Abstract
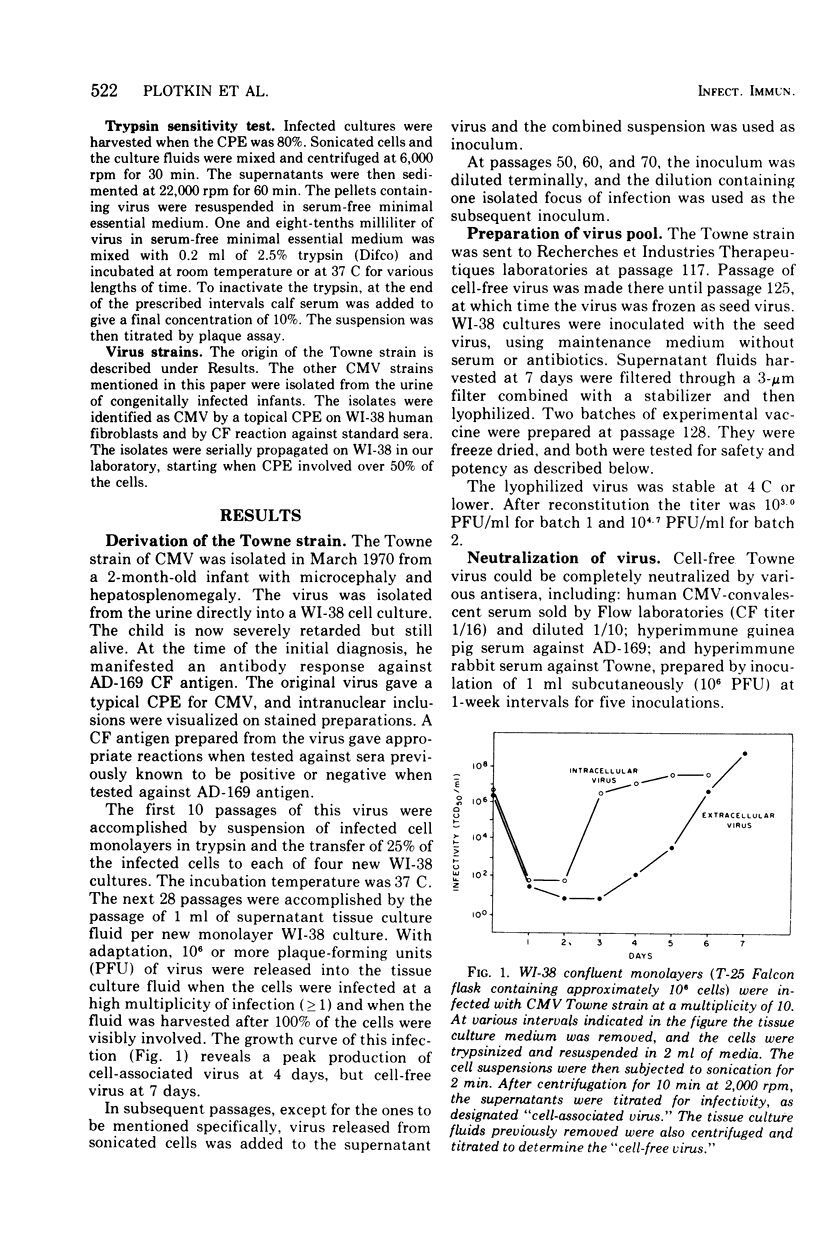
A strain of human cytomegalovirus called Towne was isolated in WI-38 human fibrolast cell cultures from the urine of an infected infant. It was then passaged 125 times in WI-38, including three clonings, and a pool was prepared in the same cell substrate for use as a potential live attenuated vaccine. The Towne virus has a broad antigenicity and cross-reacts with the AD-169 strain. Several markers of the Towne virus were found which differentiated it from fresh isolates. One of these was resistance of the former to trypsin. The Towne virus was tested for freedom from oncogenicity or other harmful effects in preparation for tests in humans.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrecht T., Rapp F. Malignant transformation of hamster embryo fibroblasts following exposure to ultraviolet-irradiated human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen H. K. Studies of human cytomegalovirus strain variations by kinetic neutralization tests. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972;38(4):297–305. doi: 10.1007/BF01262820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong D., Ely M., Steger L. Post-transfusion cytomegaloviremia and persistence of cytomegalovirus in blood. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):159–163. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.159-163.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill A. E., Chubb R. C., Baxendale W. The attenuation, with loss of oncogenicity, of the herpes-type virus of Marek's disease (strain HPRS-16) on passage in cell culture. J Gen Virol. 1969 Jun;4(4):557–564. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-4-4-557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darai G., Munk K. Human embryonic lung cells abortively infected with Herpes virus hominis type 2 show some properties of cell transformation. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 28;241(113):268–269. doi: 10.1038/newbio241268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deibel R., Smith R., Clarke L. M., Decher W., Jacobs J. Cytomegalovirus infections in New York State. N Y State J Med. 1974 May;74(5):785–791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diosi P., Moldovan E., Tomescu N. Latent cytomegalovirus infection in blood donors. Br Med J. 1969 Dec 13;4(5684):660–662. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5684.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elek S. D., Stern H. Development of a vaccine against mental retardation caused by cytomegalovirus infection in utero. Lancet. 1974 Jan 5;1(7845):1–5. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92997-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa T., Fioretti A., Plotkin S. Growth characteristics of cytomegalovirus in human fibroblasts with demonstration of protein synthesis early in viral replication. J Virol. 1973 Jun;11(6):991–997. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.6.991-997.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G., Scriba M., Joyner C. R., Harrison F. S., Jr, Von Essen R., Paloheimo J., Klemola E. Antibody responses to the Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegaloviruses after open-heart and other surgery. N Engl J Med. 1970 May 7;282(19):1068–1074. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197005072821904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y. T., Huang E. S., Pagano J. S. Antisera to human cytomegaloviruses prepared in the guinea pig: specific immunofluorescence and complement fixation tests. J Immunol. 1974 Feb;112(2):528–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Just M., Buergin-Wolff A., Emoedi G., Hernandez R. Immunisation trials with live attenuated cytomegalovirus TOWNE 125. Infection. 1975;3(2):111–114. doi: 10.1007/BF01641052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanich R. E., Craighead J. E. Human cytomegalovirus infection of cultured fibroblasts. II. Viral replicative sequence of a wild and an adapted strain. Lab Invest. 1972 Sep;27(3):273–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Carp R. I. Effect of proteolytic enzymes on the infectivity of a number of herpesviruses. J Infect Dis. 1973 Dec;128(6):788–790. