Abstract
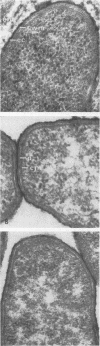
Ultrastructural identification and localization of the fraction 1 “envelope” antigen in the plague bacillus Yersinia pestis were the primary objectives of this brief study. The antigenicity of extra-cellular material between the bacilli in undisturbed cultured colonies and that of the pathogen per se were measured and correlated by means of the semi quantitative complement fixation method after incubation for 72 h at 37 C. When the amount of extracellular substance in wild-type T1 (virulent) bacteria was compared by electron microscopy with that in avirulent strains of Y. pestis, with and without passage through guinea pigs, we found that the material of interest was greatly attenuated or even absent in colonies that had not been passed through animals, whereas passage markedly augmented production of the material. We also explored the requirement for larger quantities of Ca2+ and Mg2+ in the culture media and discovered that without these ions production of the extracellular material was limited. These observations support the hypothesis that this extracellular substance between cultured Y. pestis bacilli of various strains represents the source of the fraction 1 envelope antigen.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAKER E. E., SOMMER H., FOSTER L. E., MEYER E., MEYER K. F. Studies on immunization against plague. I. The isolation and characterization of the soluble antigen of Pasteurella pestis. J Immunol. 1952 Feb;68(2):131–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., JACKSON S. The virulence-enhancing effect of iron on nonpigmented mutants of virulent strains of Pasteurella pestis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Dec;37(6):577–583. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W. VIRULENCE OF PASTEURELLA PESTIS AND IMMUNITY TO PLAGUE. Ergeb Mikrobiol Immunitatsforsch Exp Ther. 1963;37:59–113. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-36742-1_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W. Virulence of Pasteurella pestis. Nature. 1957 Jun 15;179(4572):1246–1247. doi: 10.1038/1791246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEN T. H., CROCKER T. T., MEYER K. F. Electron microscopic study of the extracellular materials of Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1956 Dec;72(6):851–857. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.6.851-857.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEN T. H., MEYER K. F. Studies on immunization against plague. VII. A hemagglutination test with the protein fraction of Pasteurella pestis: a serologic comparison of virulent and avirulent strains with observations on the structure of the bacterial cells and its relationship to infection and immunity. J Immunol. 1954 Apr;72(4):282–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEN T. H., QUAN S. F., MEYER K. F. Studies on immunization against plague. II. The complement-fixation test. J Immunol. 1952 Feb;68(2):147–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEN T. H. THE ANTIGENIC STRUCTURE OF PASTEURELLA PESTIS AND ITS RELATIONSHIP TO VIRULENCE AND IMMUNITY. Acta Trop. 1965;22:97–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. H., Meyer K. F. An evaluation of Pasteurella pestis fraction-1-specific antibody for the confirmation of plague infections. Bull World Health Organ. 1966;34(6):911–918. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONAVAN J. E., HAM D., FUKUI G. M., SURGALLA M. J. Role of the capsule of Pasteurella pestis in bubonic plague in the guinea pig. J Infect Dis. 1961 Sep-Oct;109:154–157. doi: 10.1093/infdis/109.2.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGLESBERG E., CHEN T. H., LEVY J. B., FOSTER L. E., MEYER K. F. Virulence in Pasteurella pestis. Science. 1954 Mar 26;119(3091):413–414. doi: 10.1126/science.119.3091.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadgil M. D., Nimbkar Y. S., Jhala H. I. Morphological variations of P. pestis in relation to requirement of Ca++ & Mg++. Indian J Pathol Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;9(4):323–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadgil M. D., Nimbkar Y. S., Jhala H. I. The role of nutrients and temperature in the growth of P.pestis for vaccine production. II. The role of Ca++ and Mg++ in plague vaccine production. Indian J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;10(3):245–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golubinskii E. P., Kirdeev V. K., Tokarev S. A. Ul'trastruktura P. pestis. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1971 Mar;48(3):13–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. J., Yang G. C., Little R. V., Brubaker R. R. Effect of Ca2+ on morphology and division of Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1974 Jun;9(6):1105–1113. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.6.1105-1113.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANSSEN W. A., LAWTON W. D., FUKUI G. M., SURGALLA M. J. THE PATHOGENESIS OF PLAGUE. I. A STUDY OF THE CORRELATION BETWEEN VIRULENCE AND RELATIVE PHAGOCYTOSIS RESISTANCE OF SOME STRAINS OF PASTEURELLA PESTIS. J Infect Dis. 1963 Sep-Oct;113:139–143. doi: 10.1093/infdis/113.2.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer K. F., Hightower J. A., McCrumb F. R. Plague immunization. VI. Vaccination with the fraction I antigen of Yersinia pestis. J Infect Dis. 1974 May;129(Suppl):S41–S45. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.supplement_1.s41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERMAN M. S., ELBERG S. S., MEYER K. F., FOSTER I. Studies on immunization against plague. III. Quantitative serological studies on an immunizing antigen of Pasteurella pestis. J Immunol. 1952 Jun;68(6):609–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva M. T., Sousa J. C. Ultrastructure of the cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane of gram-negative bacteria with different fixation techniques. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):953–962. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.953-962.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surgalla M. J., Beesley E. D., Albizo J. M. Practical applications of new laboratory methods for plague investigations. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;42(6):993–997. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Metz E., Eisler D. M., Hottle G. A. Immunogenicity of plague vaccines in mice and guinea pigs. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Jul;22(1):84–88. doi: 10.1128/am.22.1.84-88.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]