Abstract
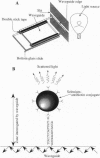
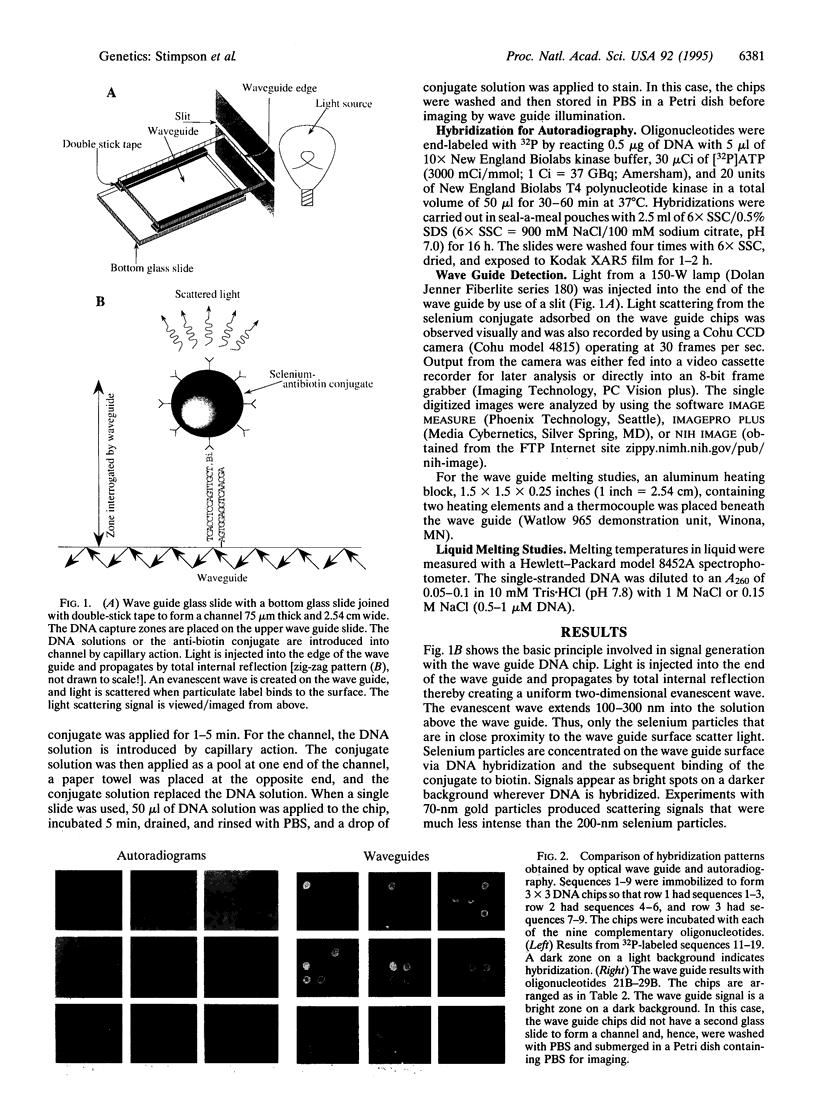
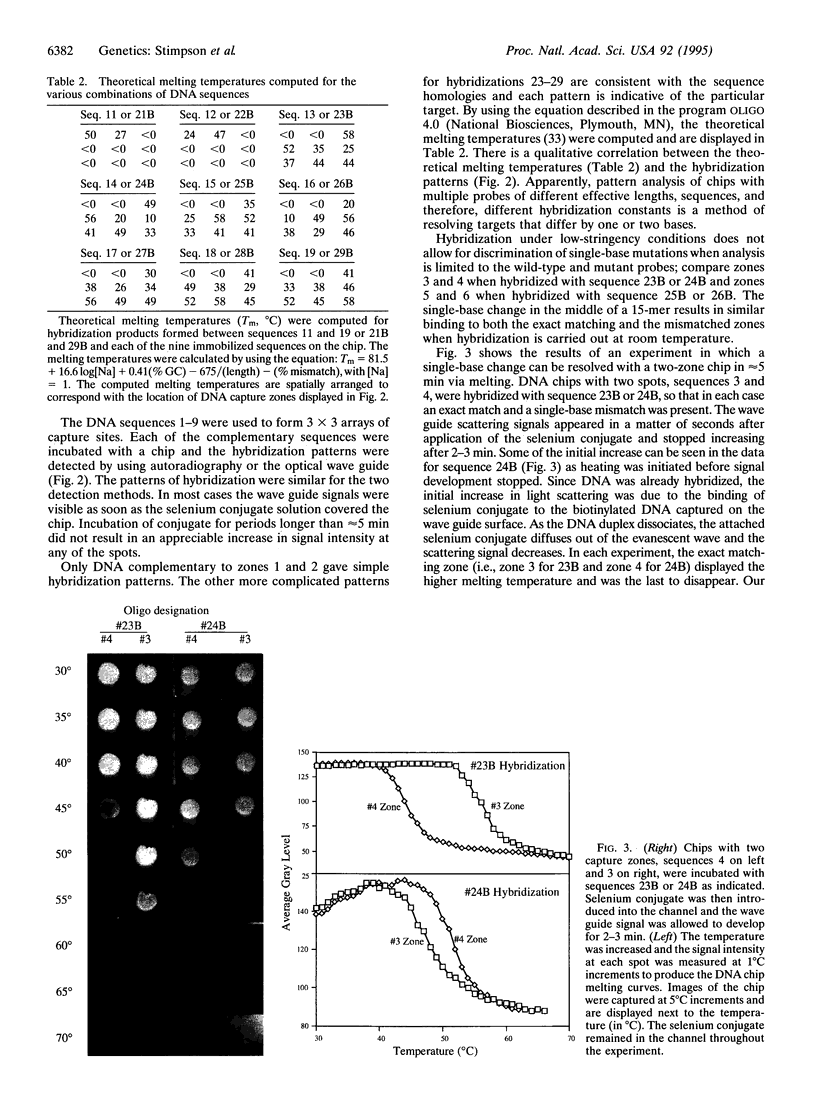
The challenge of the Human Genome Project is to increase the rate of DNA sequence acquisition by two orders of magnitude to complete sequencing of the human genome by the year 2000. The present work describes a rapid detection method using a two-dimensional optical wave guide that allows measurement of real-time binding or melting of a light-scattering label on a DNA array. A particulate label on the target DNA acts as a light-scattering source when illuminated by the evanescent wave of the wave guide and only the label bound to the surface generates a signal. Imaging/visual examination of the scattered light permits interrogation of the entire array simultaneously. Hybridization specificity is equivalent to that obtained with a conventional system using autoradiography. Wave guide melting curves are consistent with those obtained in the liquid phase and single-base discrimination is facile. Dilution experiments showed an apparent lower limit of detection at 0.4 nM oligonucleotide. This performance is comparable to the best currently known fluorescence-based systems. In addition, wave guide detection allows manipulation of hybridization stringency during detection and thereby reduces DNA chip complexity. It is anticipated that this methodology will provide a powerful tool for diagnostic applications that require rapid cost-effective detection of variations from known sequences.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bains W., Smith G. C. A novel method for nucleic acid sequence determination. J Theor Biol. 1988 Dec 7;135(3):303–307. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(88)80246-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldino F., Jr, Chesselet M. F., Lewis M. E. High-resolution in situ hybridization histochemistry. Methods Enzymol. 1989;168:761–777. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)68057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozon D., Zielenski J., Rininsland F., Tsui L. C. Identification of four new mutations in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene: I148T, L1077P, Y1092X, 2183AA-->G. Hum Mutat. 1994;3(3):330–332. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380030329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broude N. E., Sano T., Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. Enhanced DNA sequencing by hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3072–3076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case-Green S. C., Southern E. M. Studies on the base pairing properties of deoxyinosine by solid phase hybridisation to oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jan 25;22(2):131–136. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.2.