Abstract
There is growing evidence that cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) interact with tumor cells and play important roles in tumor progression and invasion. Podoplanin is a type-1 transmembrane glycoprotein expressed in a variety of normal human tissues, including lymphatic endothelium. Tumor cell expression of podoplanin correlates with nodal metastasis and poor prognosis in squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of oral cavity and esophagus. Recently, podoplanin-positive CAFs have been shown to exert adverse or beneficial prognostic effect on different cancer types. However, the significance of podoplanin-positive CAFs in esophageal SCC has not been investigated. This is the first study to investigate podoplanin expression in CAFs and tumor cells by immunohistochemistry in 59 cases of surgically resected esophageal SCC. We found significant association of podoplanin expression between CAFs and tumor cells (P = 0.031). Although the abundance of podoplanin-positive CAFs per se had no prognostic effect, concordant podoplanin expression in CAFs and tumor cells (both high or both low) was strongly associated with short survival (P = 0.00088). Multivariate analysis showed that concordant podoplanin expression was the strongest independent adverse prognostic factor (hazard ratio: 3.62; 95% confidence interval: 1.69-7.77; P = 0.00094). Our data suggest that interaction between podoplanin-positive CAFs and tumor cells is important in tumor biology of esophageal SCC.
Keywords: Podoplanin, cancer-associated fibroblast, esophagus, squamous cell carcinoma, prognosis
Introduction
Podoplanin is a type 1 transmembrane mucin-like glycoprotein, which was originally named due to its expression in renal glomerular podocytes of rats [1]. It was later found in a variety of normal human tissues, including lymphatic endothelial cells, glomerular podocytes, heart, lung, placenta, skeletal muscle, myoepithelial cells, myofibroblasts, mesothelial cells, osteoblasts, Schwann cells, follicular dendritic cells, and occasionally in the basal layer of epidermis and esophageal mucosa [2-11]. The physiological functions and pathways of podoplanin are largely unknown. They are probably involved in regulation of renal glomerular filtration and lymphangiogenesis [12,13].
Podoplanin has been observed to be variably expressed in SCC of esophagus, oral cavity, larynx, skin and uterine cervix [10,14-16]. Tumor cell expression of podoplanin has been demonstrated to play a role in lymphangiogenesis, nodal metastasis [17], carcinogenesis [18,19], cell motility, tumor invasiveness [14], platelet aggregation and hematogenous metastasis [20]. High podoplanin expression in tumor cells has been found to correlate with nodal metastasis and poor prognosis in esophageal SCC [10,21-23].
Podoplanin has also been found to be expressed in some cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs). Abundance of podoplanin-positive CAFs has been shown to correlate with poor prognosis and/or nodal metastasis in a number of cancers, including intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma [24], pulmonary adenocarcinoma [25-27], pulmonary SCC [28], invasive ductal breast carcinoma [29,30], pancreatic ductal carcinoma [31], malignant melanoma [32] and esophageal adenocarcinoma [33]. In contrast, abundance of podoplanin-positive CAFs has been noted to be associated with favorable prognosis or less nodal metastasis in other cancers, such as colorectal carcinoma [34,35] and uterine cervical carcinoma [36]. However, the prognostic significance of podoplanin-positive CAFs in esophageal SCC remains unknown.
Here we investigate podoplanin-positive CAFs in 59 surgically resected esophageal SCC by immunohistochemistry. The result is correlated with clinicopathologic features and patient survival to determine the prognostic significance.
Materials and methods
Patients
A total of 59 cases of surgically resected esophageal SCC were recruited for this study. These cases had been previously studied for tumor cell expression of podoplanin [10]. Forty-three of the patients received pre-operative concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT). Pathologic and pre-operative clinical staging was performed according to the 7th edition of AJCC Cancer Staging Manual [37].
Immunohistochemistry
Resected esophageal SCC and adjacent normal tissue were fixed in 10% buffered neutral formalin, dehydrated and embedded in paraffin. Tissue sections were stained for hematoxylin and eosin for morphologic evaluation. Additional 4-μm-thick sections were taken, deparaffinized and rehydrated for immunohistochemical study. We used a mouse anti-human D2-40 monoclonal antibody (Dako, Glostrup, Denmark, 1:100) as the primary antibody and followed a previously published protocol for immunohistochemical study [15]. Positive staining for lymphatic endothelial cells in sections served as internal control.
The immunostained slides were evaluated by two pathologists (W.-Y. C. and C.-J. Y.) under a dual-head microscope without knowing the clinicopathologic information. The area percentage of podoplanin-positive CAFs within total tumor stroma was estimated directly under microscope (Figure 1). The tumor cell expression of podoplanin had been evaluated in a previous study using an immunoreactive score by multiplying staining intensity and quantity [10].
