Abstract
In recent years, distinct signaling pathways involving specific complexes of cytoplasmic proteins have been shown to orchestrate estrogen action. These pathways might supplement or augment genomic effects of estrogen that are attributable to transcriptional activation by liganded receptor. Signals might be transduced through phosphorylation of the estrogen receptors (ERs), or indirectly through effects upon transcriptional coactivators or cell receptors. Estrogen signaling is coupled to growth factor signaling with feedback mechanisms directly impacting function of growth factor receptors. These signaling pathways regulate important physiological processes, such as cell growth and apoptosis. Here, we focus on cytoplasmic signaling pathways leading to activation of ERs.
Recent developments have clarified the role of cytoplasmic proteins and signaling pathways leading to activation of the estrogen receptors (ERα and ERβ). Here, we derive common themes from recent reports of cytoplasmic signaling modules that influence estrogen action. Ligand-dependent or ligand-independent ER activation has been shown to be accomplished by compounds other than steroidal estrogens, such as cAMP, dopamine and growth factors through signaling pathways that involve cytoplasmic proteins or protein kinases (reviewed in Ref. [1]).
We approach this complex topic from the perspective that estrogen signaling is more complicated than the canonical ‘genomic’ pathway. It is useful to conceptualize estrogen action in vivo not as a strictly linear signal, but rather as acting through collateral, possibly divergent pathways. In contrast to experimental model systems that are overly simplistic, in vivo estrogen might activate cytoplasmic pathways in some tissues before transcription, and these pathways might enhance genomic actions of estradiol or influence cell function before (or in the absence of) gene transcription. Because the designation ‘nonclassical’ or ‘nongenomic’ is imprecise, we focus on specific cytoplasmic signaling pathways.
The genomic pathway
The effects of estrogen in hormone-responsive tissues are caused by changes in gene expression modulated by the ERs that are members of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily of transcription factors. The ERs are modular transcription factors containing two transcription activation functions, af-1 (see Glossary) located in the N-terminal A/B domain, and AF-2 located within the C-terminal ligand-binding domain. Although AF-2 function is dependent upon ligand binding, AF-1 functions independent of ligand binding but synergizes with AF-2 in the promotion of ligand-dependent transcription activation by the receptor (reviewed in Ref. [2]). Ligand binding by ERs produces a conformational change in their AF-2 domains that allows them to bind transcriptional coactivators and recruit them to responsive promoters. Numerous cofactors have been implicated in ER action, including p160 family members, p300/cbp, pcaf, DRIP/ARC/TRAP complexes, and other factors (reviewed in Ref. [3]). Recruitment of coactivator complexes results in histone acetylation by cofactors, chromatin remodeling and recruitment of RNA polymerase II to the promoter.
Estrogen and the ERK1/2, p44/42 MAPK pathway
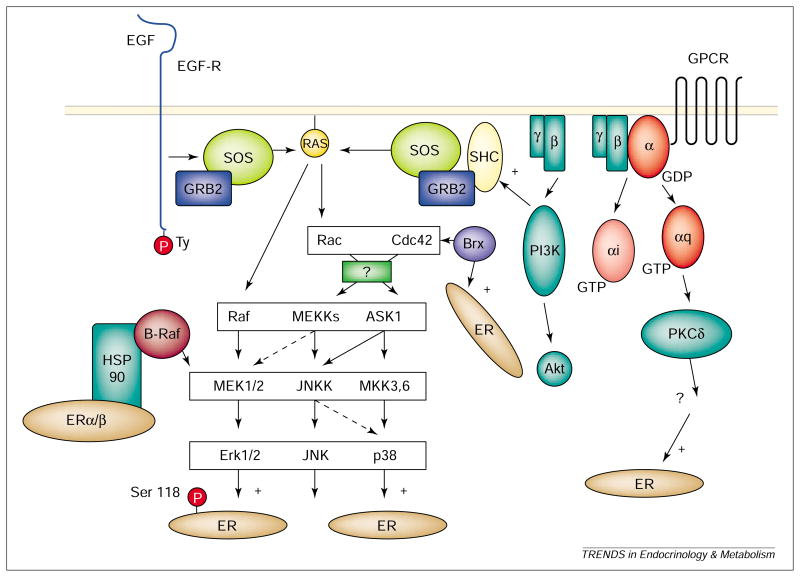
Interest in the role of egf in estrogen action arose from the findings that EGF mimicked estrogen action, and that antibodies to EGF inhibited estrogen-induced growth [4]. Coupling between EGF and estrogen was shown to involve ERα, the nuclear localization of which was promoted by EGF [5]. Activation of the egf-r resulted in phosphorylation of Ser118 of ERα by p44/42 mapk, an erk [6,7] (Fig. 1). The physiological relevance of this pathway was underscored by the absence of estrogen-mediated EGF effects in αerko mice [8].
