Abstract
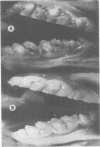
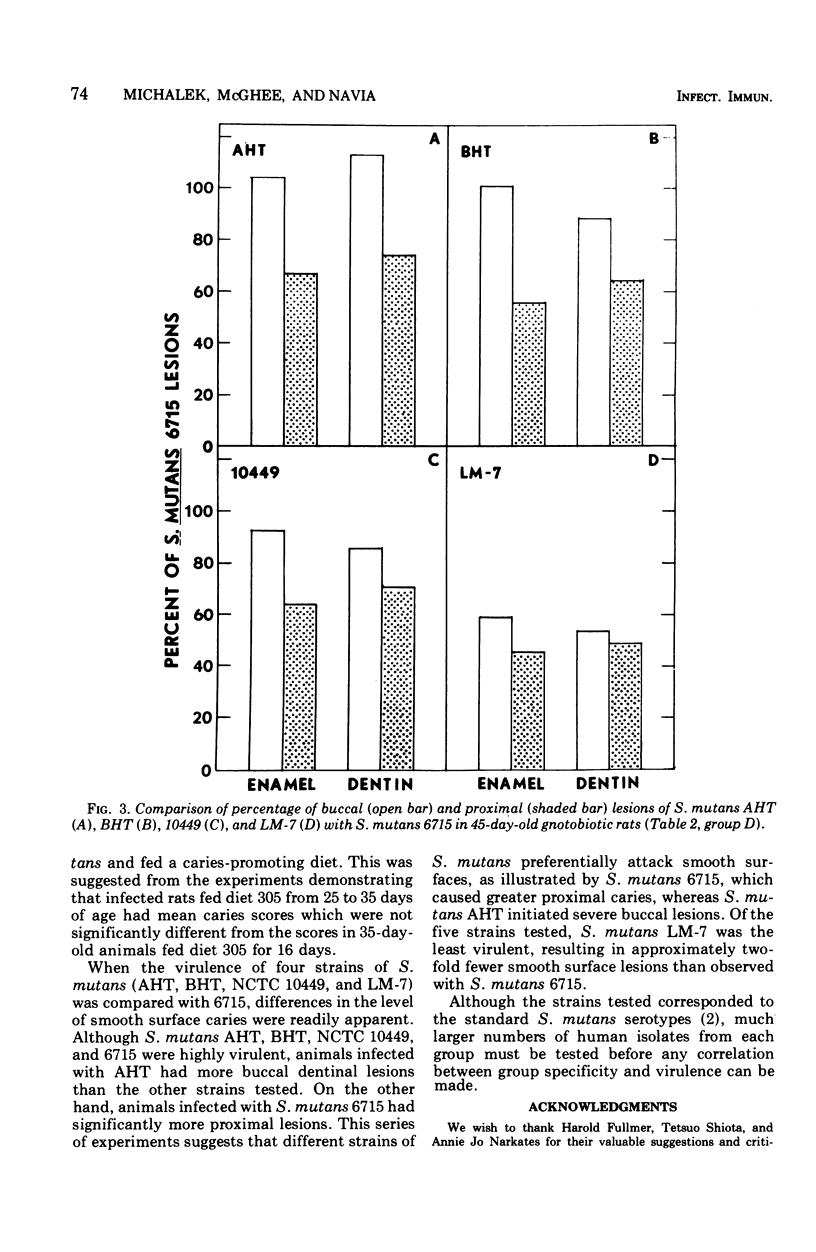
Gnotobiotic rats infected with Streptococcus mutans 6715 at 19 days of age and fed a purified diet (305) containing 5% sucrose developed extensive caries lesions on all molar surfaces within 16 days (35 days of age). Approximately twice as many lesions developed when infected rats were maintained until 45 days of age, whereas noninfected rats did not develop caries when fed diet 305. Gnotobiotic rats infected with S. mutans 6715 and fed a purified diet containing no sucrose (300) until day 25 and subsequently fed diet 305 for 10 days developed lesions similar to rats fed diet 305 for 16 days. Furthermore, rats infected with S. mutans 6715 and fed diet 300 until 45 days of age developed approximately one-half the smooth surface lesions as infected rats fed diet 305 for the same length of time. The level of caries on buccal and proximal molar surfaces in 45-day-old gnotobiotic rats varied when animals were infected with S. mutans AHT, BHT, NCTC 10449, 6715, or LM-7. Animals infected with S. mutans AHT showed more severe lesions on the buccal surfaces than those observed in animals infected with the other strains of S. mutans tested, whereas S. mutans 6715 caused significantly more caries on proximal surfaces. On the other hand, rats infected with S. mutans LM-7 exhibited the lowest level of caries on all molar surfaces of the five strains of S. mutans tested.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORGSTROM B., DAHLQVIST A., GUSTAFSSON B. E., LUNDH G., MALMQUIST J. Trypsin, invertase and amylase content of feces of germfree rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Oct;102:154–155. doi: 10.3181/00379727-102-25174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratthall D. Demonstration of five serological groups of streptococcal strains resembling Streptococcus mutans. Odontol Revy. 1970;21(2):143–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J. Presence of various types of non-haemolytic streptococci in dental plaque and in other sites of the oral cavity in man. Odontol Revy. 1967;18(1):55–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J. Zooglea-forming streptococci, resembling Streptococcus sanguis, isolated from dental plaque in man. Odontol Revy. 1965;16(4):348–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlton G., Fitzgerald D. B., Keyes P. H. Hydrogen ion activity in dental plaques of hamsters during metabolism of sucrose, glucose and fructose. Arch Oral Biol. 1971 Jun;16(6):655–661. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(71)90069-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlton G., Fitzgerald R. J., Keyes P. H. Determination of saliva and dental plaque pH in hamsters with glass micro-electrodes. Arch Oral Biol. 1971 Jun;16(6):649–654. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(71)90068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critchley P., Wood J. M., Saxton C. A., Leach S. A. The polymerisation of dietary sugars by dental plaque. Caries Res. 1967;1(2):112–129. doi: 10.1159/000259506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwardsson S. Characteristics of caries-inducing human streptococci resembling Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 Jun;13(6):637–646. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90142-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZGERALD R. J., JORDAN H. V., STANLEY H. R. Experimental caries and gingival pathologic changes in the gnotobiotic rat. J Dent Res. 1960 Sep-Oct;39:923–935. doi: 10.1177/00220345600390052701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Banghart S. B. Synthesis of extracellular dextran by cariogenic bacteria and its presence in human dental plaque. Arch Oral Biol. 1967 Jan;12(1):11–23. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(67)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Berman K. S., Knoettner P., Kapsimalis B. Dental caries and alveolar bone loss in gnotobiotic rats infected with capsule forming streptococci of human origin. Arch Oral Biol. 1966 Jun;11(6):549–560. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(66)90220-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Fitzgerald R. J. Dextran-induced agglutination of Streptococcus mutans, and its potential role in the formation of microbial dental plaques. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):341–346. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.341-346.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Keyes P. H. Inhibition of insoluble dextran synthesis, plaque formation and dental caries in hamsters by low molecular weight dextran. Arch Oral Biol. 1969 Jun;14(6):721–724. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(69)90193-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Nygaard M. Synthesis of insoluble dextran and its significance in the formation of gelatinous deposits by plaque-forming streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 Oct;13(10):1249–1262. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R. M., Blackmore D. K., Drucker D. B. The role of gnotobiotic animals in the study of dental caries. Br Dent J. 1973 Jun 19;134(12):537–540. doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.4803033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggenheim B. Extracellular polysaccharides and microbial plaque. Int Dent J. 1970 Dec;20(4):657–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggenheim B., Newbrun E. Extracellular glucosyltransferase activity of an HS strain of Streptococcus mutans. Helv Odontol Acta. 1969 Oct;13(2):84–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggenheim B. Streptococci of dental plaques. Caries Res. 1968;2(2):147–163. doi: 10.1159/000259553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYES P. H. Dental caries in the molar teeth of rats. II. A method for diagnosing and scoring several types of lesions simultaneously. J Dent Res. 1958 Nov-Dec;37(6):1088–1099. doi: 10.1177/00220345580370060901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRASSE B. THE EFFECT OF CARIES-INDUCING STREPTOCOCCI IN HAMSTERS FED DIETS WITH SUCROSE OR GLUCOSE. Arch Oral Biol. 1965 Mar-Apr;10:223–226. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(65)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyes P. H. Research in dental caries. J Am Dent Assoc. 1968 Jun;76(6):1357–1373. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1968.0186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larje O., Larson R. H. Reduction of dental caries in rats by intermittent feeding with sucrose substitutes. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 Sep;15(9):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90153-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepkovsky S., Furuta F., Ozone K., Koike T. The proteases, amylase and lipase of the pancreas and intestinal contents of germ-free and conventional rats. Br J Nutr. 1966;20(2):257–261. doi: 10.1079/bjn19660026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe R. M., Keyes P. H., Howell A., Jr An in vitro method for assessing the plaque forming ability of oral bacteria. Arch Oral Biol. 1967 Dec;12(12):1653–1656. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(67)90200-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menaker L., Navia J. M. Effect of undernutrition during the perinatal period on caries development in the rat. 11. Caries susceptibility in underfed rats supplemented with protein or caloric additions during the suckling period. J Dent Res. 1973 Jul-Aug;52(4):680–687. doi: 10.1177/00220345730520040701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navia J. M., Lopez H., Harris R. S. Purified diet for dental caries research with rats. J Nutr. 1969 Jan;97(1):133–140. doi: 10.1093/jn/97.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORLAND F. J., BLAYNEY J. R., HARRISON R. W., REYNIERS J. A., TREXLER P. C., ERVIN R. F., GORDON H. A., WAGNER M. Experimental caries in germfree rats inoculated with enterococci. J Am Dent Assoc. 1955 Mar;50(3):259–272. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1955.0061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORLAND F. J., BLAYNEY J. R., HARRISON R. W., REYNIERS J. A., TREXLER P. C., WAGNER M., GORDON H. A., LUCKEY T. D. Use of the germfree animal technic in the study of experimental dental caries. I. Basic observations on rats reared free of all microorganisms. J Dent Res. 1954 Apr;33(2):147–174. doi: 10.1177/00220345540330020201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREXLER P. C. The use of plastics in the design of isolator systems. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 May 8;78:29–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb53093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbman M. A., Smith D. J. Effects of local immunization with Streptococcus mutans on induction of salivary immunoglobulin A antibody and experimental dental caries in rats. Infect Immun. 1974 Jun;9(6):1079–1091. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.6.1079-1091.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzer J. M., Freedman M. L., Fitzgerald R. J., Larson R. H. Diminished virulence of glucan synthesis-defective mutants of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):197–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.197-203.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. M., Critchley P. The extracellular polysaccharide produced from sucrose by a cariogenic streptococcus. Arch Oral Biol. 1966 Oct;11(10):1039–1042. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(66)90204-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZINNER D. D., JABLON J. M., ARAN A. P., SASLAW M. S. EXPERIMENTAL CARIES INDUCED IN ANIMALS BY STREPTOCOCCI OF HUMAN ORIGIN. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Mar;118:766–770. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]