Figure 1.
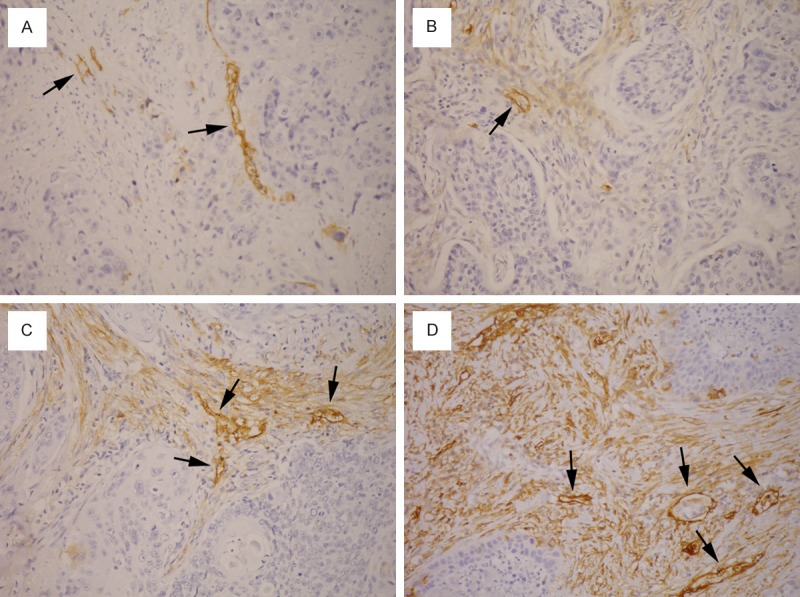
Podoplanin-positive cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in tumor stroma of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. The area percentage of CAFs is as follows: (A) 0%; (B) 15%; (C) 65%; (D) 95%. Lymphatic endothelial cells (arrows) serve as internal positive control.
Statistical analysis
Differences in categorical data were assessed by a chi-square test, and Yates’ correction was performed if expected frequencies less than 5 were encountered. Differences in percentage of podoplanin-positive CAFs and age between groups were assessed by the Mann-Whitney U-test. Overall survival was analyzed by the Kaplan-Meier method and compared by log-rank tests. The influence of parameters on survival was first analyzed using univariate Cox regression, and statistically significant parameters were further analyzed by multivariate Cox regression. A P-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using the WinSTAT® for Excel (R. Fitch Software, Bad Krozingen, Germany).
Results
Podoplanin-positive CAFs and clinicopathologic characteristics
The area percentage of podoplanin-positive CAFs within tumor stroma was between 0% and 95%, with a median of 25%. A percentage of 25% or higher was considered high podoplanin expression in CAFs, whereas a percentage lower than 25% was considered low expression. The clinicopathologic features of patients grouped by podoplanin-positive CAFs were listed in Table 1. We found no correlation of podoplanin-positive CAFs with age at diagnosis, gender, preoperative CCRT, tumor grade, lymphatic vessel invasion, pT classification, pN, pM, pathologic stage, cT, cN, cM or clinical stage.
Table 1.
Clinicopathologic characteristics of cases grouped by abundance of podoplanin-positive cancer-associated fibroblasts
| Characteristic | Podoplanin-positive CAFs | Total (n = 59) | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||
| Low (n = 28) | High (n = 31) | |||
| Podoplanin in tumor cells (%) | ||||
| High | 9 (32) | 16 (52) | 25 (42) | 0.13 |
| Low | 19 (68) | 15 (48) | 34 (58) | |
| Age at diagnosis | ||||
| Mean ± SD | 59 ± 14 | 55 ± 11 | 57 ± 13 | 0.19 |
| Median (min; max) | 59 (38; 100) | 56 (38; 78) | 56 (38; 100) | |
| Gender (%) | ||||
| Female | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 1 (2) | 0.96 |
| Male | 27 (96) | 31 (100) | 58 (98) | |