Fig. 1.
Cytoplasmic signaling pathways influencing the action of ER. Activation of EGF-R by EGF leads to Ras-Raf-MEK-Erk1/2 (MAPK)-mediated phosphorylation of ERα at Ser118. Activation of p38MAPKs leads to activation of ERα/β. PKCδ has also been shown to affect ER activation. In some pathways, unidentified intermediates have been indicated by question marks. Not all signaling pathways are shown. Abbreviations: see Glossary.
Tremblay et al. showed that phosphorylation of Ser124 in the AF-1 domain of mouse ERβ (analogous to Ser118 in human ERα) increases receptor interaction with src-1 [9]. The effect is blocked by PD98059 (which binds mek1 and blocks activation of ERKs), but is not inhibited by the pkc inhibitor, staurosporine [9]. The effect was independent of AF-2 [6,7,9]. This model is not without controversy, however, because phosphorylation of Ser118 in ERα was not found to be essential for coactivator recruitment by AF-1 of ERα [10]. In fact, e2 led to phosphorylation of Ser118 by a mechanism that did not involve activation of p44MAPK in MCF-7 cells [11]. Ser118 might therefore be phosphorylated by kinases other than ERKs under different conditions or in different tissues. In support of this, Ser118 was phosphorylated upon ligand-dependent association of ERα with TFIIH by CDK7, which is a component of cak, a cyclin-dependent kinase in the transcription complex [12].
Not only does phosphorylation by MAPK activate ERα/β, but E2 also influences activation of MAPK. EGF-mediated DNA synthesis was attenuated by the antiestrogen ICI164 384 [5]. In vivo, estrogen-induced activation of MAPK and pi3k (but not pka or PKC) led to mitogenesis in MCF-7 cells, which was blocked by PI3K inhibitors and PD98059 [13]. A link between cytoplasmic signaling and cell-cycle regulation was suggested by the demonstration that a transcriptionally inactive ER induced mitogenesis upon estrogen treatment of NIH3T3 cells [14]. PD98059 inhibited MAPK phosphorylation in both αERKO and wild-type cortical explant cultures, but ICI182 780 blocked ERK phosphorylation only in the latter [15]. E2 led to activation of MAPK within 5 min and MAPK translocation to the nucleus after either E2 or EGF treatment [16]. MAPK activation by E2 involved mobilization of intracellular calcium stores in MCF-7 cells through a pathway that does not involve Raf-1 or ip3 [16]. The authors suggest that E2 activation of MAPK involves calcium as second messenger; thus, there is a feed-forward system with E2 activating MAPK, and MAPK activating ER [16].
E2 was reported to stimulate the tgf -β3 promoter in the presence of EGF [17], an effect that was blocked by PD98059 or a PKC inhibitor (GF109203), but not by the PKA inhibitor H89; however, the effect did not require phosphorylation of Ser118, because the ERα-mutant S118A behaved similar to the wild-type receptor [17]. Gene regulation in vivo might therefore be more complex than phosphorylation of Ser118 alone [17].
Some transcriptional coactivators recruited by liganded ERs are also targets of the p44/42 MAPK pathway. Rowan et al. showed that SRC-1 expressed in COS-1 cells is phosphorylated and demonstrated the phosphorylation in vitro of SRC-1 by MAPK [18]. aib-1 was also phosphorylated in vitro by MAPK and coexpression of constitutively active MEK1 enhanced the ability of a GAL4dbd–AIB-1 chimera to activate a reporter [19]. The effect was attributed to increased recruitment of p300 and a consequent increase in hat activity. Janknecht et al. demonstrated phosphorylation of CBP in vitro by MAPK and showed that overexpression of p44MAPK and constitutively active Raf-1 enhanced transcriptional activation by a GAL4DBD–CBP chimera [20]. Additional studies showed MAPK-dependent activation of CBP by ngf in PC12 cells and of CBP and p300 by phenylephrine in cardiac cells [21,22]. Mechanistic consequence was addressed by Ait-Si-Ali et al. [23], who showed that phosphorylation of CBP by p44MAPK stimulates its HAT activity.