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drmanac R., Drmanac S., Labat I., Crkvenjakov R., Vicentic A., Gemmell A. Sequencing by hybridization: towards an automated sequencing of one million M13 clones arrayed on membranes. Electrophoresis. 1992 Aug;13(8):566–573. doi: 10.1002/elps.11501301115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drmanac R., Labat I., Brukner I., Crkvenjakov R. Sequencing of megabase plus DNA by hybridization: theory of the method. Genomics. 1989 Feb;4(2):114–128. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90290-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drmanac R., Labat I., Crkvenjakov R. An algorithm for the DNA sequence generation from k-tuple word contents of the minimal number of random fragments. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1991 Apr;8(5):1085–1102. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1991.10507867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodor S. P., Rava R. P., Huang X. C., Pease A. C., Holmes C. P., Adams C. L. Multiplexed biochemical assays with biological chips. Nature. 1993 Aug 5;364(6437):555–556. doi: 10.1038/364555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodor S. P., Read J. L., Pirrung M. C., Stryer L., Lu A. T., Solas D. Light-directed, spatially addressable parallel chemical synthesis. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):767–773. doi: 10.1126/science.1990438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs J. W., Fodor S. P. Combinatorial chemistry--applications of light-directed chemical synthesis. Trends Biotechnol. 1994 Jan;12(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0167-7799(94)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. F., Pickett S. C., Barker D. L. Autoradiography using storage phosphor technology. Electrophoresis. 1990 May;11(5):355–360. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150110503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki E. S., Chehab F. F. Analysis of gene sequences by hybridization of PCR-amplified DNA to covalently bound oligonucleotide probes. The reverse dot blot method. Methods Mol Biol. 1994;28:225–236. doi: 10.1385/0-89603-254-x:225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livshits M. A., Florentiev V. L., Mirzabekov A. D. Dissociation of duplexes formed by hybridization of DNA with gel-immobilized oligonucleotides. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1994 Feb;11(4):783–795. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1994.10508032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lysov YuP, Chernyi A. A., Balaeff A. A., Beattie K. L., Mirzabekov A. D. DNA sequencing by hybridization to oligonucleotide matrix. Calculation of continuous stacking hybridization efficiency. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1994 Feb;11(4):797–812. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1994.10508033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lysov Iu P., Florent'ev V. L., Khorlin A. A., Khrapko K. R., Shik V. V. Opredelenie nukleotidnoi posledovatel'nosti DNK gibridizatsiei s oligonukleotidami. Novyi metod. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1988;303(6):1508–1511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maskos U., Southern E. M. A study of oligonucleotide reassociation using large arrays of oligonucleotides synthesised on a glass support. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Oct 11;21(20):4663–4669. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.20.4663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maskos U., Southern E. M. Oligonucleotide hybridizations on glass supports: a novel linker for oligonucleotide synthesis and hybridization properties of oligonucleotides synthesised in situ. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1679–1684. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maskos U., Southern E. M. Parallel analysis of oligodeoxyribonucleotide (oligonucleotide) interactions. I. Analysis of factors influencing oligonucleotide duplex formation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1675–1678. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirzabekov A. D. DNA sequencing by hybridization--a megasequencing method and a diagnostic tool? Trends Biotechnol. 1994 Jan;12(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0167-7799(94)90008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pease A. C., Solas D., Sullivan E. J., Cronin M. T., Holmes C. P., Fodor S. P. Light-generated oligonucleotide arrays for rapid DNA sequence analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):5022–5026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.5022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevzner P. A., Lysov YuP, Khrapko K. R., Belyavsky A. V., Florentiev V. L., Mirzabekov A. D. Improved chips for sequencing by hybridization. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1991 Oct;9(2):399–410. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1991.10507920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strezoska Z., Paunesku T., Radosavljević D., Labat I., Drmanac R., Crkvenjakov R. DNA sequencing by hybridization: 100 bases read by a non-gel-based method. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10089–10093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tizard R., Cate R. L., Ramachandran K. L., Wysk M., Voyta J. C., Murphy O. J., Bronstein I. Imaging of DNA sequences with chemiluminescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4514–4518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zielenski J., Rozmahel R., Bozon D., Kerem B., Grzelczak Z., Riordan J. R., Rommens J., Tsui L. C. Genomic DNA sequence of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene. Genomics. 1991 May;10(1):214–228. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90503-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]