Abstract
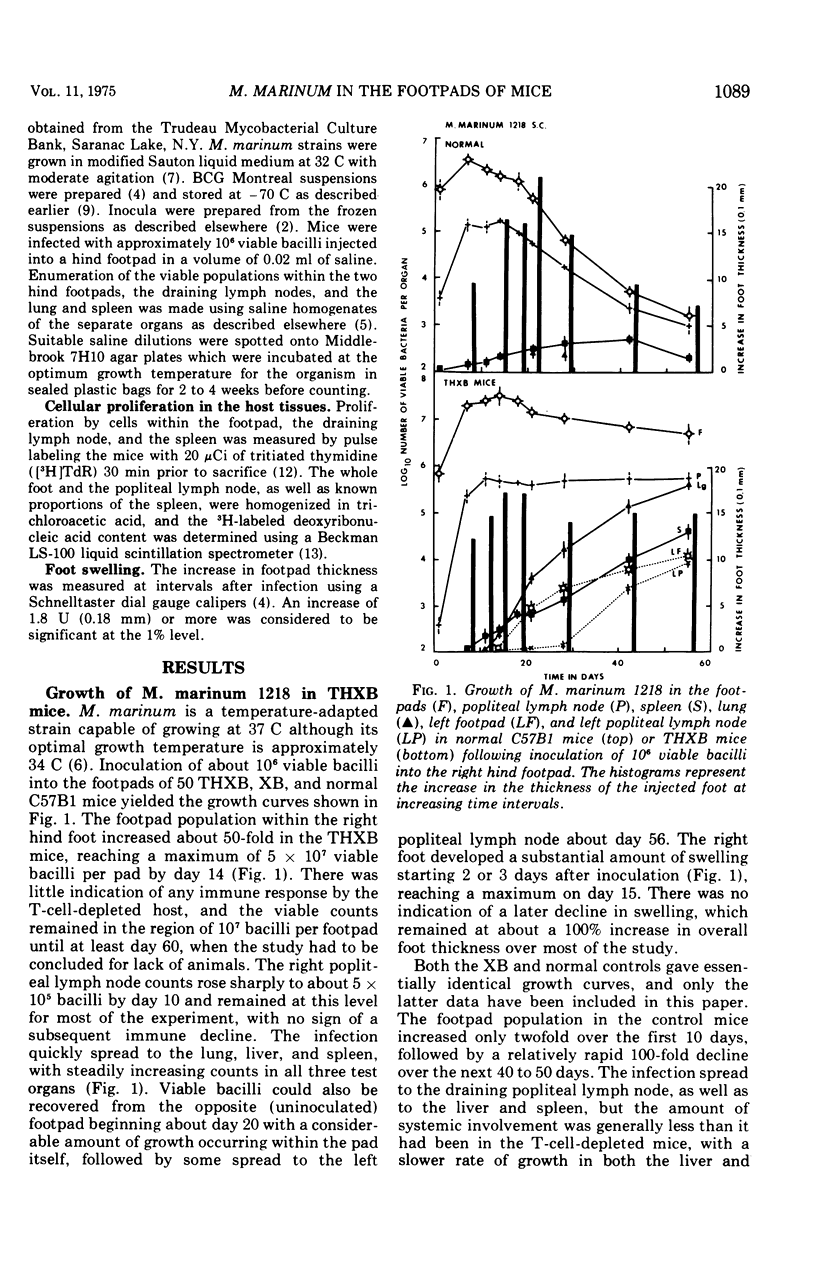
Mycobacterium marinum strains 1218 and 1219 were inoculated into the hind footpads of T-cell-depleted specific pathogen-free C57B1/6 mice, and the growth and survival of the organisms at the site of injection, the draining popliteal lymph node, and the spleen and lung were quantitated for up to 70 days. T-cell depletion largely ablated the normal cell-mediated antituberculous response to the M. marinum population. The mice were able to control the further growth of the inoculum within the footpad only after it had reached 5 to 10 times that present in the normal controls. The high temperature-adapted strain (37 C; strain no. 1218) induced an increasing infection in the liver, spleen, and lungs of the THXB mice, and the infection eventually spread to the opposite footpad and to the tail skin. Strain 1219 gave rise to considerable systemic involvement in the THXB host despite its inability to survive at 37 C, but the size of the splenic and lung populations was considerably lower than in the 1218-infected animals. Both M. marinum infections persisted in the tissues of the T-cell-depleted mice with no indication of a cell-mediated immune response. Footpad swelling in the M. marinum-infected mice was not greatly reduced by T-cell depletion, and, if anything, tended to persist at high levels long after the swelling of the control feet had gone into a decline. On the other hand, incorporation of tritiated thymidine by cells within the infected footpads, the draining lymph node, and the spleen was considerably reduced in the T-cell-depleted host compared with control values. Late in the infection, there was a significant increase in the amount of label taken up by the cells in the footpads of the T-cell-depleted host.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Collins F. M., Mackaness G. B. The relationship of delayed hypersensitivity to acquired antituberculous immunity. I. Tuberculin sensitivity and resistance to reinfection in BCG-vaccinated mice. Cell Immunol. 1970 Sep;1(3):253–265. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Montalbine V., Morrison N. E. Growth and immunogenicity of photochromogenic strains of mycobacteria in the footpads of normal mice. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):1079–1087. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.1079-1087.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Montalbine V. Relative immunogenicity of streptomycin-sensitive and -resistant strains of BCG. Infect Immun. 1973 Sep;8(3):381–387. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.3.381-387.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Montalbine V. Relative immunogenicity of streptomycin-susceptible and -resistant strains of BCG. II. Effect of the route of inoculation on growth and immunogenicity. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 Jan;111(1):43–51. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.111.