Association of ERα with Src–sh2
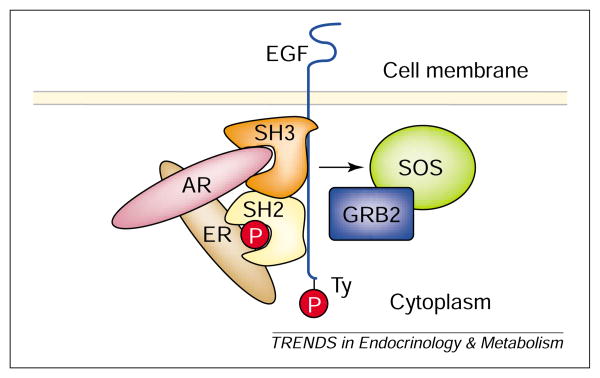
A multiprotein complex of ERKs and nuclear receptors and SH2/SH3 regions of tyrosine kinase receptors has been described. Migliaccio et al. [24] found that antiestrogens blocked progestin-stimulated proliferation in breast cancer cells, and suggested that ERα links the Src–p21Ras–ERK pathway to ligand-activated prB. Ligand-dependent binding of PR to SH3 domains involved a polyproline region in the N-terminus of PRB [25]. In the human prostate cell line (LNCaP) E2 led to association of ERβ with Src and activated the Src–Raf-1–ERK2 pathway through a tertiary complex with ar, ERβ and Src. Binding of ERα to SH2 required phosphotyrosine residue 537 (443 in ERβ) [26]. A Src/Shc/ERK pathway involving ERα, ERβ and AR was demonstrated both in primary calvaria cell cultures and an osteocytic cell line [27]. At present the relationships of these complexes to the previously reported Ras–Raf–MAPK pathway remains uncertain, but is extremely intriguing, because it involves a direct link between ER and growth factor receptors (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
A possible molecular mechanism coupling transmembrane receptors to ER signaling. ER binds directly to the SH2 region of EGF through the carboxyl region. AR associates with ER, and also interacts with the SH3 region of EGF-R through the N-terminus of AR. Binding of EGF might contribute to augmentation of estrogen action through this molecular mechanism. Abbreviations: see Glossary.
ER activation by p38 MAPK
ERα and ERβ might be activated by p38MAPK (Fig. 1). mekk1, but not RAF or MEKK2, increased ligand-dependent expression of an ere-driven reporter in Ishikawa cells and the effect was blocked by ICI182 780, but not PD98059 [28]. brx augmented activation of ERβ in the presence of ligand, an effect that was blocked by the p38MAPK inhibitor, SB202190, but not by PD98059 [29]. Brx binds to nuclear receptors, including ERα [30]. Activation of ERα by Brx required Cdc42 [30], a small GTP-binding protein upstream of jnk and p38MAPK. Furthermore, MEKK6-EE, a constitutively active mutant known to activate p38MAPKs, increased ERβ activity [29]. Interestingly, Brx contains a region with sequence identity to a protein A-kinase anchoring protein [30,31], suggesting that Brx might target substrates to specific subcellular regions.
Estrogen and 4-hydroxy-tamoxifen induced apoptosis in stably transfected ER-positive HeLa cells, and the effect was blocked by SB203580, a p38MAPK inhibitor [32]. ER was required, because the effect was not seen in ER-negative HeLa and MCF-10F cells [32]. Src enhanced ERα AF-1 activity through two independent mechanisms, one involving Ser118 (Raf-1–MEK–ERK) and a distinct MEKK–jnkk–JNK pathway that did not. PD98059 only partially inhibited Src activation, but a dominant negative Rac mutant (S17N) and a dominant negative inhibiting MEKK1 mutant (K432M) abolished it [33]. Curiously, in HeLa cells, p38MAPK and ERKs inhibited the response, an effect that could be caused by a lack of an accessory protein not supplied in this system. It might not be possible to distinguish between a p38 pathway and a JNK-dependent effect based solely on the information provided [33], because a p38 inhibitor, such as SB202190, was not used, and MEKK1 might indirectly influence p38 activation via JNKK1 [28]. With one exception [33], reports suggest that p38-dependent activation of ER is limited to ligand-dependent effects [28,29,30].
PKA and estrogen signaling
PKA, a cAMP-dependent protein kinase, has been shown to augment the function of ER [34,35]. Aronica et al. described ligand-independent activation of an ERE-containing reporter [36]. Estrogen treatment rapidly increased cAMP levels in uterus and breast cancer cells [36]. PKA catalytic subunits α or β were also shown to enhance activity of an estrogen-dependent reporter [37]. Because PKA alters the ER agonist or antagonist profiles of tamoxifen and other serms [37], this ER activation pathway is of potential clinical significance. Phosphopeptide mapping confirmed that estrogens, ICI164 384, PKA and PKC promoted phosphorylation of ERα on Ser104, 106 and 118 [38]. The pathway led to ligand-independent activation of endogenous promoters of estrogen-responsive genes [39]. Three mechanisms involving PKA have been described: direct phosphorylation of the ER, phosphorylation of cofactors and effects mediated through creb.