| Pre-operative CCRT (%) | ||||
| Yes | 20 (71) | 22 (71) | 42 (71) | 0.96 |
| No | 8 (29) | 9 (29) | 17 (29) | |
| Tumor grade (%) | ||||
| Grade 1 | 2 (7) | 1 (3) | 3 (5) | 0.96 |
| Grade 2 | 22 (79) | 22 (71) | 44 (75) | |
| Grade 3 | 4 (14) | 8 (26) | 12 (20) | |
| Lymphatic vessel invasion (%) | ||||
| Yes | 13 (46) | 12 (39) | 25 (42) | 0.55 |
| No | 15 (54) | 19 (61) | 34 (58) | |
| pT (%) | ||||
| pT1-2 | 6 (21) | 3 (10) | 9 (15) | 0.37 |
| pT3-4 | 22 (79) | 28 (90) | 50 (85) | |
| pN (%) | ||||
| pN0 | 11 (39) | 18 (58) | 29 (49) | 0.15 |
| pN1-3 | 17 (61) | 13 (42) | 30 (51) | |
| pM (%) | ||||
| pM0 | 27 (96) | 27 (87) | 54 (92) | 0.41 |
| pM1 | 1 (4) | 4 (13) | 5 (8) | |
| Pathologic stage (%) | ||||
| I/II | 11 (39) | 15 (48) | 26 (44) | 0.48 |
| III/IV | 17 (61) | 16 (51) | 33 (56) | |
| cT (%)* | ||||
| cT1-2 | 9 (36) | 7 (28) | 16 (32) | 0.54 |
| cT3-4 | 16 (64) | 18 (72) | 34 (68) | |
| cN (%)* | ||||
| cN0 | 6 (26) | 8 (33) | 14 (30) | 0.59 |
| cN1-3 | 17 (74) | 16 (67) | 33 (70) | |
| cM (%)* | ||||
| cM0 | 21 (95) | 21 (91) | 42 (93) | 0.96 |
| cM1 | 1 (5) | 2 (9) | 3 (7) | |
| Clinical stage (%)* | ||||
| I/II | 10 (40) | 10 (38) | 20 (39) | 0.91 |
| III/IV | 15 (60) | 16 (62) | 31 (61) | |
Some cases excluded due to incomplete pre-treatment clinical staging;
CAFs = cancer-associated fibroblasts; SD = standard deviation; CCRT = concurrent chemoradiotherapy.
Podoplanin expression in CAFs and tumor cells
Abundance of podoplanin-positive CAFs in tumor stroma was associated with high podoplanin expression in tumor cells (Figure 2; P = 0.031 with Mann-Whitney U-test). Thirty-five cases (59.3%) had concordant podoplanin expression (both high or both low) in tumor cells and CAFs, whereas the expression was discordant in 24 cases (40.7%) (Figure 3).
Figure 2.
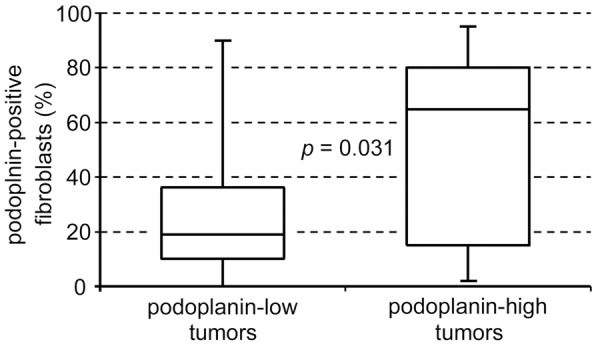
The abundance of podoplanin-positive CAFs correlates with tumor cell expression of podoplanin (P = 0.031; Mann-Whitney U-test).
Figure 3.
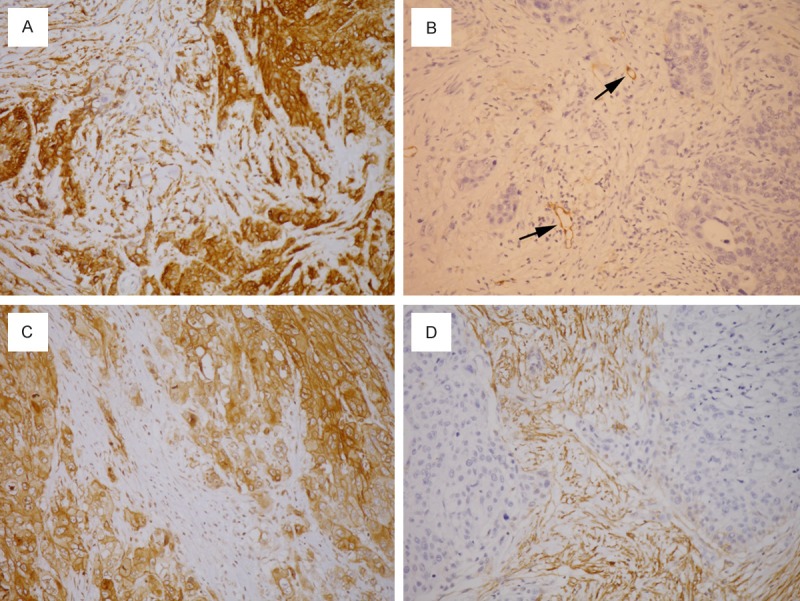
Concordant podoplanin expression in tumor cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs): (A) both high; (B) both low. Discordant podoplanin expression in tumor cells and CAFs: (C) high in tumor cells and low in CAFs; (D) low in tumor cells and high in CAFs. Lymphatic endothelial cells (arrows) serve as internal positive control.
