Abstract
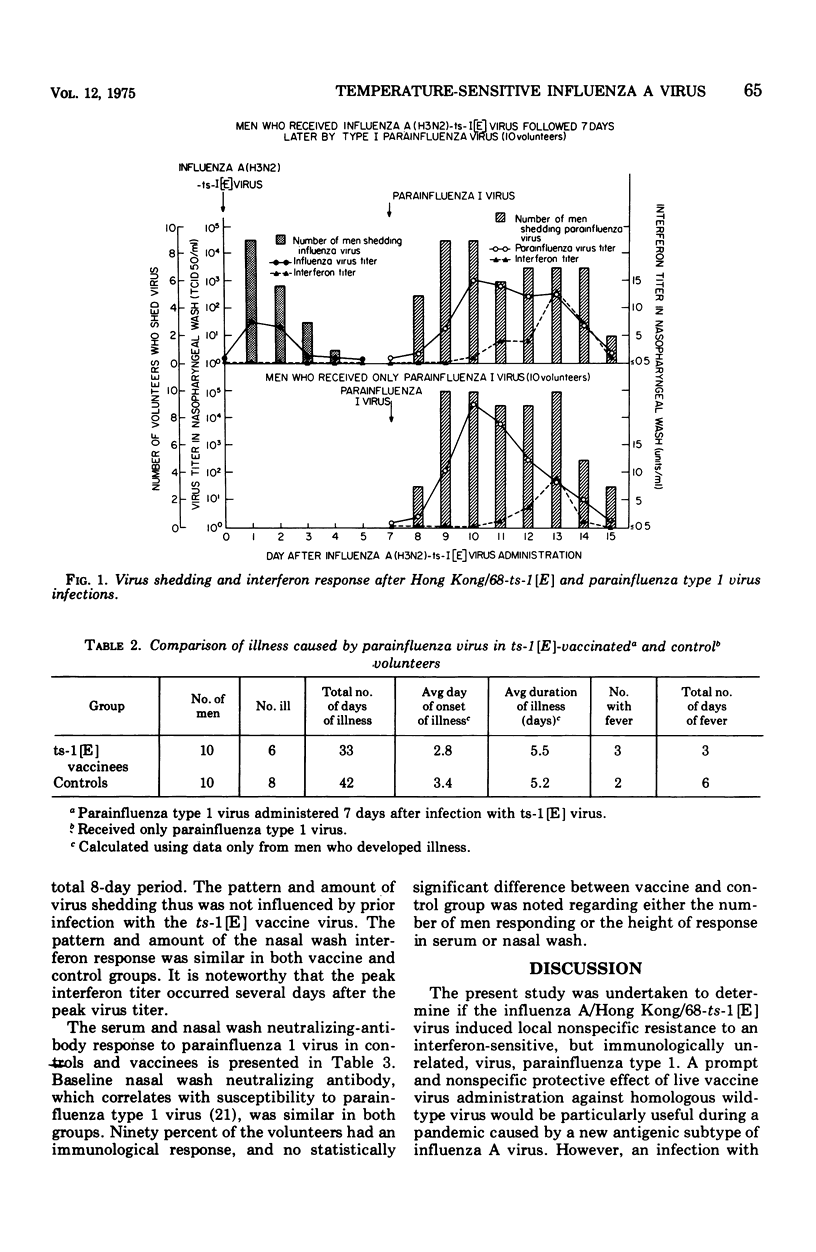
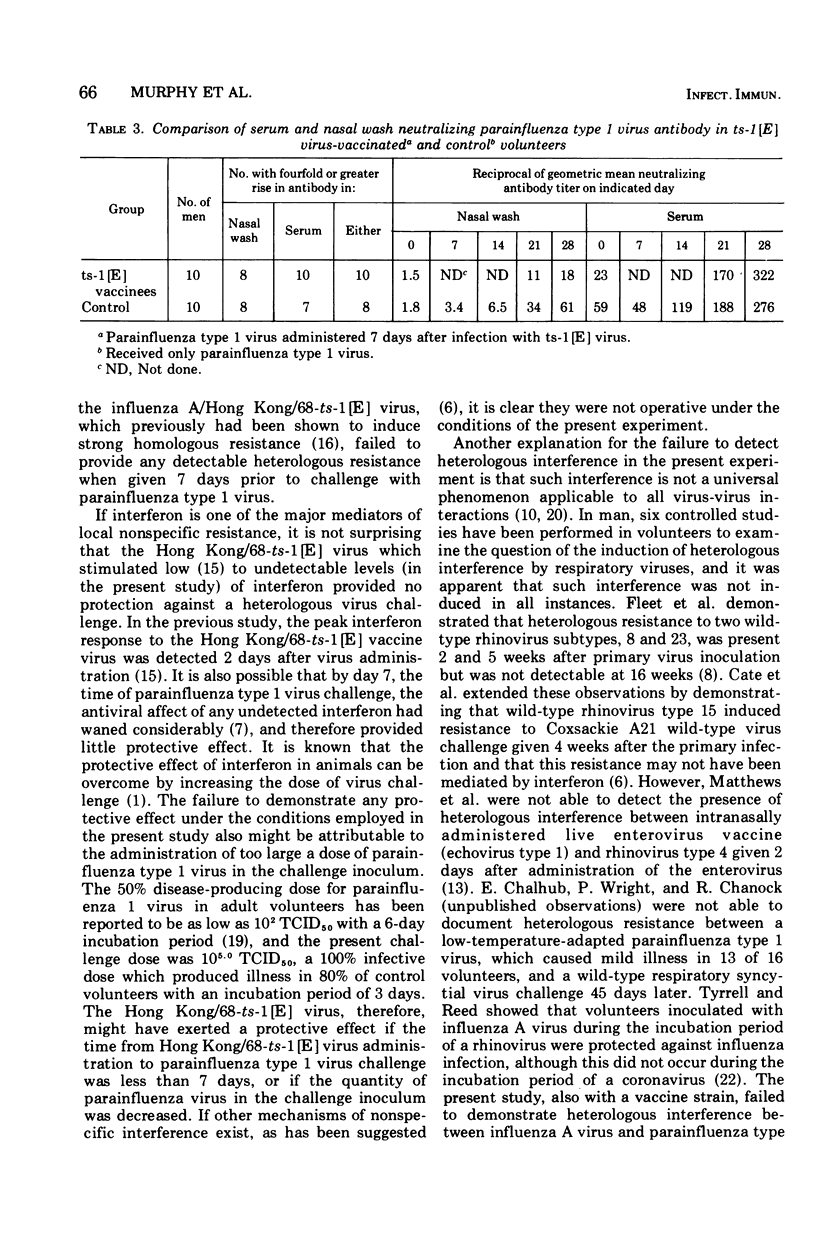
The present investigation was undertaken to determine if a candidate live vaccine virus, influenza A/Hong Kong/68-ts-1 [E] (H3N2), induced heterologous interference against an interferon-sensitive, wild-type, parainfluenza type 1 challenge virus. The parainfluenza virus was administered 7 days after Hong Kong/68-ts-1 [E] virus infection. The clinical response, daily quantitative virus shedding, interferon production, and serum and nasal wash antibody responses were determined in an experimental group (influenza A virus followed by parainfluenza virus) and 10 volunteers in a control group (parainfluenza virus only). The volunteers were selected on the basis of susceptibility to the two viruses, i.e. serum hemagglutination-inhibition antibody titer of is less than or greater to 1:8 for influenza virus and low nasal wash antibody titer (is less than or greater to 1:8) for parainfluenza virus. Despite a 100% infection rate in the Hong Kong/68-ts-1 [E] vaccinees, no heterologous interference was induced against the parainfluenza type 1 virus challenge.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOVARNICK M. R., MILLER J. C., SNYDER J. C. The influence of certain salts, amino acids, sugars, and proteins on the stability of rickettsiae. J Bacteriol. 1950 Apr;59(4):509–522. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.4.509-522.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron S., Buckler C. E., Friedman R. M., McCloskey R. V. Role of interferon during viremia. II. Protective action of circulating interferon. J Immunol. 1966 Jan;96(1):17–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne E. B., Rosenstein B. J., Jaworski A. A., Jaworski R. A. A statewide mass measles immunization program. JAMA. 1967 Feb 27;199(9):619–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATE T. R., COUCH R. B., JOHNSON K. M. STUDIES WITH RHINOVIRUSES IN VOLUNTEERS: PRODUCTION OF ILLNESS, EFFECT OF NATURALLLY ACQUIRED ANTIBODY, AND DEMONSTRATION OF A PROTECTIVE EFFECT NOT ASSOCIATED WITH SERUM ANTIBODY. J Clin Invest. 