Studies in HeLa cells showed that EGF and PKA activation were distinct pathways leading to ERα activation [40]. PKA-mediated ER activation was abolished by cholera toxin ct/ibmx activation and the PKA inhibitor H-89, but not by the PKC inhibitor bimd [40]. By contrast, EGF-stimulated ER activation was not blocked by either inhibitor [40]. As expected, EGF did not require the lbd of ER, but activation of PKA did require AF-2. Consistent with the notion of separate pathways, mutation of ERα Ser118 did not abolish the cAMP-mediated activation [40]. Experiments in αT3 cells showed ligand-independent stimulation of ERα-dependent promoter activity to be blocked by H-89 and antiestrogens, but not by PD98059 [39]. Lamb et al. reported ligand-independent stimulation of ERα activity involving cAMP and cyclin D1 [40]. An association between ERα and cyclin D1 has been described [41]. Lamb et al. found that activation of cAMP enhanced formation of the cyclin D1–ERα complex and they proposed a role for cyclin D1 and estrogen in mammary development [40]. Because PKA activation of ERα is cell-type specific [37], and is promoter context dependent [42,43], it is likely that factors, in addition to cyclin D1, contribute to PKA-mediated ER activation.
PKA and ER phosphorylation
Phosphorylation of ERα is known to enhance receptor function, yet it is unlikely that PKA-mediated effects are limited to direct phosphorylation of ER. Chen et al. found that PKA phosphorylated Ser236 of ERα in vitro, resulting in inhibition of dimerization [44]. E2 removed the inhibition, but ICI182 780 did not. The functional effects of Ser236 phosphorylation were tested in COS-1 cells, in which overall ligand-independent activation was modest [44]. For the ERE-G-CAT reporter, mutation of Ser236 to glutamate (HEGO236E) did not abolish PKA-augmented ligand-dependent activation, which suggests that ligand-dependent activation by PKA does not involve Ser236 [44]. Some reports suggest the AF-1 region of ERα is not essential to PKA-mediated activation, because mutants lacking the region were activated by cAMP [37,44], and the response was blocked by antiestrogens [36,37,43].
Phosphorylation of cofactors
Transcription cofactors recruited to promoters by liganded ERs are also targets for PKA. In COS-1 cells the ability of SRC-1 to enhance PR activity was increased by 8-Br-cAMP [45]. The effect was dependent on MAPK and was not caused by direct phosphorylation of SRC-1 by PKA [45]. CBP activity can also be enhanced by the PKA pathway [21,46–48]. Assessment of the ability of GAL4DBD–CBP chimeras to activate reporters showed that signaling from PKA to CBP did not require MAPK activity because it was not blocked by PD98059 [21] or enhanced by RasR12 [47]. The ability of a GAL4DBD–CBP chimera lacking HAT activity to activate a reporter was enhanced by 8-Br-cAMP [48]. By contrast, HAT activity of CBP was required for activation of the transcription factor Pit-1 by forskolin [46].
CREB-mediated estrogen effects
Recently, Lazennec et al. examined the mechanism of PKA synergy with E2/ERα in chinese hamster ovary and SK-BR-3 breast cancer cells and found that the effect was cell-line dependent [49]. However, mutation of potential phosphorylation sites in ERα (Ser236, 305, 338 and 518) did not negate the synergy observed, suggesting that phosphorylation of ERα was not required [49]. The limiting factor was shown to be CREB [49]. In vivo, acute and long-term treatment with estrogen altered CREB protein levels in rat central nervous system tissues [50]. Furthermore, estrogen led to rapid phosphorylation of CREB in cortical tissues [51,52]. Studies of mouse dopaminergic neurons showed that E2 – bsa stimulated neuron dendritic growth through a signaling pathway involving the rapid release of intracellular calcium stores requiring PKA activity that led to phosphorylation of CREB [53]. The effect was not inhibited by ICI182 780 [53]. The differences between cell lines and tissues suggest that mechanisms of PKA-mediated estrogen signaling might vary greatly among tissues.