Survival
The abundance of podoplanin-positive CAFs per se had no significant influence on survival (Figure 4A; P = 0.75). Interestingly, when the level of podoplanin expression in tumor cells was taken into consideration, opposite prognostic effect of podoplanin-positive CAFs was found in podoplanin-high vs. podoplanin-low tu-mors. In patients with podoplanin-low tumor cells, abundance of podoplanin-positive CAFs was a favorable prognostic factor (Figure 4B; P = 0.014). Conversely, in patients with podoplanin-high tumor cells, abundance of podoplanin-positive CAFs was an adverse prognostic factor (Figure 4C; P = 0.018). In addition, concordant expression of podoplanin in CAFs and tumor cells (both high or both low) was strongly associated with short survival in esophageal SCC patients (Figure 4D; P = 0.00088).
Figure 4.
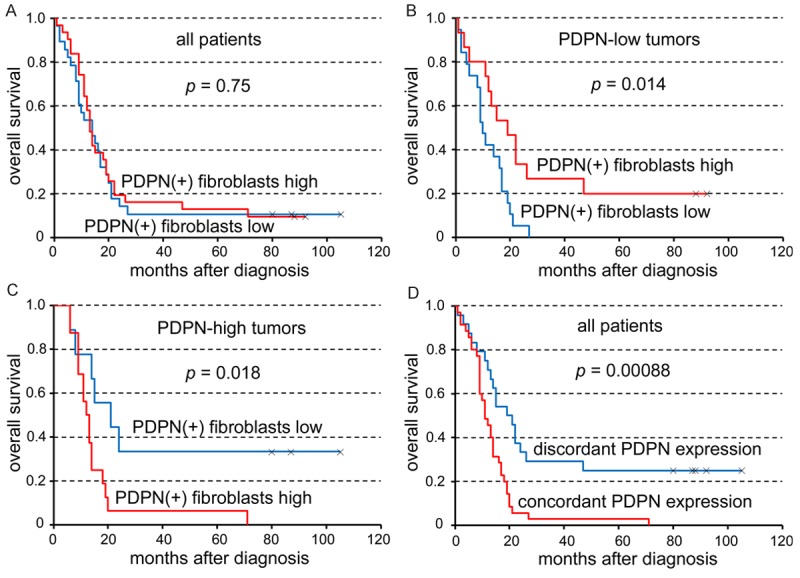
The abundance of podoplanin (PDPN)-positive cancer-associated fibroblasts per se has no prognostic effect (A). The prognostic effect of PDPN-positive fibroblasts is opposite in PDPN-low (B) and PDPN-high (C) tumors. Concordant PDPN expression (both high or both low) in fibroblasts and tumor cells is significantly associated with short survival (D).
The hazard ratios (HRs) and P-values of independent clinicopathologic parameters using univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were listed in Table 2. In univariate analyses, concordant podoplanin expression (HR: 2.63; 95% confidence interval: 1.44-4.79; P = 0.0017), advanced pT classification (HR: 3.79; 95% confidence interval: 1.47-9.76; P = 0.0058) and clinical nodal metastasis (HR: 2.41; 95% confidence interval: 1.17-4.98; P = 0.017) were statistically significant adverse prognostic factors. Further multivariate analysis of these three parameters showed that concordant podoplanin expression was the strongest independent adverse prognostic factor (HR: 3.62; 95% confidence interval: 1.69-7.77; P = 0.00094). Advanced pT classification was the other independent adverse prognostic factor (HR: 3.45; 95% confidence interval: 1.27-9.35; P = 0.015), whereas clinical nodal metastasis had only a trend of poor prognosis (HR: 1.94; 95% confidence interval: 0.92-4.11; P = 0.084) in multivariate analysis.
Table 2.