1964 Jan;43:56–67. doi: 10.1172/JCI104894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cate T. R., Douglas R. G., Jr, Couch R. B. Interferon and resistance to upper respiratory virus illness. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jun;131(2):631–636. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finter N. B. Interferon in mice: protection against small doses of virus. J Gen Virol. 1967 Jul;1(3):395–397. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-1-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleet W. F., Couch R. B., Cate T. R., Knight V. Homologous and heterologous resistance to rhinovirus common cold. Am J Epidemiol. 1965 Sep;82(2):185–196. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glezen P., Denny F. W. Epidemiology of acute lower respiratory disease in children. N Engl J Med. 1973 Mar 8;288(10):498–505. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197303082881005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENLE W. Interference phenomena between animal viruses; a review. J Immunol. 1950 Mar;64(3):203–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. A., Baron S., Chanock R. M. Sensitivity of common respiratory viruses to an interferon inducer in human cells. Lancet. 1969 Jul 26;2(7613):187–188. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91425-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNIGHT V. THE USE OF VOLUNTEERS IN MEDICAL VIROLOGY. Prog Med Virol. 1964;6:1–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews T. H., Reed S. E., Tyrrell D. A. The effect of prior inoculation with an enterovirus (LEV 4) on rhinovirus infection of volunteers. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1974;45(1-2):106–112. doi: 10.1007/BF01240547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor T. E., Dick E. C., Peterson J. A., Docherty D. E. Failure of naturally acquired rhinovirus infections to produce temporal immunity to heterologous serotypes. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1192–1193. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1192-1193.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. R., Baron S., Chalhub E. G., Uhlendorf C. P., Chanock R. M. Temperature-sensitive mutants of influenza virus. IV. Induction of interferon in the nasopharynx by wild-type and a temperature-sensitive recombinant virus. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):488–493. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. R., Chalhub E. G., Nusinoff S. R., Chanock R. M. Temperature-sensitive mutants of influenza virus. II. Attenuation of ts recombinants for man. J Infect Dis. 1972 Aug;126(2):170–178. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.2.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. R., Chalhub E. G., Nusinoff S. R., Kasel J., Chanock R. M. Temperature-sensitive mutants of influenza virus. 3. Further characterization of the ts-1(E) influenza A recombinant (H3N2) virus in man. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):479–487. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oie H. K., Buckler C. E., Uhlendorf C. P., Hill D. A., Baron S. Improved assays for a variety of interferons. 1. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Sep;140(4):1178–1181. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REICHELDERFER T. E., CHANOCK R. M., CRAIGHEAD J. E., HUEBNER R. J., TURNER H. C., JAMES W., WARD T. G. Infection of human volunteers with type 2 hemadsorption virus. Science. 1958 Oct 3;128(3327):779–780. doi: 10.1126/science.128.3327.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. B., Purcell R. H., Bellanti J. A., Chanock R. M. Protective effect of antibody to parainfluenza type 1 virus. N Engl J Med. 1966 Nov 24;275(21):1145–1152. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196611242752101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vella P. P., Weibel R. E., Woodhour A. F., Mascoli C. C., Leagus M. B., Ittensohn O. L., Stokes J., Jr, Hilleman M. R. Respiratory virus vaccines. 8. Field evaluation of trivalent parainfluenza virus vaccine among preschool children in families, 1967-1968. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1969 Apr;99(4):526–541. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1969.99.4P1.526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheelock E. F., Larke R. P., Caroline N. L. Interference in human viral infections: present status and prospects for the future. Prog Med Virol. 1968;10:286–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