Activation of ER by PKC
PKC is not a single entity, but comprises 11 isoforms, and has been shown to promote activation of ERα [35,54] by a mechanism distinct from that of EGF or PKA [55,56]. Activation of PKC by tpa led to phosphorylation of Ser118 of ERα [54]. Lahooti et al. examined the pathway using murine ERα in the liganded and unliganded state and found that receptor activity was stimulated by PKCδ, a Ca2+-dependent protein kinase, but not by PKCα or ε [56]. The effect required Ser122 of murine ER (analogous to Ser118 in human ERα) [56]. In agreement with the observations of others, stimulation was cell-type and promoter specific [56].
Evidence suggests that several PKC signaling pathways exist. An IP3-PKCa pathway in HepG2 cells was sensitive to inhibition with ICI182 780 and the plc inhibitor U73122 [57]. In αT3–1 cells, however, gnrh treatment stimulated estrogen-independent activation of an ERE-containing reporter via a pathway sensitive to both PKC inhibitors and PD98059 [58]. The authors suggest a PKC-MAPK-linked signaling pathway in these cells. Membrane-associated PKC-linked signaling pathways might exist that do not involve ERα/β. Sylvia et al. [59] described a membrane-linked estrogen-induced growth pathway in rat chondrocytes whereby E2–BSA led to increases in PKCα within three min, an effect that was not inhibited by ICI182 780. This pathway required phosphatidylinositol-PLC, rather than phosphatidylcholine-PLC or phospholipase D, and was coupled to a G-protein sensitive to inhibition by GDPβS [60].
For PKC and ER (or E2) a feedback system is present. PKC has been shown to affect binding of labeled estradiol in osteoblasts [61] and the mouse uterus [62]. In the latter, inhibition of PKC led to increased estradiol binding in the cytosol, presumably because of post-transcriptional or post-translational modification of the ER by PKCα or PKCβII [62]. In endometrial cancers, PKCα expression is inversely correlated with the presence of ER as determined by western blot [63]. Similar observations were made in breast cancers [64]. In rat or rabbit corpora lutea or cultured rat granulosa cells, estrogen treatment led to a 2-3-fold upregulation of PKCδ expression [65]. By contrast, in MCF-7 cells, estrogen treatment led to reduction in PKCδ mRNA and protein, but to no changes in other PKC isoforms [66]. Both upregulation and downregulation occurred over five days, a time course much longer than that in rat chondrocytes, in which it occurred within 90 min. The upregulation of PKCδ is of interest, because PKCδ is involved in growth regulation of MCF-7 cells [67]. Based on these observations, multiple feedback pathways appear to link PKC and estrogen signaling.
Feedback of estrogen to IGF-IR and EGF-R
Not only do growth factors such as EGF and igf-i promote activation of ERs, but signals from activated ERs are also transmitted to transmembrane receptor complexes for these factors. Estrogen elicited tyrosine phosphorylation of the EGF receptor [68] and caused association of ERα with igf-ir and phosphorylation of the receptor [69]. E2 also enhanced IGF-IR signaling in MCF-7 cells, but not by an increase in IGF-IR protein expression [70]. E2 led to an increase in IRS-1 expression and the p85 regulatory unit of PI3K at 48 h [70]. In MCF-7 cells, this resulted in increased PI3K activity and Akt phosphorylation by estrogen in combination with IGF-I [70]. These findings are interesting given direct association of ERα with the p85 subunit of PI3K (reviewed in Ref. [71]), and are consistent with the theme of synergistic activity between tyrosine kinase receptors and estrogen. Notably, IGF-IR and ER colocalize in the same cells in the female rat brain [72], as well as in reproductive tissues.
Conclusions and perspectives
It is clear that growth factors transmit signals to the genome and coactivators through nuclear receptors, including ER. Findings from several laboratories indicate the presence of integrated feedback loops involving growth factors and estrogen signaling. Recent reports describe specific complexes involving multiple receptors with cytoplasmic domains of growth factor receptors, thus revealing at least one molecular mechanism responsible for the coupling of growth factors and estrogen action.
A key feature of cytoplasmic signaling pathways of estrogen action is the heterogeneity, cell-line, tissue- and factor-specific natures of the responses. Assembly or disassembly of distinct cytoplasmic modules can dictate cell- and tissue-specific responses with remarkable plasticity that might contribute to regulatory flexibility in response to estrogens. The biological context of the signal (estrogen) determines the nature of the response, because specific messages might be transmitted differently, depending upon the temporal existence of a specific cytoplasmic estrogen-signaling module. Specificity of action is accomplished through subcellular compartmentalization of cytoplasmic signaling modules, The proteins that serve as scaffolds for these modules are just beginning to be discovered.
Acknowledgments
We thank George Anderson for help in preparation of the article and Domenica Rubino and John Wu for critical reading. P.H.D. is supported in part by a grant from the DoD.