Univariate and multivariate survival analyses using Cox regression
| Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
||||||
| Parameter | n | HR | 95% CI | P-value | HR | 95% CI | p-value |
| PDPN in CAFs | |||||||
| High/low | 31/28 | 0.92 | (0.53-1.57) | 0.75 | |||
| PDPN in TCs | |||||||
| High/low | 25/34 | 0.90 | (0.52-1.56) | 0.71 | |||
| Concordant PDPN | |||||||
| Yes/no | 35/24 | 2.63 | (1.44-4.79) | 0.0017 | 3.62 | (1.69-7.77) | 0.00094 |
| pT | |||||||
| T3-4/T1-2 | 50/9 | 3.79 | (1.47-9.76) | 0.0058 | 3.45 | (1.27-9.35) | 0.015 |
| pN | |||||||
| N1-3/N0 | 30/29 | 1.22 | (0.71-2.10) | 0.47 | |||
| pM | |||||||
| M1/M0 | 5/54 | 1.48 | (0.58-3.81) | 0.41 | |||
| cT | |||||||
| T3-4/T1-2 | 34/16 | 1.38 | (0.72-2.64) | 0.33 | |||
| cN | |||||||
| N1-3/N0 | 33/14 | 2.41 | (1.17-4.98) | 0.017 | 1.94 | (0.92-4.11) | 0.084 |
| cM | |||||||
| M1/M0 | 3/42 | 0.91 | (0.28-2.98) | 0.87 | |||
| Tumor grade | |||||||
| G3/G1-2 | 12/47 | 0.82 | (0.42-1.59) | 0.55 | |||
| Age at diagnosis | |||||||
| ≥ 56/< 56 | 33/26 | 0.80 | (0.46-1.39) | 0.43 | |||
| Pre-Op CCRT | |||||||
| Yes/no | 42/17 | 1.12 | (0.61-2.08) | 0.72 | |||
HR = hazard ratio; 95% CI = 95% confidence interval; PDPN = podoplanin; CAFs = cancer-associated fibroblasts; TCs = tumor cells; Concordant PDPN = concordant expression of podoplanin in cancer-associated fibroblasts and tumor cells; Pre-Op CCRT = pre-operative concurrent chemoradiotherapy.
Discussion
Our study showed that simultaneously high or low podoplanin expression in CAFs and tumor cells was an independent adverse prognostic factor in esophageal SCC patients. Unlike other tumor types in which the level of podoplanin-positive CAFs alone serves as an adverse [24-33] or favorable [34-36] prognostic factor, our finding suggests that the interaction of podoplanin expression between CAFs and tumor cells has significant impact on the biological behavior of esophageal SCC.
Podoplanin is variably expressed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) [10,14]. Previously, we found that high podoplanin expression of esophageal SCC tumor cells correlates with clinical nodal metastasis, which is associated with short survival [10]. We also found an adverse prognostic effect in a cohort of esophageal SCC patients after chemoradiotherapy [21]. Subsequent studies showed that high podoplanin expression of tumor cells correlates with poor prognosis and nodal metastasis in other cohorts of esophageal SCC patients as well [22,23].
Podoplanin-positive CAFs have been demonstrated to induce lymphangiogenesis and correlate with lymphatic invasion and nodal metastasis in human tumors [27]. In an animal study using subcutaneous injection of A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cells into SCID mice, simultaneous injection of isolated podoplanin-positive fibroblasts enhanced tumor formation, nodal metastasis and pulmonary metastasis [26]. Knockdown of podoplanin in fibroblasts decreased the augmenting effect of tumor formation and in vitro colony formation, whereas overexpression of podoplanin in fibroblasts hastened the tumor formation [26]. These findings may explain the association of podoplanin-positive CAFs with nodal metastasis and short survival in several types of cancers, including cholangiocarcinoma, pulmonary adenocarcinoma, pulmonary SCC, invasive ductal breast carcinoma, pancreatic ductal carcinoma, malignant melanoma and esophageal adenocarcinoma [24-33]. Similar adverse prognostic effect of podoplanin-positive CAFs was also observed in our cases of esophageal SCC with high tumor cell expression of podoplanin (Figure 4C).
In contrast, podoplanin-positive CAFs have been found to be associated with favorable prognosis or less nodal metastasis in colorectal carcinoma and uterine cervical carcinoma [34-36]. It has been shown that in co-cultured colorectal cancer cell lines and fibroblasts, transfection of CAFs with podoplanin siRNA significantly increased tumor invasion in a Matrigel model [34]. This finding supports a favorable prognostic effect of podoplanin-positive CAFs in certain cancer types. Such association was also observed in our esophageal SCC with low tumor cell expression of podoplanin (Figure 4B).
The contradictory effects of podoplanin-positive CAFs in different cancer types were seen in esophageal SCC by our study when there was different level of podoplanin expression in tumor cells. It implicates that the complex interaction between CAFs and cancer cells has pronounced effect in tumor microenvironment. The correlation of podoplanin expression between CAFs and tumor cells in our present study (Figure 2) also supports the presence of interaction. The communication between tumor cells and CAFs has been shown by few earlier studies. For example, oral SCC cells were found to secrete interleukin-1β (IL-1β), which stimulates fibroblasts to secrete transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), which in turn induces podoplanin expression in oral SCC cells, resulting in cancer progression [38]. The IL-1β secreted by SCC cells also has an autocrine effect and can stimulate SCC cells to secrete tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), which acts as a paracrine signal to promote the activity of CAFs and thereby to enhance cancer cell invasion [39].
