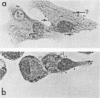
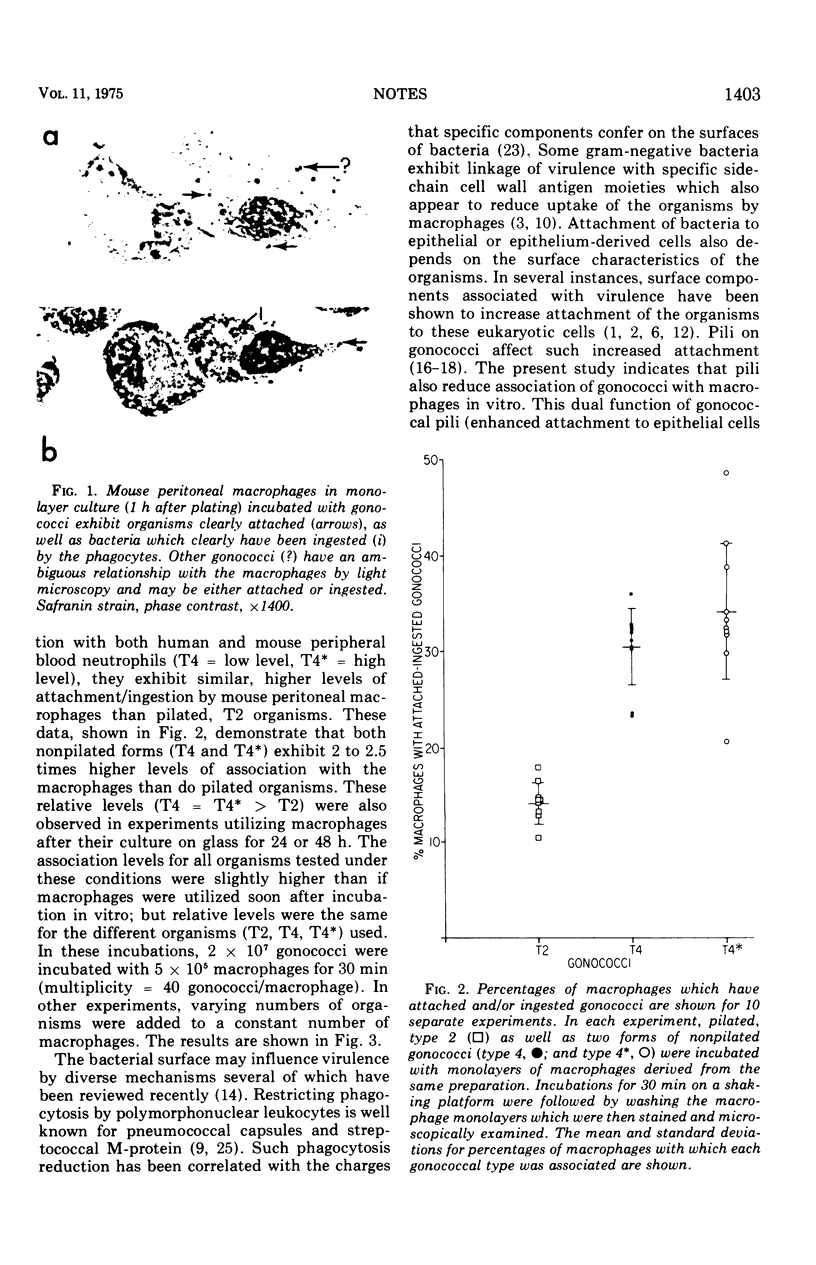
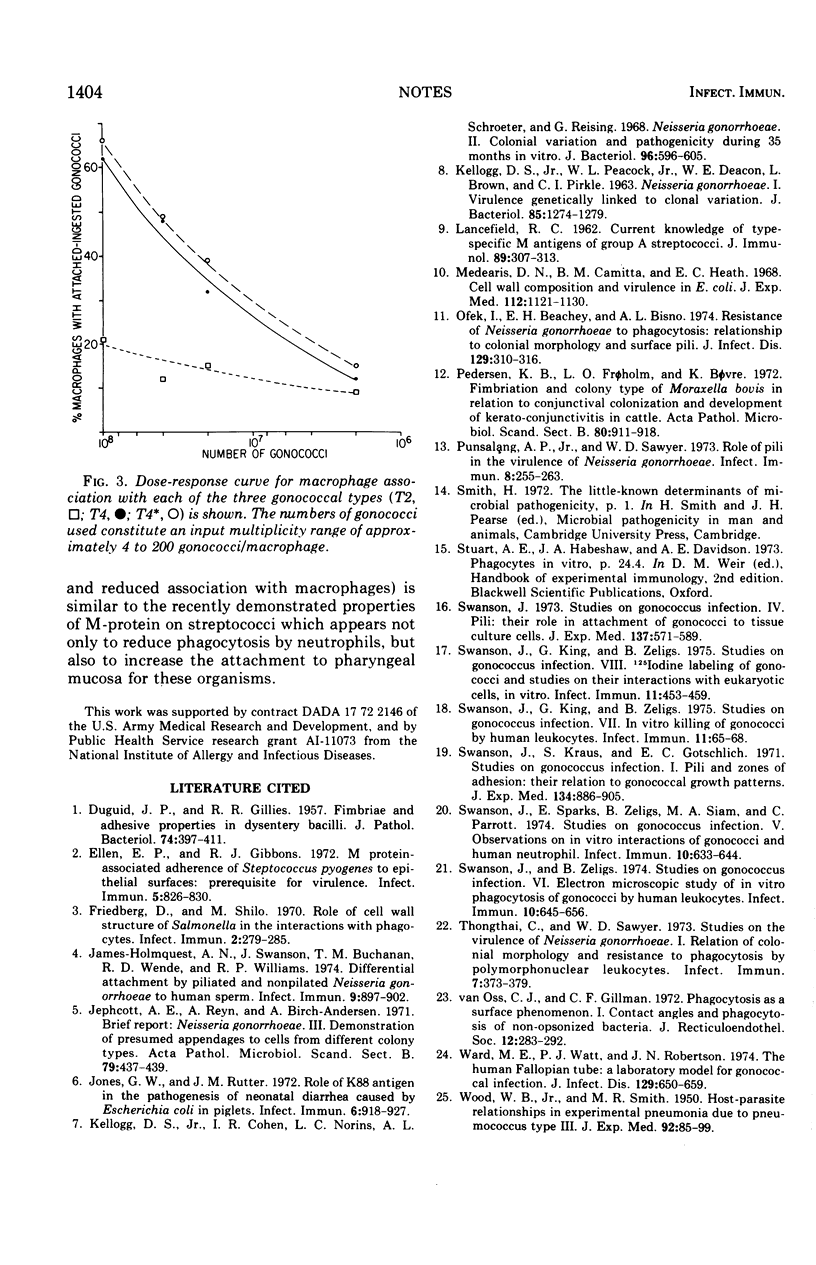
Abstract
Pili, in addition to enhancing attachment of gonococci to tissue culture cells, appear to reduce association (attachment/ingestion) of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with mouse peritoneal macrophages in vitro.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ellen R. P., Gibbons R. J. M protein-associated adherence of Streptococcus pyogenes to epithelial surfaces: prerequisite for virulence. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):826–830. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.826-830.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg D., Shilo M. Role of cell wall structure of salmonella in the interaction with phagocytes. Infect Immun. 1970 Sep;2(3):279–285. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.3.279-285.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James-Holmquest A. N., Swanson J., Buchanan T. M., Wende R. D., Williams R. P. Differential attachment by piliated and nonpiliated Neisseria gonorrhoeae to human sperm. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):897–902. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.897-902.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jephcott A. E., Reyn A., Birch-Andersen A. Neisseria gonorrhoeae 3. Demonstration of presumed appendages to cells from different colony types. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(3):437–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00086.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Rutter J. M. Role of the K88 antigen in the pathogenesis of neonatal diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli in piglets. Infect Immun. 1972 Dec;6(6):918–927. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.6.918-927.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Cohen I. R., Norins L. C., Schroeter A. L., Reising G. Neisseria gonorrhoeae. II. Colonial variation and pathogenicity during 35 months in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):596–605. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.596-605.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Current knowledge of type-specific M antigens of group A streptococci. J Immunol. 1962 Sep;89:307–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Beachey E. H., Bisno A. L. Resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to phagocytosis: relationship to colonial morphology and surface pili. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):310–316. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K. B., Froholm L. O., Bovre K. Fimbriation and colony type of Moraxella bovis in relation to conjunctival colonization and development of keratoconjunctivitis in cattle. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(6):911–918. doi: 10.1111/j.0365-5563.1973.tb00019.