Glossary
- AF
activation function
- AIB
amplified in breast cancer
- AR
androgen receptor
- ASK
apoptosis signal-regulating kinase
- BIMD
bisindolylmaleimide
- Brx
breast cancer nuclear hormone receptor auxiliary factor
- BSA
bovine serum albumin
- CAK
Cdk-activating kinase
- CBP
CREB-binding protein
- CREB
cyclic AMP response element-binding protein
- CT/IBMX
cholera toxin and isobutylmethylxanthine
- DBD
DNA binding domain
- E2
estradiol
- EGF
epidermal growth factor
- EGF-R
EGF receptor
- ER
estrogen receptor
- ERE
estrogen response element
- ERK
extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- ERKO
estrogen receptor knockout
- GPCR
G-protein-coupled receptor
- GRB2
growth factor receptor-binding protein 2
- HAT
histone acetyl transferase
- HSP
heat shock protein
- IGF-I
insulin-like growth factor
- IGF-IR
IGF-I receptor
- IP3
inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate
- JNK
c-Jun N-terminal kinase
- JNKK
JNK kinase
- LBD
ligand-binding domain
- MAPK
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MEK
MAPK/ERK kinase
- MEKK
MEK kinase
- NGF
nerve growth factor
- CAF
p300/CBP-associated factor
- PI3K
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- PKA
protein kinase A
- PKC
protein kinase C
- PLC
phospholipase C
- PR
progesterone receptor
- SERM
selective estrogen response modulator
- SH
Src homology
- Shc
SH2-containing protein
- SRC-1
steroid receptor coactivator 1
- SOS
son of sevenless
- TPA
phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate
- TGF-β
transforming growth factor β
Contributor Information
Paul H. Driggers, Email: pdriggers@rocketmail.com, Dept of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, 4301 Jones Bridge Rd, Bethesda, MD, USA.
James H. Segars, Pediatric and Reproductive Endocrinology Branch, NICHD, NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA
References
- 1.Smith CL. Cross-talk between peptide growth factor and estrogen receptor signaling pathways. Biol Reprod. 1998;58:627–632. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod58.3.627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tsai M, et al. Molecular mechanisms of action of steroid/thyroid receptor superfamily members. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:451–486. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.002315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.McKenna N, et al. Combinatorial control of gene expression by nuclear receptors and coregulators. Cell. 2002;108:465–474. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00641-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nelson KG, et al. Epidermal growth factor replaces estrogen in the stimulation of female genital-tract growth and differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991;88:21–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ignar-Trowbridge DM, et al. Coupling of dual signaling pathways: epidermal growth factor action involves the estrogen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992;89:4658–4662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kato S, et al. Activation of the estrogen receptor through phosphorylation by mitogen-activated protein kinase. Science. 1995;270:1491–1494. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5241.1491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bunone G, et al. Activation of the unliganded estrogen receptor by EGF involves the MAP kinase pathway and direct phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1996;15:2174–2183. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Curtis SW, et al. Physiological coupling of growth factor and steroid receptor signaling pathways: estrogen receptor-knockout mice lack estrogen-like response to epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:12626–12630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.22.12626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tremblay A, et al. Ligand-independent recruitment of SRC-1 to estrogen receptor β through phosphorylation of activation function AF-1. Mol Cell. 1999;3:513–519. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80479-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Webb P, et al. Estrogen receptor activation function 1 works by binding p160 coactivator proteins. Mol Endocrinol. 1998;12:1605–1618. doi: 10.1210/mend.12.10.0185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Joel PB, et al. Estradiol-induced phosphorylation of serine 118 in the estrogen receptor is independent of p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:13317–13323. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.21.13317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chen D, et al. Activation of estrogen receptor α by S118 phosphorylation involves a ligand-dependent interaction with TFIIH and participation of CDK7. Mol Cell. 2000;6:127–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lobenhofer EK, et al. Inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity in MCF-7 cells prevents estrogen-induced mitogenesis. Cell Growth Differ. 2000;11:99–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Castoria G, et al. Non-transcriptional action of oestradiol and progestin triggers DNA synthesis. EMBO J. 1999;18:2500–2510. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.9.2500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Singh M, et al. Estrogen-induced activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in the cerebral cortex of estrogen receptor-α-knockout mice. J Neurosci. 2000;20:1694–1700. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-05-01694.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Improta-Brears T, et al. Estrogen-induced activation of mitrogen-activated protein kinase requires mobilization of intracellular calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:4686–4691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.8.4686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lu D, Giguere V. Requirement of Ras-dependent pathways for activation of the transforming growth factor β3 promoter by estradiol. Endocrinology. 2001;142:751–759. doi: 10.1210/endo.142.2.7937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rowan B, et al. Phosphorylation of steroid receptor coactivator-1. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:4475–4483. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.6.4475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Font de Mora J, et al. AIB1 is a conduit for kinase-mediated growth factor signaling to the estrogen receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:5041–5047. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.14.5041-5047.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Janknecht R, et al. MAP kinase-dependent transcriptional coactivation by Elk-1 and its cofactor CBP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;228:831–837. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1996.1740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Liu Y, et al. Nerve growth factor upregulates the transcriptional activity of CBP through activation of the p42/p44 MAPK cascade. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:32400–32407. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.49.32400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gusterson R, et al. The transcriptional coactivators CBP and p300 are activated via phenylephrine through the p42/p44 MAPK cascade. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:2517–2524. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M104626200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ait-Si-Ali S, et al. Phosphorylation by p44 MAP kinase-ERK1 stimulates CBP histone acetyl transferase activity in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;262:157–162. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.1132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Migliaccio A, et al. Activation of the Src-p21ras-Erk pathway by progesterone receptor via cross-talk with estrogen receptor. EMBO J. 1998;17:2008–2018. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.7.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Boonyaratanakornkit V, et al. Progesterone receptor contains a proline-rich motif that directly interacts with SH3 domains and activates c-src family tyrosine kinases. Mol Cell. 2001;8:269–280. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(01)00304-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Migliaccio A, et al. Steroid-induced androgen receptor-oestradiol receptor β-Src complex triggers prostate cancer cell proliferation. EMBO J. 2000;19:5406–5417. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.20.5406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kousteni S, et al. Nongenotropic, sex-nonspecific signaling through the estrogen or androgen receptors: dissociation from transcriptional activity. Cell. 2001;104:719–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lee H, et al. MEKK1 activation of human estrogen receptor α and stimulation of the agonistic activity of 4-hydroxytamoxifen in endometrial and ovarian cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol. 2000;14:1882–1896. doi: 10.1210/mend.14.11.0554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Driggers PH, et al. The proto-oncoprotein Brx activates estrogen receptor β by a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:46792–46797. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M106927200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Rubino D, et al. Characterization of Brx, a novel Dbl family member that modulates estrogen receptor action. Oncogene. 1998;16:2513–2516. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Diviani D, et al. AKAP-lbc anchors protein kinase A and nucleates Gα12-selective Rho-mediated stress fiber formation. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:44247–44257. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M106629200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zhang CC, et al. Activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway by estrogen or by 4-hydroxytamoxifen is coupled to estrogen receptor-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:479–486. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.1.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Feng W, et al. Potentiation of estrogen receptor activation function 1 (AF-1) by Src-JNK through a serine 118-independent pathway. Mol Endocrinol. 2001;15:32–45. doi: 10.1210/mend.15.1.0590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Aronica SM, et al. Estrogen action via the cAMP signaling pathway: stimulation of adenylate cyclase and cAMP-regulated gene transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91:8517–8521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.18.8517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Cho H, et al. Synergistic activation of estrogen receptor-mediated transcription by estradiol and protein kinase activators. Mol Endocrinol. 1993;7:441–452. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.3.7683375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Aronica SM, et al. Stimulation of estrogen receptor-mediated transcription and alteration in the phosphorylation state of the rat uterine estrogen receptor by estrogen, cyclic adenosine monophosphate, and insulin-like growth factor-I. Mol Endocrinol. 1993;7:743–752. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.6.7689695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Fujimoto N, et al. Alteration in the agonist/antagonist balance of antiestrogens by activation of protein kinase A signaling pathways in breast cancer cells: antiestrogen selectivity and promoter dependence. Mol Endocrinol. 1994;8:296–304. doi: 10.1210/mend.8.3.7517003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Le Goff P, et al. Phosphorylation of the human estrogen receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:4458–4466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Schreihofer DA, et al. Ligand-independent activation of pituitary ER: dependence on PKA-stimulated pathways. Endocrinology. 2001;142:3361–3368. doi: 10.1210/endo.142.8.8333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lamb J, et al. Regulation of the functional interaction between cyclin D1 and the estrogen receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:8667–8675. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.23.8667-8675.