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.6.788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar M. L., Nankervis G. A., Gold E. Inapparent congenital cytomegalovirus infection. A follow-up study. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jun 28;288(26):1370–1372. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197306282882603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D. J., Montagnier L., Latarjet R. Growth in agarose of human cells infected with cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):327–332. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.327-332.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minamishima Y., Graham B. J., Benyesh-Melnick M. Neutralizing antibodies to cytomegaloviruses in normal simian and human sera. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):368–373. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.368-373.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monif G. R., Egan E. A., 2nd, Held B., Eitzman D. V. The correlation of maternal cytomegalovirus infection during varying stages in gestation with neonatal involvement. J Pediatr. 1972 Jan;80(1):17–20. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80446-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E., Walker D. L. Virulence and attenuation of murine cytomegalovirus. Infect Immun. 1971 Feb;3(2):228–236. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.2.228-236.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perham T. G., Caul E. O., Conway P. J., Mott M. G. Cytomegalovirus infection in blood donors--a prospective study. Br J Haematol. 1971 Mar;20(3):307–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb07041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M., Szmuness W., Millian S. J., David D. S. A serologic study of cytomegalovirus infections associated with blood transfusions. N Engl J Med. 1971 May 20;284(20):1125–1131. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197105202842004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyman T. A. Postperfusion syndrome. A review and report of 21 cases. Am Heart J. 1966 Jul;72(1):116–123. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(66)90634-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds D. W., Stagno S., Stubbs K. G., Dahle A. J., Livingston M. M., Saxon S. S., Alford C. A. Inapparent congenital cytomegalovirus infection with elevated cord IgM levels. Casual relation with auditory and mental deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1974 Feb 7;290(6):291–296. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197402072900601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagno S., Reynolds D. W., Lakeman A., Charamella L. J., Alford C. A. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection: consecutive occurrence due to viruses with similar antigenic compositions. Pediatrics. 1973 Dec;52(6):788–794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr J. G., Bart R. D., Jr, Gold E. Inapparent congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Clinical and epidemiologic characteristics in early infancy. N Engl J Med. 1970 May 7;282(19):1075–1078. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197005072821905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. P., Barker L. F., Ketcham A. S., Meyer H. M., Jr Asymptomatic cytomegalovirus infection following blood transfusion in tumor surgery. JAMA. 1970 Feb 23;211(8):1341–1344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonka V., Benyesh-Melnick M. Interactions of human cytomegalovirus with human fibroblasts. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):213–220. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.213-220.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. B., Alexander E. R. Seroepidemiology of infectious due to members of the herpesvirus group. Am J Epidemiol. 1971 Nov;94(5):496–507. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. B., French L. Plaque assay of cytomegalovirus strains of human origin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Nov;135(2):253–258. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