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punsalang A. P., Jr, Sawyer W. D. Role of pili in the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):255–263. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.255-263.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., King G., Zeligs B. Studies on gonococcus infection. VII. In vitro killing of gonococci by human leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):65–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.65-68.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., King G., Zeligs B. Studies on gonococcus infection. VIII. 125Iodine labeling of gonococci and studies on their in vitro interactions with eukaryotic cells. Infect Immun. 1975 Mar;11(3):453–459. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.3.453-459.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Kraus S. J., Gotschlich E. C. Studies on gonococcus infection. I. Pili and zones of adhesion: their relation to gonococcal growth patterns. J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):886–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Sparks E., Zeligs B., Siam M. A., Parrott C. Studies on gonococcus infection. V. Observations on in vitro interactions of gonococci and human neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):633–644. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.633-644.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. IV. Pili: their role in attachment of gonococci to tissue culture cells. J Exp Med. 1973 Mar 1;137(3):571–589. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Zeligs B. Studies on gonococcus infection. VI. Electron microscopic study on in vitro phagocytosis of gonococci by human leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):645–656. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.645-656.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thongthai C., Sawyer W. D. Studies on the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Relation of colonial morphology and resistance to phagocytosis by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):373–379. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.373-379.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Oss C. J., Gillman C. F. Phagocytosis as a surface phenomenon. Contact angles and phagocytosis of non-opsonized bacteria. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1972 Sep;12(3):283–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD W. B., SMITH M. R. Host-parasite relationships in experimental pneumonia due to pneumococcus type III. J Exp Med. 1950 Jul 1;92(1):85–100. doi: 10.1084/jem.92.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. E., Watt P. J., Robertson J. N. The human fallopian tube: a laboratory model for gonococcal infection. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jun;129(6):650–659. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.6.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]