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Neuman E, et al. Cyclin D1 stimulation of estrogen receptor transcriptional activity independent of cdk4. Mol Cell Biol. 1997;17:5338–5347. doi: 10.1128/mcb.17.9.5338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ince BA, et al. Activation of transcriptionally inactive human estrogen receptors by cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate and ligands including antiestrogens. Mol Endocrinol. 1994;8:1397–1406. doi: 10.1210/mend.8.10.7531820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.El-Tanani MKK, et al. Interaction between estradiol and cAMP in the regulation of specific gene expression. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1996;124:71–77. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(96)03930-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Chen D, et al. Phosphorylation of human estrogen receptor α by protein kinase A regulates dimerization. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:1002–1015. doi: 10.1128/mcb.19.2.1002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Rowan B, et al. 8-Bromo-cyclic AMP induces phosphorylation of two sites in SRC-1 that facilitate ligand-independent activation of the chicken progesterone receptor and are critical for functional cooperation between SRC-1 and CREB binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:8720–8730. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.23.8720-8730.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Lan X, et al. Signal-specific co-activator domain requirements for Pit-1 activation. Nature. 1998;395:301–306. doi: 10.1038/26270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Zanger K, et al. A novel mechanism for cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate regulation of gene expression by CREB-binding protein. Mol Endocrinol. 1999;13:268–275. doi: 10.1210/mend.13.2.0245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Chawla S, et al. CBP: a signal-regulated transcriptional coactivator controlled by nuclear calcium and CaM kinase IV. Science. 1998;281:1505–1509. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5382.1505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lazennec G, et al. Involvement of cyclic AMP-response element-binding protein (CREB) and estrogen receptor phosphorylation in the synergistic activation of the estrogen receptor by estradiol and protein kinase activators. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2001;77:193–203. doi: 10.1016/s0960-0760(01)00060-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Carlstrom L, et al. Estrogen modulation of the cyclic AMP-response element-binding protein pathway. Neuroendocrinology. 2001;74:227–243. doi: 10.1159/000054690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Gu Q, et al. 17β-Estradiol potentiates kainate-induced currents via activation of the cAMP cascade. J Neurosci. 1996;16:3620–3629. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-11-03620.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Zhou Y, et al. Estrogen rapidly induces the phosphorylation of the cAMP-response element-binding protein in rat brain. Endocrinology. 1996;137:2163–2166. doi: 10.1210/endo.137.5.8612562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Beyer C, et al. Estrogenic stimulation of neurite growth in midbrain dopaminergic neurons depends on cAMP-protein kinase A signaling. J Neurosci Res. 2000;59:107–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Joel PB, et al. Estradiol and phorbol ester cause phosphorylation of serine 118 in the human estrogen receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1995;9:1041–1052. doi: 10.1210/mend.9.8.7476978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Ignar-Trowbridge DM, et al. Peptide growth factor cross-talk with the estrogen receptor requires the A/B domain and occurs independently of protein kinase C or estradiol. Endocrinology. 1996;137:1735–1744. doi: 10.1210/endo.137.5.8612509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Lahooti H, et al. Modulation of mouse estrogen receptor transcription activity by protein kinase C δ. J Mol Endocrinol. 1998;20:245–259. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0200245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Marino M, et al. Estradiol-induced IP3 mediates the estrogen receptor activity expressed in human cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001;182:19–26. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(01)00556-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Demay F, et al. Steroid-independent activation of ER by GnRH in gonadotrope pituitary cells. Endocrinology. 2001;142:3340–3347. doi: 10.1210/endo.142.8.8337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Sylvia VL, et al. 17β-Estradiol-BSA conjugates and 17β-Estradiol regulate growth plate chondrocytes by common membrane associated mechanisms involving PKC dependent and independent signal transduction. J Cell Biochem. 2001;81:413–429. doi: 10.1002/1097-4644(20010601)81:3<413::aid-jcb1055>3.0.co;2-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Sylvia VL, et al. The membrane effects of 17β-Estradiol on chondrocyte phenotypic expression are mediated by activation of protein kinase C through phospholipase C and G-proteins. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2000;73:211–224. doi: 10.1016/s0960-0760(00)00078-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Migliaccio S, et al. Endogenous protein kinase-C activation in osteoblast-like cells modulates responsiveness to estrogen and estrogen receptor levels. Mol Endocrinol. 1993;7:1133–1143. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.9.8247015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Migliaccio S, et al. Modulation of estrogen receptor levels in mouse uterus by protein kinase C isoenzymes. Endocrinology. 1998;139:4598–4606. doi: 10.1210/endo.139.11.6300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Fournier DB, et al. Protein kinase C α expression is inversely related to ER status in endometrial carcinoma: possible role in AP-1-mediated proliferation of ER-negative endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2001;81:366–372. doi: 10.1006/gyno.2001.6164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]