In the previous studies on podoplanin-positive CAFs, tumor cell expression of podoplanin was either rare as in pulmonary adenocarcinoma [25], invasive ductal breast carcinoma [29] and esophageal adenocarcinoma [33] or absent as in pancreatic ductal carcinoma and colorectal carcinoma [31,34,35]. On the other hand, significant proportions of podoplanin-positive tumor cells were found in pulmonary SCC [28], uterine cervical carcinoma [36] and malignant melanoma [32], but no correlation of podoplanin expression between tumor cells and CAFs was mentioned. Our study is the first to investigate the interaction of podoplanin expression between tumor cells and CAFs and its possible influence on prognosis. Moreover, we found for the first time that concordant podoplanin expression in both tumor cells and CAFs has significant prognostic implication.
Recently, two distinct subtypes of CAFs with different tumor-promoting capabilities were found in oral SCC [40]. One subtype has a transcriptome and secretome closer to normal fibroblasts (CAF-N), whereas the other has a more divergent expression pattern (CAF-D). Using an animal model of tumor xerografting, both subtypes of CAFs supported higher tumor incidence and deeper invasion, but CAF-N was more efficient than CAF-D in enhancing tumor incidence. CAF-N included more intrinsically motile fibroblasts maintained by autocrine production of hyaluronan, and the motility of CAF-N was essential for invasion of adjacent SCC cells. In contrast, CAF-D included fewer motile fibroblasts but synthesized higher levels of TGF-β1. TGF-β1 did not stimulate CAF-D migration but enhanced invasion and expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers in SCC cells. Interestingly, they found that podoplanin was underexpressed in CAFs (as a whole) compared with normal oral fibroblasts, but the expression levels of podoplanin in two subtypes of CAFs were not clearly described. It appears that the role CAFs play in tumor cell-stromal cell interactions is very sophisticated and remains to be defined.
In conclusion, this is the first study to show that concordant podoplanin expression in CAFs and tumor cells is an independent adverse prognostic factor in esophageal SCC patients. The prognostic impact is highly significant only when podoplanin expression in tumor cells and CAFs is simultaneously assessed. Our result suggests that interaction between podoplanin-positive CAFs and tumor cells is important in tumor biology of esophageal SCC. Additional studies on large cohorts of patients and further functional investigations are warranted.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from The Department of Education, Taiwan, ROC (EMRPD1D0611, to C. H.) and the Chang Gung Medical Research Program (CMRPD1C0041, to W.-Y. C.).
Disclosure of conflict of interest
None.
References
- 1.Breiteneder-Geleff S, Matsui K, Soleiman A, Meraner P, Poczewski H, Kalt R, Schaffner G, Kerjaschki D. Podoplanin, novel 43-kd membrane protein of glomerular epithelial cells, is down-regulated in puromycin nephrosis. Am J Pathol. 1997;151:1141–1152. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Breiteneder-Geleff S, Soleiman A, Kowalski H, Horvat R, Amann G, Kriehuber E, Diem K, Weninger W, Tschachler E, Alitalo K, Kerjaschki D. Angiosarcomas express mixed endothelial phenotypes of blood and lymphatic capillaries: podoplanin as a specific marker for lymphatic endothelium. Am J Pathol. 1999;154:385–394. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65285-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Martín-Villar E, Scholl FG, Gamallo C, Yurrita MM, Muñoz-Guerra M, Cruces J, Quintanilla M. Characterization of human PA2.26 antigen (T1alpha-2, podoplanin), a small membrane mucin induced in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 2005;113:899–910. doi: 10.1002/ijc.20656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kanner WA, Galgano MT, Atkins KA. Podoplanin expression in basal and myoepithelial cells: utility and potential pitfalls. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2010;18:226–230. doi: 10.1097/PAI.0b013e3181c65141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ordóñez NG. Podoplanin: a novel diagnostic immunohistochemical marker. Adv Anat Pathol. 2006;13:83–88. doi: 10.1097/01.pap.0000213007.48479.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jokinen CH, Dadras SS, Goldblum JR, van de Rijn M, West RB, Rubin BP. Diagnostic implications of podoplanin expression in peripheral nerve sheath neoplasms. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008;129:886–893. doi: 10.1309/M7D5KTVYYE51XYQA. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yu H, Gibson JA, Pinkus GS, Hornick JL. Podoplanin (D2-40) is a novel marker for follicular dendritic cell tumors. Am J Clin Pathol. 2007;128:776–782. doi: 10.1309/7P8U659JBJCV6EEU. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Xie Q, Chen L, Fu K, Harter J, Young KH, Sunkara J, Novak D, Villanueva-Siles E, Ratech H. Podoplanin (D2-40): a new immunohistochemical marker for reactive follicular dendritic cells and follicular dendritic cell sarcomas. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2008;1:276–284. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schacht V, Dadras SS, Johnson LA, Jackson DG, Hong YK, Detmar M. Up-regulation of the lymphatic marker podoplanin, a mucin-type transmembrane glycoprotein, in human squamous cell carcinomas and germ cell tumors. Am J Pathol. 2005;166:913–921. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62311-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chuang WY, Yeh CJ, Wu YC, Chao YK, Liu YH, Tseng CK, Chang HK, Liu HP, Hsueh C. Tumor cell expression of podoplanin correlates with nodal metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Histol Histopathol. 2009;24:1021–1027. doi: 10.14670/HH-24.1021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chuang WY, Chang YS, Yeh CJ, Wu YC, Hsueh C. Role of podoplanin expression in squamous cell carcinoma of upper aerodigestive tract. Histol Histopathol. 2013;28:293–299. doi: 10.14670/HH-28.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Koop K, Eikmans M, Wehland M, Baelde H, Ijpelaar D, Kreutz R, Kawachi H, Kerjaschki D, de Heer E, Bruijn JA. Selective loss of podoplanin protein expression accompanies proteinuria and precedes alterations in podocyte morphology in a spontaneous proteinuric rat model. Am J Pathol. 2008;173:315–26. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.080063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Schacht V, Ramirez MI, Hong YK, Hirakawa S, Feng D, Harvey N, Williams M, Dvorak AM, Dvorak HF, Oliver G, Detmar M. T1alpha/podoplanin deficiency disrupts normal lymphatic vasculature formation and causes lymphedema. EMBO J. 2003;22:3546–3556. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wicki A, Lehembre F, Wick N, Hantusch B, Kerjaschki D, Christofori G. Tumor invasion in the absence of epithelial-mesenchymal transition: podoplanin-mediated remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton. Cancer Cell. 2006;9:261–272. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yuan P, Temam S, El-Naggar A, Zhou X, Liu DD, Lee JJ, Mao L. Overexpression of podoplanin in oral cancer and its association with poor clinical outcome. Cancer. 2006;107:563–569. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dumoff KL, Chu C, Xu X, Pasha T, Zhang PJ, Acs G. Low D2-40 immunoreactivity correlates with lymphatic invasion and nodal metastasis in early-stage squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Mod Pathol. 2005;18:97–104. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3800269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Cueni LN, Hegyi I, Shin JW, Albinger-Hegyi A, Gruber S, Kunstfeld R, Moch H, Detmar M. Tumor lymphangiogenesis and metastasis to lymph nodes induced by cancer cell expression of podoplanin. Am J Pathol. 2010;177:1004–1016. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kawaguchi H, El-Naggar AK, Papadimitrakopoulou V, Ren H, Fan YH, Feng L, Lee JJ, Kim E, Hong WK, Lippman SM, Mao L. Podoplanin: a novel marker for oral cancer risk in patients with oral premalignancy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008;26:354–360. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.13.4072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Durchdewald M, Guinea-Viniegra J, Haag D, Riehl A, Lichter P, Hahn M, Wagner EF, Angel P, Hess J. Podoplanin is a novel fos target gene in skin carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2008;68:6877–6883. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kunita A, Kashima TG, Morishita Y, Fukayama M, Kato Y, Tsuruo T, Fujita N. The platelet aggregation-inducing factor aggrus/podoplanin promotes pulmonary metastasis. Am J Pathol. 2007;170:1337–1347. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.060790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chao YK, Chuang WY, Yeh CJ, Wu YC, Liu YH, Hsieh MJ, Cheng AJ, Hsueh C, Liu HP. Prognostic significance of high podoplanin expression after chemoradiotherapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. J Surg Oncol. 2012;105:183–188. doi: 10.1002/jso.22068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rahadiani N, Ikeda J, Makino T, Tian T, Qiu Y, Mamat S, Wang Y, Doki Y, Aozasa K, Morii E. Tumorigenic role of podoplanin in esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:1311–1323. doi: 10.1245/s10434-009-0895-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Saigusa S, Mohri Y, Ohi M, Toiyama Y, Ishino Y, Okugawa Y, Tanaka K, Inoue Y, Kusunoki M. Podoplanin and SOX2 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma after neoadjuvant chemo-radiotherapy. Oncol Rep. 2011;26:1069–1074. doi: 10.3892/or.2011.1408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Aishima S, Nishihara Y, Iguchi T, Taguchi K, Taketomi A, Maehara Y, Tsuneyoshi M. Lymphatic spread is related to VEGF-C expression and D2-40-positive myofibroblasts in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Mod Pathol. 2008;21:256–264. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3800985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kawase A, Ishii G, Nagai K, Ito T, Nagano T, Murata Y, Hishida T, Nishimura M, Yoshida J, Suzuki K, Ochiai A. Podoplanin expression by cancer associated fibroblasts predicts poor prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2008;123:1053–1059. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hoshino A, Ishii G, Ito T, Aoyagi K, Ohtaki Y, Nagai K, Sasaki H, Ochiai A. Podoplanin-positive fibroblasts enhance lung adenocarcinoma tumor formation: podoplanin in fibroblast functions for tumor progression. Cancer Res. 2011;71:4769–4779. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kitano H, Kageyama S, Hewitt SM, Hayashi R, Doki Y, Ozaki Y, Fujino S, Takikita M, Kubo H, Fukuoka J. Podoplanin expression in cancerous stroma induces lymphangiogenesis and predicts lymphatic spread and patient survival. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2010;134:1520–1527. doi: 10.1043/2009-0114-OA.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ono S, Ishii G, Nagai K, Takuwa T, Yoshida J, Nishimura M, Hishida T, Aokage K, Fujii S, Ikeda N, Ochiai A. Podoplanin-positive cancer-associated fibroblasts could have prognostic value independent of cancer cell phenotype in stage I lung squamous cell carcinoma: usefulness of combining analysis of both cancer cell phenotype and cancer-associated fibroblast phenotype. Chest. 2013;143:963–970. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-0913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Pula B, Jethon A, Piotrowska A, Gomulkiewicz A, Owczarek T, Calik J, Wojnar A, Witkiewicz W, Rys J, Ugorski M, Dziegiel P, Podhorska-Okolow M. Podoplanin expression by cancer-associated fibroblasts predicts poor outcome in invasive ductal breast carcinoma. Histopathology. 2011;59:1249–1260. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2011.04060.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Schoppmann SF, Berghoff A, Dinhof C, Jakesz R, Gnant M, Dubsky P, Jesch B, Heinzl H, Birner P. Podoplanin-expressing cancer-associated fibroblasts are associated with poor prognosis in invasive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;134:237–244. doi: 10.1007/s10549-012-1984-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Shindo K, Aishima S, Ohuchida K, Fujiwara K, Fujino M, Mizuuchi Y, Hattori M, Mizumoto K, Tanaka M, Oda Y. Podoplanin expression in cancer-associated fibroblasts enhances tumor progression of invasive ductal carcinoma of the pancreas. Mol Cancer. 2013;12:168. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kan S, Konishi E, Arita T, Ikemoto C, Takenaka H, Yanagisawa A, Katoh N, Asai J. Podoplanin expression in cancer-associated fibroblasts predicts aggressive behavior in melanoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2014;41:561–7. doi: 10.1111/cup.12322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Schoppmann SF, Jesch B, Riegler MF, Maroske F, Schwameis K, Jomrich G, Birner P. Podoplanin expressing cancer associated fibroblasts are associated with unfavourable prognosis in adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2013;30:441–446. doi: 10.1007/s10585-012-9549-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Yamanashi T, Nakanishi Y, Fujii G, Akishima-Fukasawa Y, Moriya Y, Kanai Y, Watanabe M, Hirohashi S. Podoplanin expression identified in stromal fibroblasts as a favorable prognostic marker in patients with colorectal carcinoma. Oncology. 2009;77:53–62. doi: 10.1159/000226112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Choi SY, Sung R, Lee SJ, Lee TG, Kim N, Yoon SM, Lee EJ, Chae HB, Youn SJ, Park SM. Podoplanin, α-smooth muscle actin or S100A4 expressing cancer-associated fibroblasts are associated with different prognosis in colorectal cancers. J Korean Med Sci. 2013;28:1293–1301. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.9.1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Carvalho FM, Zaganelli FL, Almeida BG, Goes JC, Baracat EC, Carvalho JP. Prognostic value of podoplanin expression in intratumoral stroma and neoplastic cells of uterine cervical carcinomas. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 2010;65:1279–1283. doi: 10.1590/S1807-59322010001200009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Edge S, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A. Esophagus and Esophagogastric Junction. In: Edge S, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A, editors. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th edition. New York: Springer; 2010. pp. 103–115. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hwang YS, Xianglan Z, Park KK, Chung WY. Functional invadopodia formation through stabilization of the PDPN transcript by IMP-3 and cancer-stromal crosstalk for PDPN expression. Carcinogenesis. 2012;33:2135–2146. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgs258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Chaudhry SI, Hooper S, Nye E, Williamson P, Harrington K, Sahai E. Autocrine IL-1β-TRAF6 signalling promotes squamous cell carcinoma invasion through paracrine TNFα signalling to carcinoma-associated fibroblasts. Oncogene. 2013;32:747–758. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Costea DE, Hills A, Osman AH, Thurlow J, Kalna G, Huang X, Pena Murillo C, Parajuli H, Suliman S, Kulasekara KK, Johannessen AC, Partridge M. Identification of two distinct carcinoma-associated fibroblast subtypes with differential tumor-promoting abilities in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2013;73:3888–3901. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


