M-. IgA-, and IgG-producing cells in the spleen, mesenteric lymph nodes, and Peyer's patches after HITB challenge. E. coli-fed and control newborn primates were naturally colonized with nasopharyngeal and enteric cross-reacting bacteria and both groups rapidly developed HITB antibodies in the absence of the homologous organisms. Human newborn stool cultures, taken at the time of discharge from the nursery, showed a 0.9% carriage rate for cross-reacting E. coli. These "carrier" infants acquired HITB antibodies more rapidly than their age-matched "noncarrier" controls.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altemeier W. A., 3rd, Robbins J. B., Smith R. T. Quantitative studies of the immunoglobulin sequence in the response of the rabbit to a somatic antigen. J Exp Med. 1966 Sep 1;124(3):443–460. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.3.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Johnston R. B., Jr, Smith D. H. Human serum activities against Hemophilus influenzae, type b. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):31–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI106793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Peter G., Johnston R. B., Jr, Wetterlow L. H., Smith D. H. Immunization of humans with polyribophosphate, the capsular antigen of Hemophilus influenzae, type b. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):39–44. doi: 10.1172/JCI106794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argaman M., Liu T. Y., Robbins J. B. Polyribitol-phosphate: an antigen of four gram-positive bacteria cross-reactive with the capsular polysaccharide of haemophilus influenzae type B. J Immunol. 1974 Feb;112(2):649–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELLANTI J. A., EITZMAN D. V., ROBBINS J. B., SMITH R. T. The development of the immune response. Studies on the agglutinin response to Salmonella flagellar antigens in the newborn rabbit. J Exp Med. 1963 Mar 1;117:479–496. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.3.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. J., Stashak P. W., Prescott B. Use of erythrocytes sensitized with purified pneumococcal polysaccharides for the assay of antibody and antibody-producing cells. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Mar;17(3):422–426. doi: 10.1128/am.17.3.422-426.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw M. W., Schneerson R., Parke J. C., Jr, Robbins J. B. Bacterial antigens cross-reactive with the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Lancet. 1971 May 29;1(7709):1095–1096. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91837-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Formal S. B., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J., Libonati J. P., Sheahan D. G., LaBrec E. H., Kalas J. P. Pathogenesis of Escherichia coli diarrhea. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jul 1;285(1):1–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197107012850101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C. A simplification of the radioactive antigen-binding test by a double label technique. J Immunol. 1971 Sep;107(3):910–911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield S., Peter G., Howie V. M., Ploussard J. H., Smith D. H. Acquisition of type-specific antibodies to Hemophilus influenzae type b. J Pediatr. 1972 Feb;80(2):204–208. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80579-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haemophilus influenzae type b: disease and immunity in humans. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Feb;78(2):259–269. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-78-2-259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison M. R. Thymus independent stimulator cells in the mixed lymphocyte reaction. J Immunol. 1973 Oct;111(4):1270–1273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson M., Alvin A. A 12-year review of acute bacterial meningitis in Stockholm. Scand J Infect Dis. 1971;3(2):141–150. doi: 10.3109/inf.1971.3.issue-2.08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodinova R., Jouja V., Lanc A. Influence of the intestinal flora on the development of immune reactions in infants. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):797–800. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.797-800.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodinová R., Jouja V., Wagner V. Serum immunoglobulins and coproantibody formation in infants after artificial intestinal colonization with Escherichia coli 083 and oral lysozyme administration. Pediatr Res. 1973 Jul;7(7):659–669. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197307000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madjid S., Madjid A. The etiology of meningitis in children of Jakarta. Paediatr Indones. 1965 Jul-Dec;5(3 Suppl):743–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. L., Handzel Z. T., Scheerson R., Robbins J. B. Induction of Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular antibody in neonatal rabbits by gastrointestinal colonization with cross-reacting Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):137–140. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.137-140.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. D. The bacterial etiology and antibiotic management of septic arthritis in infants and children. Pediatrics. 1972 Sep;50(3):437–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parke J. C., Jr, Schneerson R., Robbins J. B. The attack rate, age incidence, racial distribution, and case fatality rate of Hemophilus influenzae type b meningitis in Mecklenbury County, North Carolina. J Pediatr. 1972 Oct;81(4):765–769. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINET H. G. Relationship of host antibody to fluctuations of Escherichia coli serotypes in the human intestine. J Bacteriol. 1962 Nov;84:896–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.5.896-901.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., Myerowitz L., Whisnant J. K., Argaman M., Schneerson R., Handzel Z. T., Gotschlich E. C. Enteric bacteria cross-reactive with Neisseria meningitidis groups A and C and Diplococcus pneumoniae types I and 3. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):651–656. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.651-656.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., Parke J. C., Jr, Schneerson R., Whisnant J. K. Quantitative measurement of "natural" and immunization-induced Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide antibodies. Pediatr Res. 1973 Mar;7(3):103–110. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197303000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues L. P., Schneerson R., Robbins J. B. Immunity to Hemophilus influenzae type b. I. The isolation, and some physicochemical, serologic and biologic properties of the capsular polysaccharide of Hemophilus influenzae type b. J Immunol. 1971 Oct;107(4):1071–1080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPRINGER G. F., HORTON R. E., FORBES M. [Origin of anti-human blood group B agglutinins in white Leghorn chicks]. J Exp Med. 1959 Aug 1;110(2):221–244. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Bradshaw M., Whisnant J. K., Myerowitz R. L., Parke J. C., Jr, Robbins J. B. An Escherichia coli antigen cross-reactive with the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b: occurrence among known serotypes, and immunochemical and biologic properties of E. coli antisera toward H. influenzae type b. J Immunol. 1972 Jun;108(6):1551–1562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Robbins J. B. Age-related susceptibility to Haemophilus influenzae type b disease in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):397–401. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.397-401.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Rodrigues L. P., Parke J. C., Jr, Robbins J. B. Immunity to disease caused by Hemophilus influenzae type b. II. Specificity and some biologic characteristics of "natural," infection-acquired, and immunization-induced antibodies to the capsular polysaccharide of Hemophilus influenzae type b. J Immunol. 1971 Oct;107(4):1081–1089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S. H. The clinical importance of Hemophilus influenzae infections in children. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1970 May;17(2):415–426. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)32419-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. N., Brunjes S. Hemophilus influenzae meningitis in adults. Review of the literature and report of 18 cases. Am J Med Sci. 1965 Dec;250(6):658–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somkuti G. A., Babel F. J. Acid protease synthesis by Mucor pusillus in chemically defined media. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1415–1418. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1415-1418.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer G. F., Horton R. E. Blood group isoantibody stimulation in man by feeding blood group-active bacteria. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jul;48(7):1280–1291. doi: 10.1172/JCI106094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sproles E. T., 3rd, Azerrad J., Williamson C., Merrill R. E. Meningitis due to Hemophilus influenzae: long-term sequelae. J Pediatr. 1969 Nov;75(5):782–788. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80300-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



