Abstract
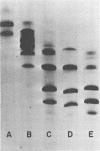
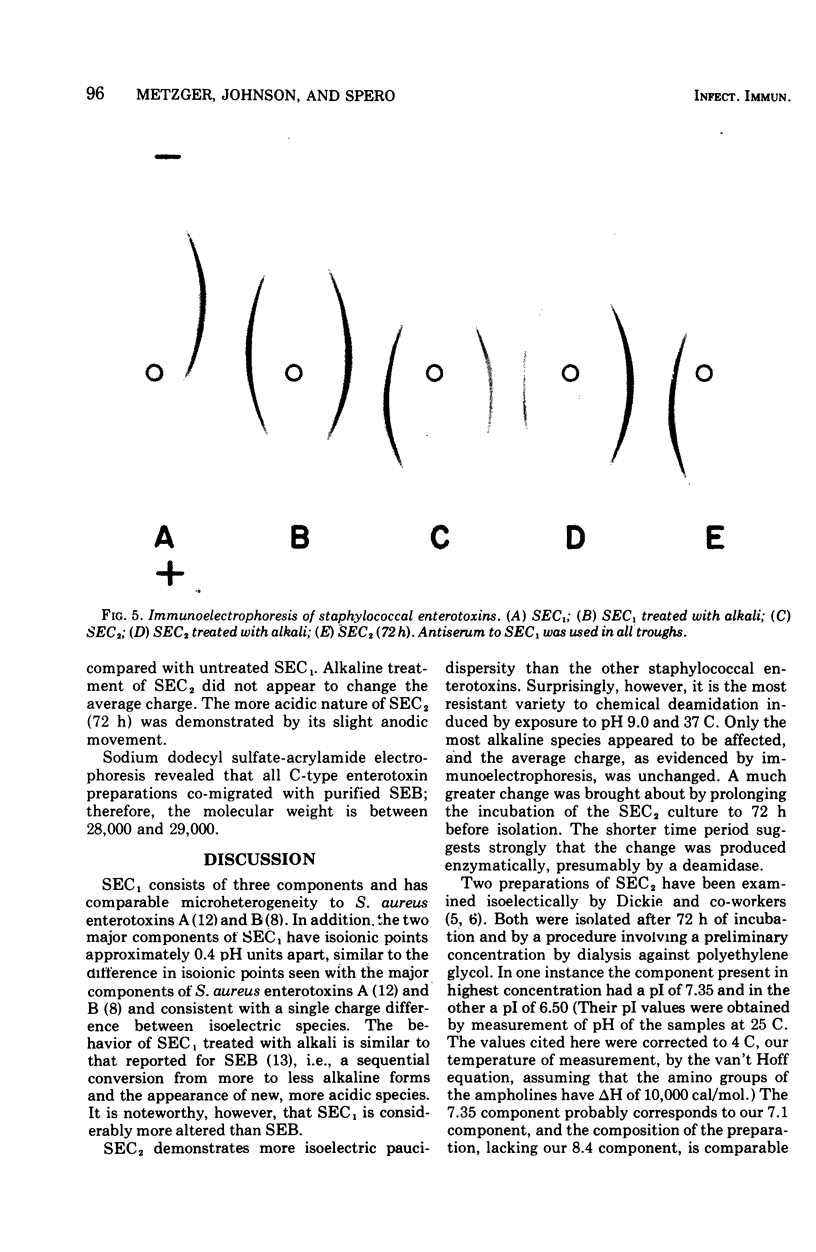
Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins C1 (SEC1) and C2 (SEC2) produced from 50-liter quantities of crude culture supernatants were purified chromatographically in a neutral or acid milieu. Microheterogenity of SEC1 was markedly increased by treatment of the purified toxin with alkali, and new more acidic charged species appeared. SEC2 was more heterogenous than any of the other S. aureus enterotoxins and was affected only slightly by treatment with alkali. Prolonged incubation of the organism during production of the SEC2 produced changes in charged species that may be related to a bacterial deamidase, since similar changes were not seen with alkaline treatment of the purified toxin. Although SEC1 and SEC2 showed complete identity immunologically, they are separate, distinct toxins, and alkali treatment of SEC1 did not produce SEC2.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avena R. M., Bergdoll M. S. Purification and some physicochemical properties of enterotoxin C, Staphylococcus aureus strain 361. Biochemistry. 1967 May;6(5):1474–1480. doi: 10.1021/bi00857a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAIRD-PARKER A. C., JOSEPH R. L. FRACTIONATION OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL ENTEROTOXIN B. Nature. 1964 May 9;202:570–571. doi: 10.1038/202570a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borja C. R., Bergdoll M. S. Purification and partial characterization of enterotoxin C produced by Staphylococcus aureus strain 137. Biochemistry. 1967 May;6(5):1467–1473. doi: 10.1021/bi00857a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang P. C., Dickie N. Fractionation of staphylococcal enterotoxin B by isoelectric focusing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 May 25;236(2):367–375. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Change P. C., Yano Y., Dighton M., Dickie N. Fractionation of staphylococcal enterotoxin C 2 by isoelectric focusing. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Nov;17(11):1367–1372. doi: 10.1139/m71-218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickie N., Yano Y., Robern H., Stavric S. On the heterogeneity of staphylococcal enterotoxin C 2 . Can J Microbiol. 1972 Jun;18(6):801–804. doi: 10.1139/m72-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis A. W., Lawrence R. C., Pritchard G. G. Production of staphylococcal enterotoxins A, B, and C under conditions of controlled pH and aeration. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):847–854. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.847-854.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger J. F., Johnson A. D., Collins W. S., 2nd Fractionation and purification of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B by electrofocusing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 26;257(1):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90269-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger J. F., Johnson A. D., Collins W. S., 2nd, McGann V. Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B release (excretion) under controlled conditions of fermentation. Appl Microbiol. 1973 May;25(5):770–773. doi: 10.1128/am.25.5.770-773.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Antigen-antibody reactions in gels. IV. Types of reactions in coordinated systems of diffusion. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1953;32(2):230–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schantz E. J., Roessler W. G., Wagman J., Spero L., Dunnery D. A., Bergdoll M. S. Purification of staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Biochemistry. 1965 Jun;4(6):1011–1016. doi: 10.1021/bi00882a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schantz E. J., Roessler W. G., Woodburn M. J., Lynch J. M., Jacoby H. M., Silverman S. J., Gorman J. C., Spero L. Purification and some chemical and physical properties of staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 1;11(3):360–366. doi: 10.1021/bi00753a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]