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Salmonellosis in orally infected specific pathogen-free C57B1 mice. Infect Immun. 1972 Feb;5(2):191–198. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.2.191-198.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Wayne L. G., v Montalbine The effect of cultural conditions on the distribution of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the spleens and lungs of specific pathogen-free mice. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974 Aug;110(2):147–156. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1974.110.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FENNER F. Homologous and heterologous immunity in infections of mice with Mycobacterium ulcerans and Mycobacterium balnei. Am Rev Tuberc. 1957 Jul;76(1):76–89. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1957.76.1.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubica G. P., Dunbar F. P., Kim T. H. Response of hypersensitive mice to the footpad injection of living homologous or heterologous mycobacteria: preliminary report. Appl Microbiol. 1973 May;25(5):718–723. doi: 10.1128/am.25.5.718-723.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison N. E., Collins F. M. Immunogenicity of an aerogenic BCG vaccine in T-cell-depleted and normal mice. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):1110–1121. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.1110-1121.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng H., Jacobsen P. L., Levy L. Analogy of Mycobacterium marinum disease to Mycobacterium leprae infection in footpads of mice. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):860–867. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.860-867.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. Importance of thymus-derived lymphocytes in cell-mediated immunity to infection. Cell Immunol. 1973 Apr;7(1):166–176. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J., Mackaness G. B. Immunological control of macrophage proliferation in vivo. Infect Immun. 1973 Jul;8(1):68–73. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.1.68-73.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees R. J. Enhanced susceptibility of thymectomized and irradiated mice to infection with Mycobacterium leprae. Nature. 1966 Aug 6;211(5049):657–658. doi: 10.1038/211657a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees R. J. Recent bacteriologic, immunologic and pathologic studies on experimental human leprosy in the mouse foot pad. Int J Lepr. 1965 Jul-Sep;33(3 Suppl):646–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard C. C., Habas J. A. Relation of infection to tissue temperature in mice infected with Mycobacterium marinum and Mycobacterium leprae. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):790–796. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.790-796.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



